ON THIS PAGE
Example: Setting Up VoIP with 802.1X and LLDP-MED on an EX Series Switch
Example: Configuring VoIP on an EX Series Switch Without Including LLDP-MED Support
Example: Configuring VoIP on an EX Series Switch Without Including LLDP-MED Support
Example: Configuring VoIP on an EX Series Switch Without Including 802.1X Authentication
Example: Setting Up VoIP with 802.1X and LLDP-MED on an EX Series Switch with ELS Support
VoIP on EX Series Switches
You can configure voice over IP (VoIP) on an EX Series switch to support IP telephones. When you use VoIP, you can connect IP telephones to the switch and configure IEEE 802.1X authentication for 802.1X-compatible IP telephones. For more information, read this topic.
Understanding 802.1X and VoIP on EX Series Switches
When you use VoIP, you can connect IP telephones to the switch and configure IEEE 802.1X authentication for 802.1X-compatible IP telephones. The 802.1X authentication provides network edge security, protecting Ethernet LANs from unauthorized user access.
VoIP is a protocol used for the transmission of voice through packet-switched networks. VoIP transmits voice calls by using a network connection instead of an analog phone line.
When VoIP is used with 802.1X, the RADIUS server authenticates the phone, and Link Layer Discovery Protocol–Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED) provides the class-of-service (CoS) parameters to the phone.
You can configure 802.1X authentication to work with VoIP in multiple supplicant or single supplicant mode. In multiple supplicant mode, the 802.1X process allows multiple supplicants to connect to the interface. Each supplicant is authenticated individually. For an example of a VoIP multiple supplicant topology, see Figure 1.
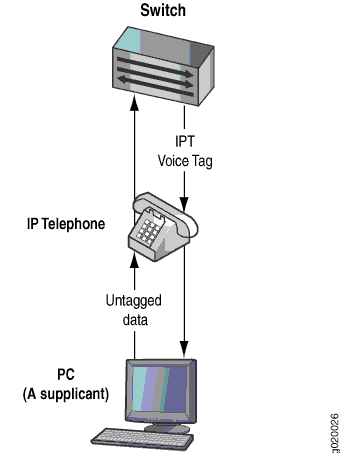
If an 802.1X-compatible IP telephone does not have an 802.1X host but has another 802.1X-compatible device connected to its data port, you can connect the phone to an interface in single supplicant mode. In single supplicant mode, the 802.1X process authenticates only the first supplicant. All other supplicants who connect later to the interface are allowed full access without any further authentication. They effectively “piggyback” on the first supplicant’s authentication. For an example of a VoIP single supplicant topology, see Figure 2 .
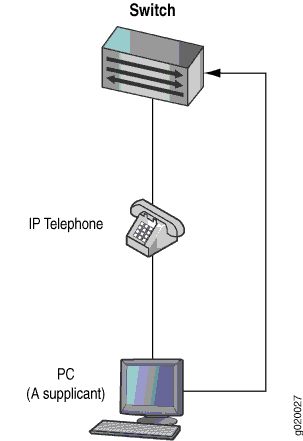
If an IP telephone does not support 802.1X, you can configure VoIP to bypass 802.1X and LLDP-MED and have the packets forwarded to a VoIP VLAN.
Multi Domain 802.1X Authentication
Multi-domain 802.1X authentication is an extension of multiple supplicant mode that allows one default VoIP device and multiple data devices to authenticate on a single port. Multi-domain 802.1X authentication provides enhanced security over multiple supplicant mode by restricting the number of authenticated data and VoIP sessions on the port. In multiple supplicant mode, any number of VoIP or data sessions can be authenticated; the number of sessions can be restricted using MAC limiting, but there is no way to apply the limit specifically to either data or VoIP sessions.
With multi-domain 802.1X authentication, the single port is divided into two domains; one is the data domain and the other is the voice domain. Multi-domain 802.1X authentication maintains separate session counts based on the domain. You can configure the maximum number of authenticated data sessions allowed on the port. The number of VoIP sessions is not configurable; only one authenticated VoIP session is allowed on the port.
If a new client attempts to authenticate on the interface after
the maximum session count has been reached, the default action is
to drop the packet and generate an error log message. You can also
configure the action to shut down the interface. The port can be manually
recovered from the down state by issuing the clear dot1x recovery-timeout command, or by can recover automatically
after a configured recovery timeout period.
Multi-domain authentication does not enforce the order of device authentication. However, for the best results, the VoIP device should be authenticated before a data device on a multi domain 802.1X-enabled port. Multi-domain authentication is supported only in multiple supplicant mode.
