- play_arrow Overview
- play_arrow Site Planning, Preparation, and Specifications
- play_arrow Initial Installation and Configuration
- Overview of Installing the SRX5600 Firewall
- Unpacking the SRX5600
- Installing the SRX5600 Mounting Hardware
- Installing the SRX5600 Using a Mechanical Lift
- Installing the SRX5600 Without a Mechanical Lift
- Connecting the SRX5600 to External Devices
- Connecting the SRX5600 to Power
- Performing the Initial Software Configuration for the SRX5600
- play_arrow Maintaining Components
- play_arrow Contacting Customer Support and Returning the Chassis or Components
- play_arrow Safety and Compliance Information
- General Safety Guidelines and Warnings
- Definitions of Safety Warning Levels
- Restricted Access Area Warning
- Fire Safety Requirements
- Qualified Personnel Warning
- Warning Statement for Norway and Sweden
- Installation Instructions Warning
- Chassis and Component Lifting Guidelines
- Ramp Warning
- Rack-Mounting and Cabinet-Mounting Warnings
- Grounded Equipment Warning
- Laser and LED Safety Guidelines and Warnings
- Radiation from Open Port Apertures Warning
- Maintenance and Operational Safety Guidelines and Warnings
- General Electrical Safety Guidelines and Warnings
- Prevention of Electrostatic Discharge Damage
- AC Power Electrical Safety Guidelines
- AC Power Disconnection Warning
- DC Power Electrical Safety Guidelines
- DC Power Disconnection Warning
- DC Power Grounding Requirements and Warning
- DC Power Wiring Sequence Warning
- DC Power Wiring Terminations Warning
- Multiple Power Supplies Disconnection Warning
- TN Power Warning
- Action to Take After an Electrical Accident
- SRX5600 Firewall Agency Approvals
- SRX5600 Firewall Compliance Statements for EMC Requirements
ON THIS PAGE
Troubleshooting the SRX5600 Firewall with Chassis and Interface Alarm Messages
Chassis Component Alarm Conditions on SRX5400, SRX5600, and SRX5800 Firewalls
Troubleshooting the SRX5600 Firewall with Alarm Relay Contacts
Troubleshooting the SRX5600 Firewall with the Craft Interface LEDs
Troubleshooting the SRX5600 Firewall with the Component LEDs
Troubleshooting the SRX5600
Troubleshooting the SRX5600 Firewall with the Junos OS CLI
The Junos OS command-line interface (CLI) is the primary tool for controlling and troubleshooting firewall hardware, Junos OS, routing protocols, and network connectivity. CLI commands display information from routing tables, information specific to routing protocols, and information about network connectivity derived from the ping and traceroute utilities.
You enter CLI commands on one or more external management devices connected to ports on the Routing Engine.
For information about using the CLI to troubleshoot Junos OS, see the appropriate Junos OS configuration guide.
Troubleshooting the SRX5600 Firewall with Chassis and Interface Alarm Messages
When the Routing Engine detects an alarm condition,
it lights the major or minor alarm LED on the craft interface as appropriate.
To view a more detailed description of the alarm cause, issue the show chassis alarms CLI command:
user@host> show chassis alarms
There are two classes of alarm messages:
Chassis alarms—Indicate a problem with a chassis component such as the cooling system or power supplies.
Interface alarms—Indicate a problem with a specific network interface.
Chassis Component Alarm Conditions on SRX5400, SRX5600, and SRX5800 Firewalls
Table 1 lists the alarms that the chassis components can generate on SRX5400, SRX5600, and SRX5800 Firewalls.
Chassis Component | Alarm Condition | Remedy | Alarm Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air filters | Change air filter. | Change air filter. | Yellow |
| Alternative media | The Firewall boots from an alternate boot device, the hard disk. The CompactFlash card is typically the primary boot device. The Routing Engine boots from the hard disk when the primary boot device fails. | Open a support case using the Case Manager link at https://www.juniper.net/support/ or call 1-888-314-5822 (toll free, US & Canada) or 1-408-745-9500 (from outside the United States). | Yellow |
| Craft interface | The craft interface has failed. | Replace failed craft interface. | Red |
| Interface Cards (MPC/IOC/Flex IOC) | An interface card is offline. | Check the card. Remove and reinsert the card. If this fails, replace failed card. | Yellow |
An interface card has failed. | Replace failed card. | Red | |
An interface card has been removed. | Insert card into empty slot. | Red | |
Volt Sensor Fail | Reboot the specified card. | Red | |
| Service Processing Card (SPC) | Abnormal exit in the current flow sessions of an SPU. | Open a support case using the Case Manager link at https://www.juniper.net/support/ or call 1-888-314-5822 (toll free, US & Canada) or 1-408-745-9500 (from outside the United States). | Red |
CPU Digital Thermal Sensor (DTS) of the SPC reaches high or over temperature threshold. | Check the status of all fan trays. | Red | |
FPC airflow temperature sensors in SRX5K-SPC3 reach high or over or crosses fire temperature threshold. | Check the status of all fan trays. | Red | |
FPC airflow temperature sensors in SRX5K-SPC3 read/access failure. | If the alarm is present consistently, then it indicates a hardware issue. Open a support case using the Case Manager link at https://www.juniper.net/support/ or call 1-888-314-5822 (toll free, US & Canada) or 1-408-745-9500 (from outside the United States). | Yellow | |
SRX5K-SPC3 checks for missing devices during boot and reports. | Open a support case using the Case Manager link at https://www.juniper.net/support/ or call 1-888-314-5822 (toll free, US & Canada) or 1-408-745-9500 (from outside the United States). | Red | |
SRX5K-SPC3 LTC Firm Ware Version Mismatch. LEDs on the front panel of the chassis indicate major alarm. | To manually upgrade the LTC Firmware Version:
| Red | |
Memory faults: DIMM failures and ECC errors. | Open a support case using the Case Manager link at https://www.juniper.net/support/ or call 1-888-314-5822 (toll free, US & Canada) or 1-408-745-9500 (from outside the United States). | Red | |
Real Time Clock battery failure. | Open a support case using the Case Manager link at https://www.juniper.net/support/ or call 1-888-314-5822 (toll free, US & Canada) or 1-408-745-9500 (from outside the United States). | Red | |
SSDs on the SRX5K-SPC3 missing or read/write to SSD is failing or SSD file system corrupt. | Replace the SSD. or Open a support case using the Case Manager link at https://www.juniper.net/support/ or call 1-888-314-5822 (toll free, US & Canada) or 1-408-745-9500 (from outside the United States). | Red | |
OPMC Boot FPGA Faults | Open a support case using the Case Manager link at https://www.juniper.net/support/ or call 1-888-314-5822 (toll free, US & Canada) or 1-408-745-9500 (from outside the United States). | Red | |
Voltage sensor faults | From the CLI use the command restart chassis-control to reboot the firewall. If SPC still doesn’t come online, then remove and insert back the SPC. | Red | |
| Fan trays | A fan tray has been removed from the chassis. | Install missing fan tray. | Red |
Fan tray not working or failed. | Replace fan tray. | Red | |
One fan in the chassis is not spinning or is spinning below required speed. | Replace fan tray. | Red | |
A higher-cooling capacity fan tray is required when an MPC or high-density SPCs are installed on the chassis. | Upgrade to a high-capacity fan tray. | Yellow | |
Fan tray under voltage. | Reseat the Fan Tray. If problem still continues open a support case using the Case Manager link at https://www.juniper.net/support/ or call 1-888-314-5822 (toll free, US & Canada) or 1-408-745-9500 (from outside the United States). | Red | |
Wrong fan tray installed. | Check and insert the appropriate fan tray. | Red | |
In SRX5800 Firewall, mix of fan trays. | Insert the appropriate fan trays. | Red | |
In SRX5800 Firewall, wrong fan tray installed on the top. | Check and insert the appropriate fan tray. | Red | |
| Host subsystem | A host subsystem has been removed. | Insert host subsystem into empty slot. | Yellow |
A host subsystem has failed. | Replace failed host subsystem. | Red | |
| Power supplies | A power supply has been removed from the chassis. | Insert power supply into empty slot. | Yellow |
A power supply has a high temperature. | Replace failed power supply or power entry module. | Red | |
A power supply input has failed. | Check power supply input connection. | Red | |
A power supply output has failed. | Check power supply output connection. | Red | |
A power supply has failed. | Replace failed power supply. | Red | |
Invalid AC power supply configuration. | When two AC power supplies are installed, insert one power supply into an odd-numbered slot and the other power supply into an even-numbered slot. | Red | |