See Also
Example: Setting Up VoIP with 802.1X and LLDP-MED on an EX Series Switch
You can configure voice over IP (VoIP) on an EX Series switch to support IP telephones. The Link Layer Discovery Protocol–Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED) protocol forwards VoIP parameters from the switch to the phone. You also configure 802.1X authentication to allow the telephone access to the LAN. Authentication is done through a backend RADIUS server.
This example describes how to configure VoIP on an EX Series switch to support an Avaya IP phone, as well as the LLDP-MED protocol and 802.1X authentication:
If your switch runs Junos OS for EX Series switches with support for the Enhanced Layer 2 Software (ELS) configuration style, see Example: Setting Up VoIP with 802.1X and LLDP-MED on an EX Series Switch with ELS Support. For ELS details, see Using the Enhanced Layer 2 Software CLI.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
Junos OS Release 9.1 or later for EX Series switches
One EX Series switch acting as an authenticator port access entity (PAE). The interfaces on the authenticator PAE form a control gate that blocks all traffic to and from supplicants until they are authenticated.
An Avaya 9620 IP telephone that supports LLDP-MED and 802.1X
Before you configure VoIP, be sure you have:
Installed your EX Series switch. See Installing and Connecting an EX3200 Switch.
Performed the initial switch configuration. See Connecting and Configuring an EX Series Switch (J-Web Procedure).
Performed basic bridging and VLAN configuration on the switch. See Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN for an EX Series Switch.
Configured the RADIUS server for 802.1X authentication and set up the access profile. See Example: Connecting a RADIUS Server for 802.1X to an EX Series Switch.
(Optional) Configured interface ge-0/0/2 for Power over Ethernet (PoE). The PoE configuration is not necessary if the VoIP supplicant is using a power adapter. For information about configuring PoE, see Configuring PoE Interfaces on EX Series Switches.
If the IP address isn't configured on the Avaya IP phone,
the phone exchanges LLDP-MED information to get the VLAN ID for the
voice VLAN. You must configure the voip statement on the
interface to designate the interface as a VoIP interface and allow
the switch to forward the VLAN name and VLAN ID for the voice VLAN
to the IP telephone. The IP telephone then uses the voice VLAN (that
is, it references the voice VLAN’s ID) to send a DHCP discover
request and exchange information with the DHCP server (voice gateway).
Overview and Topology
Instead of using a regular telephone, you connect an IP telephone directly to the switch. An IP phone has all the hardware and software needed to handle VoIP. You also can power an IP telephone by connecting it to one of the Power over Ethernet (PoE) interfaces on the switch.
In this example, the access interface ge-0/0/2 on the EX4200 switch is connected to an Avaya 9620 IP telephone. Avaya phones have a built-in bridge that allows you to connect a desktop PC to the phone, so the desktop and phone in a single office require only one interface on the switch. The EX Series switch is connected to a RADIUS server on interface ge-0/0/10 (see Figure 3).
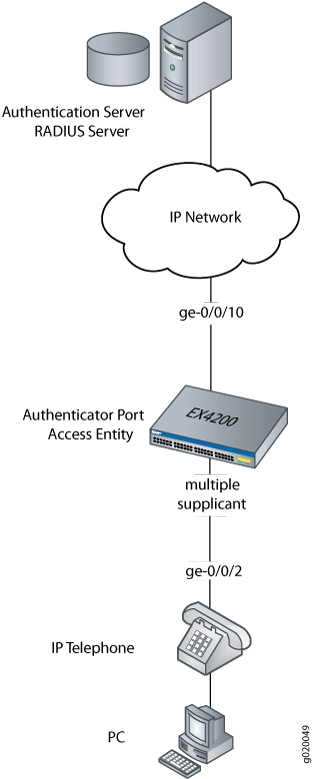
In this example, you configure VoIP parameters and specify the forwarding class assured-forward for voice traffic to provide the highest quality of service.
Table 1 describes the components used in this VoIP configuration example.
| Property | Settings |
|---|---|
Switch hardware |
EX4200 switch |
VLAN names |
data-vlan voice-vlan |
Connection to Avaya phone—with integrated hub, to connect phone and desktop PC to a single interface (requires PoE) |
ge-0/0/2 |
One RADIUS server |
Provides backend database connected to the switch through interface ge-0/0/10. |
As well as configuring a VoIP for interface ge-0/0/2, you configure:
802.1X authentication. Authentication is set to multiple supplicant to support more than one supplicant's access to the LAN through interface ge-0/0/2.
LLDP-MED protocol information. The switch uses LLDP-MED to forward VoIP parameters to the phone. Using LLDP-MED ensures that voice traffic gets tagged and prioritized with the correct values at the source itself. For example, 802.1p class of service and 802.1Q tag information can be sent to the IP telephone.