Invalid DC power supply configuration. | When two DC power supplies are installed, insert one power supply into an odd-numbered slot and the other power supply into an even-numbered slot. | Red | |
Mix of AC and DC power supplies. | Do not mix AC and DC power supplies. For DC power, remove the AC power supply. For AC power, remove the DC power supply. | Red | |
Not enough power supplies. | Install an additional power supply. | Red | |
| Routing Engine | Excessive framing errors on console port. An excessive framing error alarm is triggered when the default framing error threshold of 20 errors per second on a serial port is exceeded. This might be caused by a faulty serial console port cable connected to the device. | Replace the serial cable connected to the device. If the cable is replaced and no excessive framing errors are detected within 5 minutes from the last detected framing error, the alarm is cleared automatically. | Yellow |
Error in reading or writing hard disk. | Reformat hard disk and install bootable image. If this fails, replace failed Routing Engine. | Yellow | |
Error in reading or writing CompactFlash card. | Reformat CompactFlash card and install bootable image. If this fails, replace failed Routing Engine. | Yellow | |
System booted from default backup Routing Engine. If you manually switched primary role, ignore this alarm condition. | Install bootable image on default primary Routing Engine. If this fails, replace failed Routing Engine. | Yellow | |
System booted from hard disk. | Install bootable image on CompactFlash card. If this fails, replace failed Routing Engine. | Yellow | |
CompactFlash card missing in boot list. | Replace failed Routing Engine. | Red | |
Hard disk missing in boot list. | Replace failed Routing Engine. | Red | |
Routing Engine failed to boot. | Replace failed Routing Engine. | Red | |
The Ethernet management interface (fxp0 or em0) on the Routing Engine is down. |
| Red | |
| System Control Board (SCB) | An SCB has been removed. | Insert SCB into empty slot. | Yellow |
An SCB temperature sensor alarm has failed. | Replace failed SCB. | Yellow | |
An SCB has failed. | Replace failed SCB. | Red | |
An SCB throughput decreased. |
| Yellow | |
An SCB PMBus Device Fail | Ignore the alarm if rasied once or twice. If the alarm is present consistently, then it indicates a hardware issue. Open a support case using the Case Manager link at https://www.juniper.net/support/ or call 1-888-314-5822 (toll free, US & Canada) or 1-408-745-9500 (from outside the United States). | Yellow | |
| Temperature | The chassis temperature has exceeded 55 degrees C (131 degrees F), the fans have been turned on to full speed, and one or more fans have failed. |
| Yellow |
The chassis temperature has exceeded 65 degrees C (149 degrees F), and the fans have been turned on to full speed. |
| Yellow | |
The chassis temperature has exceeded 65 degrees C (149 degrees F), and a fan has failed. If this condition persists for more than 4 minutes, the Firewall shuts down. |
| Red | |
Chassis temperature has exceeded 75 degrees C (167 degrees F). If this condition persists for more than 4 minutes, the Firewall shuts down. |
| Red | |
The temperature sensor has failed. |
| Red |
Backup Routing Engine Alarms
For Firewalls with primary and backup Routing Engines, a primary Routing Engine can generate alarms for events that occur on a backup Routing Engine. Table 2 lists chassis alarms generated for a backup Routing Engine.
Because the failure occurs on the backup Routing Engine, alarm severity for some events (such as Ethernet interface failures) is yellow instead of red.
For information about configuring redundant Routing Engines, see the Junos OS High Availability Library for Routing Devices.
Chassis Component | Alarm Condition | Remedy | Alarm Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alternative media | The backup Routing Engine boots from an alternate boot device, the hard disk. The CompactFlash card is typically the primary boot device. The Routing Engine boots from the hard disk when the primary boot device fails. | Open a support case using the Case Manager link at https://www.juniper.net/support/ or call 1-888-314-5822 (toll free, US & Canada) or 1-408-745-9500 (from outside the United States). | Yellow |
| Boot Device | The boot device (CompactFlash or hard disk) is missing in boot list on the backup Routing Engine. | Replace failed backup Routing Engine. | Red |
| Ethernet | The Ethernet management interface (fxp0 or em0) on the backup Routing Engine is down. |
| Yellow |
| FRU Offline | The backup Routing Engine has stopped communicating with the primary Routing Engine. | Open a support case using the Case Manager link at https://www.juniper.net/support/ or call 1-888-314-5822 (toll free, US & Canada) or 1-408-745-9500 (from outside the United States). | Yellow |
| Hard Disk | Error in reading or writing hard disk on the backup Routing Engine. | Reformat hard disk and install bootable image. If this fails, replace failed backup Routing Engine. | Yellow |
| Multibit Memory ECC | The backup Routing Engine reports a multibit ECC error. |
| Yellow |
Troubleshooting the SRX5600 Firewall with Alarm Relay Contacts
The craft interface has two alarm relay contacts for connecting the firewall to external alarm devices. Whenever a system condition triggers either the major or minor alarm on the craft interface, the alarm relay contacts are also activated. The alarm relay contacts are located on the upper right of the craft interface.
Troubleshooting the SRX5600 Firewall with the Craft Interface LEDs
The craft interface is the panel on the front of the firewall located above the card cage that contains LEDs and buttons that allow you to troubleshoot the device.
LEDs on the craft interface include the following:
Alarm LEDs—One large red circular LED and one large yellow triangular LED, located on the upper right of the craft interface, indicate two levels of alarm conditions. The circular red LED lights to indicate a critical condition that can result in a system shutdown. The triangular yellow LED lights to indicate a less severe condition that requires monitoring or maintenance. Both LEDs can be lit simultaneously. A condition that causes an alarm LED to light also activates the corresponding alarm relay contact on the craft interface.
Host subsystem LEDs—Three LEDs, MASTER, ONLINE, and OFFLINE, indicate the status of the host subsystem. A green MASTER LED indicates that the host is functioning as primary. The ONLINE LED indicates the host is online. The OFFLINE LED indicates the host is offline. The host subsystem LEDs are located on the left of the craft interface and are labeled RE0 and RE1.
Power supply LEDs—Two LEDs (PEM) indicate the status of each power supply. Green indicates that the power supply is functioning normally. Red indicates that the power supply is not functioning normally. The power supply LEDs are located in the center craft interface, and are labeled 0 through 3.
Card OK/Fail LEDs—Two LEDs, OK and FAIL, indicate the status of the card in each slot in the card cage. Green indicates OK and red indicates a failure. The card OK/Fail LEDs are located along the bottom of the craft interface, and are labeled 0 through 5.
SCB LEDs—Two LEDs, OK and FAIL, indicate the status of each SCB. Green indicates OK and red indicates a failure. The SCB LEDs are located in the center of the craft interface along the bottom, and are labeled 0 and 1.
Fan LEDs—Two LEDs indicate the status of the fan. Green indicates OK and red indicates FAIL. The fan LEDs are located on the upper left of the craft interface.
Troubleshooting the SRX5600 Firewall with the Component LEDs
The following LEDs are located on various firewall components and display the status of those components:
Card LED—One LED labeled OK/FAIL on each card in the card cage indicates the card’s status.
MIC and port module LED—One LED labeled OK/FAIL on each MIC installed in an MPC, and each port module installed in a Flex IOC indicates the MIC or port module’s status.
SCB LEDs—Three LEDs, labeled FABRIC ACTIVE, FABRIC ONLY, and OK/FAIL , on each SCB faceplate indicate the status of the SCB. If no LEDs are lit, the master Routing Engine might still be booting, or the SCB is not receiving power.
Routing Engine LEDs—Four LEDs, labeled MASTER, HDD, ONLINE, and FAIL on the Routing Engine faceplate indicate the status of the Routing Engine and hard disk drive.
Power supply LEDs—Three or four LEDs on each power supply faceplate indicate the status of that power supply.
Troubleshooting the SRX5600 Firewall Cooling System
Problem
Description
The fans in a fan tray are not functioning normally.
Solution
Follow these guidelines to troubleshoot the fans:
Check the fan LEDs and alarm LEDs on the craft interface.
If the major alarm LED on the craft interface lights, use the CLI to get information about the source of an alarm condition:
user@host> show chassis alarms.If the CLI output lists only one fan failure, and the other fans are functioning normally, the fan is most likely faulty and you must replace the fan tray.
Place your hand near the exhaust vents at the side of the chassis to determine whether the fans are pushing air out of the chassis.
If the fan tray is removed, a minor alarm and a major alarm occur.
The following conditions automatically cause the fans to run at full speed and also trigger the indicated alarm:
A fan fails (major alarm).
The firewall temperature exceeds the “temperature warm” threshold (minor alarm).
The temperature of the firewall exceeds the maximum (“temperature hot”) threshold (major alarm and automatic shutdown of the power supplies).
Troubleshooting SRX5600 Firewall Interface Cards
Problem
Description
The interface cards (IOCs, Flex IOCs, or MPCs) are not functioning normally.
Solution
Monitor the green LED labeled OK on the craft interface corresponding to the slot as soon as an interface card is seated in an operating firewall.
The Routing Engine downloads the interface card’s software to it under two conditions: the interface card is present when the Routing Engine boots Junos OS, and the interface card is installed and requested online through the CLI or push button on the front panel. The interface card then runs diagnostics, during which the OK LED blinks. When the interface card is online and functioning normally, the OK LED lights green steadily.
Make sure the interface card is properly seated in the midplane. Check that each ejector handle has been turned clockwise and is tight.
Check the OK/FAIL LED on the interface card and OK and FAIL LEDs for the slot on the craft interface. When the interface card is online and functioning normally, the OK LED lights green steadily.
Issue the CLI
show chassis fpccommand to check the status of installed interface cards. As shown in the sample output, the value Online in the column labeled State indicates that the interface card is functioning normally:content_copy zoom_out_mapuser@host> show chassis fpc Temp CPU Utilization (%) Memory Utilization (%) Slot State (C) Total Interrupt DRAM (MB) Heap Buffer 0 Online 41 9 0 1024 15 57 1 Online 43 5 0 1024 16 57 2 Online 43 11 0 1024 16 57 3 Empty 4 Empty 5 Online 42 6 0 1024 16 57For more detailed output, add the
detailoption. The following example does not specify a slot number, which is optional:content_copy zoom_out_mapuser@host> show chassis fpc detail Slot 0 information: State Online Temperature 41 degrees C / 105 degrees F Total CPU DRAM 1024 MB Total RLDRAM 256 MB Total DDR DRAM 4096 MB Start time: 2007-07-10 12:28:33 PDT Uptime: 1 hour, 33 minutes, 52 seconds Slot 1 information: State Online Temperature 43 degrees C / 109 degrees F Total CPU DRAM 1024 MB Total RLDRAM 256 MB Total DDR DRAM 4096 MB Start time: 2007-07-10 12:28:38 PDT Uptime: 1 hour, 33 minutes, 47 seconds Slot 2 information: State Online Temperature 43 degrees C / 109 degrees F Total CPU DRAM 1024 MB Total RLDRAM 256 MB Total DDR DRAM 4096 MB Start time: 2007-07-10 12:28:40 PDT Uptime: 1 hour, 33 minutes, 45 seconds Slot 5 information: State Online Temperature 42 degrees C / 107 degrees F Total CPU DRAM 1024 MB Total RLDRAM 256 MB Total DDR DRAM 4096 MB Start time: 2007-07-10 12:28:42 PDT Uptime: 1 hour, 33 minutes, 43 seconds
For further description of the output from the command, see Junos OS System Basics and Services Command Reference at www.juniper.net/documentation/.
Troubleshooting SRX5600 Firewall MICs and Port Modules
Problem
Description
The MICs or port modules are not functioning normally.
Solution
Check the status of each port on a port module by looking at the LED located on the port module faceplate.
Check the status of a port module by issuing the
show chassis fpc pic-statusCLI command. The port module slots in the Flex IOC are numbered from 0 through 1:content_copy zoom_out_mapuser@host> show chassis fpc pic-status Slot 0 Online SRX5k SPC PIC 0 Online SPU Cp-Flow PIC 1 Online SPU Flow Slot 3 Online SRX5k DPC 4X 10GE PIC 0 Online 1x 10GE(LAN/WAN) RichQ PIC 1 Online 1x 10GE(LAN/WAN) RichQ PIC 2 Online 1x 10GE(LAN/WAN) RichQ PIC 3 Online 1x 10GE(LAN/WAN) RichQ Slot 5 Online SRX5k FIOC PIC 0 Online 16x 1GE TX PIC 1 Online 4x 10GE XFP
For further description of the output from the command, see Junos OS System Basics and Services Command Reference at www.juniper.net/documentation/.
Troubleshooting SRX5600 Firewall SPCs
Problem
Description
A Services Processing Card (SPC) is not functioning normally.
Solution
Make sure the SPC is properly seated in the midplane. Check that each ejector handle has been turned clockwise and is tight.
Issue the CLI
show chassis fpccommand to check the status of installed SPCs. As shown in the sample output, the value Online in the column labeled State indicates that the SPC is functioning normally:content_copy zoom_out_mapuser@host> show chassis fpc Slot State (C) Total Interrupt DRAM (MB) Heap Buffer 0 Online 35 4 0 1024 13 25 1 Online 47 3 0 1024 13 25 2 Online 37 8 0 2048 18 14
For more detailed output, add the
detailoption. The following example does not specify a slot number, which is optional:content_copy zoom_out_mapuser@host> show chassis fpc detail Slot 0 information: State Online Temperature 35 Total CPU DRAM 1024 MB Total RLDRAM 259 MB Total DDR DRAM 4864 MB Start time: 2013-12-10 02:58:16 PST Uptime: 1 day, 11 hours, 59 minutes, 15 seconds Max Power Consumption 585 Watts Slot 1 information: State Online Temperature 47 Total CPU DRAM 1024 MB Total RLDRAM 259 MB Total DDR DRAM 4864 MB Start time: 2013-12-10 02:55:30 PST Uptime: 1 day, 12 hours, 2 minutes, 1 second Max Power Consumption 585 Watts Slot 2 information: State Online Temperature 37 Total CPU DRAM 2048 MB Total RLDRAM 1036 MB Total DDR DRAM 6656 MB Start time: 2013-12-10 02:58:07 PST Uptime: 1 day, 11 hours, 59 minutes, 24 seconds Max Power Consumption 570 Watts
For further description of the output from the command, see Junos OS System Basics and Services Command Reference at www.juniper.net/documentation/.
Troubleshooting the SRX5600 Firewall Power System
Problem
Description
The power system is not functioning normally.
Solution
Check the LEDs on each power supply faceplate.
If an AC power supply is correctly installed and functioning normally, the AC OK and DC OK LEDs light steadily, and the PS FAIL LED is not lit.
If a DC power supply is correctly installed and functioning normally, the PWR OK, BREAKER ON, and INPUT OK LEDs light steadily.
Issue the CLI
show chassis environment pemcommand to check the status of installed power supplies. As shown in the sample output, the value Online in the rows labeled State indicates that each of the power supply is functioning normally:content_copy zoom_out_mapuser@host> show chassis environment pem PEM 0 status: State Online Temperature OK DC Output Voltage(V) Current(A) Power(W) Load(%) 47 9 423 20 PEM 1 status: State Online Temperature OK DC Output Voltage(V) Current(A) Power(W) Load(%) 47 19 893 56 PEM 2 status: State Present PEM 3 status: State Present
If a power supply is not functioning normally, perform the following steps to diagnose and correct the problem:
If a major alarm condition occurs, issue the
show chassis alarmscommand to determine the source of the problem.Check that the AC input switch (—) or DC circuit breaker (|) is in the on position and that the power supply is receiving power.
Verify that the source circuit breaker has the proper current rating. Each power supply must be connected to a separate source circuit breaker.
Verify that the AC power cord or DC power cables from the power source to the firewall are not damaged. If the insulation is cracked or broken, immediately replace the cord or cable.
Connect the power supply to a different power source with a new power cord or power cables. If the power supply status LEDs indicate that the power supply is not operating normally, the power supply is the source of the problem. Replace the power supply with a spare.
If all power supplies have failed, the system temperature might have exceeded the threshold, causing the system to shut down.
Note:If the system temperature exceeds the threshold, Junos OS shuts down all power supplies so that no status is displayed.
Junos OS also can shut down one of the power supplies for other reasons. In this case, the remaining power supplies provide power to the firewall, and you can still view the system status through the CLI or display.
To restart a high-capacity AC power supply after a shut down due to an over-temperature situation:
Move the power switch on the power supply to the off (o) position.
Turn off power to where the AC line goes into the power distribution module (PDM) area.
Wait for the power supply LEDs to fade out and for the fans inside the power supply to shutdown. This can take up to 10 seconds.
CAUTION:Do not attempt to power-on the power supply if the LED is still lit and the fan is still running. If you do, the firewall will not reboot.
Turn on power to where the AC line goes into the power distribution module (PDM) area.
Move the power switch on the power supply to the on (|) position.
Verify that the LEDs on the power supply faceplate are properly lit.
Issue the CLI
show chassis environment pemcommand and verify the State isONLINEand the Temperature isOK.
To restart a high-capacity DC power supply after a shut down due to an over-temperature situation:
Switch off the circuit breaker(s) on the DC distribution panel to remove power to the chassis and power supplies.
Switch on the circuit breaker(s) on the distribution panel to power up the chassis and power supplies.
Note:The power switch on the power supplies is not part of the outer or inner DC circuits and therefore does not need to be switched off when restarting the chassis.
If output power is not load-balancing correctly in the same zone on a firewall with a high-capacity AC or DC power supply module, connect two feeds and change the DIP switch to 1 to boost the voltage on the power supply module.
Each High Capacity AC or DC power supply accepts two AC or DC feeds in two unique AC or DC receptacles. It is possible to operate with one feed, but there is a reduction in the power supply output. The DIP switch must be set according to the number of AC or DC feeds that are present for the power supply.
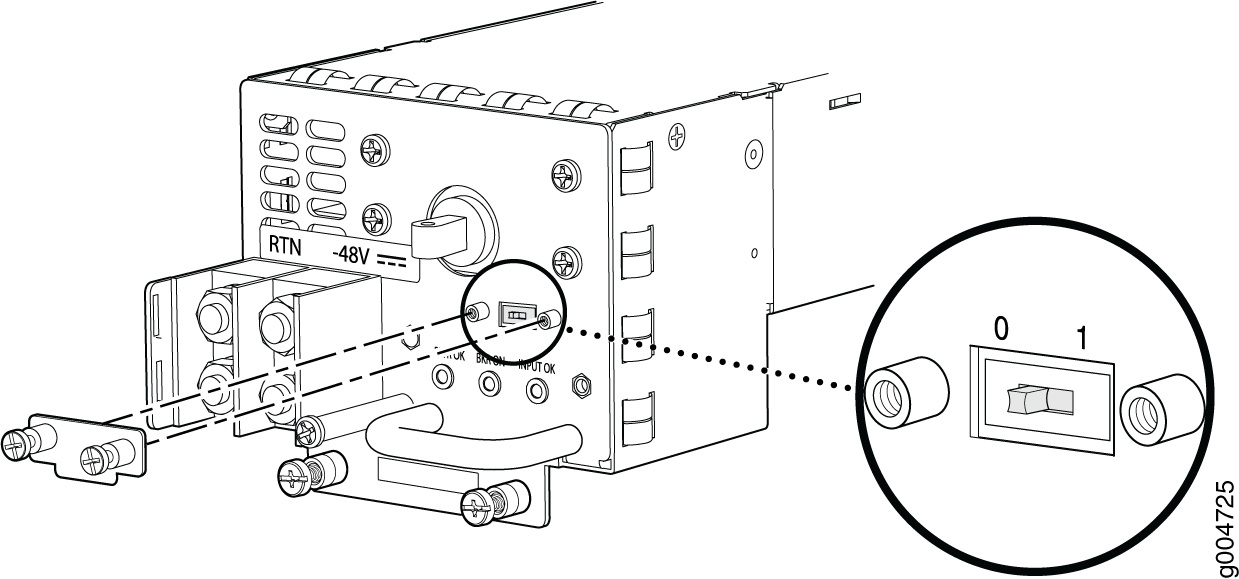
Position – 0 indicates that only one AC or DC feed is provided.
Position – 1 indicates that two AC or DC feeds are provided.
The following example shows what should be the DIP switch position based on the number of AC or DC input feeds expected and connected to the PEM:
Issue the CLI
show chassis powercommand and check how many feeds are connected.The sample out put below is the output of a chassis with AC power supplies:
content_copy zoom_out_mapuser@host# run show chassis power PEM 0: State: Online AC input: OK (1 feed expected, 1 feed connected) Capacity: 2050 W (maximum 2050 W) DC output: 423 W (zone 0, 9 A at 47 V, 20% of capacity) PEM 1: State: Online AC input: OK (1 feed expected, 2 feed connected) Capacity: 1590 W (maximum 1590 W) DC output: 893 W (zone 0, 19 A at 47 V, 56% of capacity) PEM 2: State: Present AC input: Out of range (1 feed expected, 1 feed connected) Capacity: 0 W (maximum 2050 W) PEM 3: State: Present AC input: Out of range (1 feed expected, 1 feed connected) Capacity: 1590 W (maximum 1590 W) DC output: 0 W (zone 0, 0 A at 0 V, 0% of capacity) System: Zone 0: Capacity: 3640 W (maximum 3640 W) Allocated power: 2002 W (1638 W remaining) Actual usage: 1316 W Total system capacity: 3640 W (maximum 3640 W) Total remaining power: 1638 WThe output of the
show chassis powercommand shows that; on PEM 0 one AC input feed is expected and one AC input feed is connected and on PEM 1 one AC input feed is expected and two AC input feeds are connected.Issue the
show chassis alarmscommand to see if there are any active alarms and the position of the PEM DIP switch.content_copy zoom_out_map> show chassis alarms 1 alarms currently active Alarm time Class Description 2018-06-14 05:05:17 PST Minor PEM 1 Dipswitch 0 Feed Connection 2
The output of the
show chassis alarmscommand shows one active alarm on PEM 1 and the position of the DIP switch as 0.In this example output, there is an alarm on PEM 1 because there is a need of only one AC feed but the PEM 1 is connected with two AC feeds and the DIP switch position is 0.
Change the PEM 1 DIP switch position to 1. This should clear the alarm.
Note:Changing the DIP switch position does not impact traffic. However, it is always recommended to do so in a maintenance window.
Issue the CLI
show chassis powercommand and check the output to see if the number of feeds expected on PEM 1 is the same as the feeds connected.content_copy zoom_out_map# run show chassis power PEM 0: State: Online AC input: OK (1 feed expected, 1 feed connected) Capacity: 2050 W (maximum 2050 W) DC output: 423 W (zone 0, 9 A at 47 V, 20% of capacity) PEM 1: State: Online AC input: OK (1 feed expected, 1 feed connected) Capacity: 1590 W (maximum 1590 W) DC output: 893 W (zone 0, 19 A at 47 V, 56% of capacity) PEM 2: State: Present AC input: Out of range (1 feed expected, 1 feed connected) Capacity: 0 W (maximum 2050 W) PEM 3: State: Present AC input: Out of range (1 feed expected, 1 feed connected) Capacity: 1590 W (maximum 1590 W) DC output: 0 W (zone 0, 0 A at 0 V, 0% of capacity) System: Zone 0: Capacity: 3640 W (maximum 3640 W) Allocated power: 2002 W (1638 W remaining) Actual usage: 1316 W Total system capacity: 3640 W (maximum 3640 W) Total remaining power: 1638 WThe output of the
show chassis powercommand shows that the number of feeds on PEM 1 expected is the same as the feeds connected.Issue the CLI
show chassis alarmscommand to check if the alarm is removed.content_copy zoom_out_map> show chassis alarms No alarms currently active
The output of the
show chassis alarmscommand shows no active alarms.
Behavior of the SRX5400, SRX5600, and SRX5800 Firewalls When the SRX5K-SCBE and SRX5K-RE-1800X4 in a Chassis Cluster Fail
It is important to understand the behavior of the SRX5400, SRX5600, and SRX5800 Firewalls when the Switch Control Board (SRX5K-SCBE) and Routing Engine (SRX5K-RE-1800X4) in the chassis cluster fail.
This procedure is also applicable for SCB3 except that SCB3 redundancy is supported.
We strongly recommend that you perform the ISHU during a maintenance window, or during the lowest possible traffic as the secondary node is not available at this time.
The SRX5K-SCBE and SRX5K-RE-1800X4 are not hot-swappable.
Four fabric planes must be active at any time in a chassis cluster. If fewer than four fabric planes are active, then the Redundancy Group (RG1+) will fail over to the secondary node.
Table 3 shows the minimum fabric plane requirements for the SCB.
Platform | Number of SRX5K-SCBs | Active Planes | Redundant Planes | Expected Behavior After the SCB and Routing Engine are Removed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SRX5400 | 1 | 4 (virtual) | 0 (virtual) | If the SCB in the primary node fails, the device will fail over to the secondary node as the primary node powers off. |
SRX5600 | 2 | 4 (virtual) | 4 (virtual) | If the active SCB in the primary node fails, the behavior of the device does not change as the redundant SCB becomes active provided all four fabric planes are in good condition. If the second SCB in the primary node fails, the device will fail over to the secondary node as the primary node powers off. |
SRX5800 | 3 | 4 | 2 | This device supports one SCB for two fabric planes, providing a redundancy of three SCBs. If the active SCB fails, the device behavior does not change as the remaining two SCBs fulfill the requirement to have four fabric planes. If the second SCB also fails, no spare planes are available in the chassis triggering inter-chassis redundancy. Therefore, RG1+ will fail over to the secondary node. |
In SRX5600 and SRX5800 Firewalls, failover does not happen when the secondary Routing Engine in slot 1 fails, while the SCB in slot 1 is inactive.
For detailed information about chassis cluster, see the Chassis Cluster User Guide for SRX Series Devices at www.juniper.net/documentation/.





