Note:A PoE configuration is not necessary if an IP telephone is using a power adapter.
Configuration
To configure VoIP, LLDP-MED, and 802.1X authentication:
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure VoIP, LLDP-MED, and 802.1X, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit] set vlans data-vlan vlan-id 77 set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 99 set vlans data-vlan interface ge-0/0/2.0 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members data-vlan set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode access set ethernet-switching-options voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 vlan voice-vlan set ethernet-switching-options voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 forwarding-class assured-forwarding set protocols lldp-med interface ge-0/0/2.0 set protocols dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/2.0 supplicant multiple
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure VoIP with LLDP-MED and 802.1X:
Configure the VLANs for voice and data:
[edit vlans] user@switch# set data-vlan vlan-id 77 user@switch# set voice-vlan vlan-id 99
Associate the VLAN data-vlan with the interface:
[edit vlans] user@switch# set data-vlan interface ge-0/0/2.0Configure the interface as an access interface, configure support for Ethernet switching, and add the data-vlan VLAN:
[edit interfaces] user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members data-vlan user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode access
Configure VoIP on the interface and specify the assured-forwarding forwarding class to provide the most dependable class of service:
[edit ethernet—switching—options] user@switch# set voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 vlan voice-vlan user@switch# set voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 forwarding-class assured-forwarding
Configure LLDP-MED protocol support:
[edit protocols] user@switch# set lldp-med interface ge-0/0/2.0
To authenticate an IP phone and a PC connected to the IP phone on the interface, configure 802.1X authentication support and specify multiple supplicant mode:
Note:If you do not want to authenticate any device, skip the 802.1X configuration on this interface.
[edit protocols] user@switch# set dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/2.0 supplicant multiple
Results
Display the results of the configuration:
[edit]
user@switch# show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode access;
vlan {
members data-vlan;
}
}
}
}
}
protocols {
lldp-med {
interface ge-0/0/2.0;
}
dot1x {
authenticator {
interface {
ge-0/0/2.0 {
supplicant multiple;
}
}
}
}
}
vlans {
data-vlan {
vlan-id 77;
interface {
ge-0/0/2.0;
}
}
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 99;
}
}
ethernet-switching options {
voip {
interface ge-0/0/2.0 {
vlan voice-vlan;
forwarding-class assured-forwarding;
}
}
}
Verification
To confirm that the configuration is working properly, perform these tasks:
- Verifying LLDP-MED Configuration
- Verifying 802.1X Authentication for IP Phone and Desktop PC
- Verifying the VLAN Association with the Interface
Verifying LLDP-MED Configuration
Purpose
Verify that LLDP-MED is enabled on the interface.
Action
user@switch> show lldp detail LLDP : Enabled Advertisement interval : 30 Second(s) Transmit delay : 2 Second(s) Hold timer : 2 Second(s) Config Trap Interval : 300 Second(s) Connection Hold timer : 60 Second(s) LLDP MED : Enabled MED fast start count : 3 Packet(s) Interface LLDP LLDP-MED Neighbor count all Enabled - 0 ge-0/0/2.0 - Enabled 0 Interface VLAN-id VLAN-name ge-0/0/0.0 0 default ge-0/0/1.0 0 employee-vlan ge-0/0/2.0 0 data-vlan ge-0/0/2.0 99 voice-vlan ge-0/0/3.0 0 employee-vlan ge-0/0/8.0 0 employee-vlan ge-0/0/10.0 0 default ge-0/0/11.0 20 employee-vlan ge-0/0/23.0 0 default LLDP basic TLVs supported: Chassis identifier, Port identifier, Port description, System name, System description, System capabilities, Management address. LLDP 802 TLVs supported: Power via MDI, Link aggregation, Maximum frame size, Port VLAN tag, Port VLAN name. LLDP MED TLVs supported: LLDP MED capabilities, Network policy, Endpoint location, Extended power Via MDI.
Meaning
The show lldp detail output shows that both
LLDP and LLDP-MED are configured on the ge-0/0/2.0 interface.
The end of the output shows the list of supported LLDP basic TLVs,
802.3 TLVs, and LLDP-MED TLVs that are supported.
Verifying 802.1X Authentication for IP Phone and Desktop PC
Purpose
Display the 802.1X configuration to confirm that the VoIP interface has access to the LAN.
Action
user@switch> show dot1x interface ge/0/0/2.0 detail
ge-0/0/2.0
Role: Authenticator
Administrative state: Auto
Supplicant mode: Multiple
Number of retries: 3
Quiet period: 60 seconds
Transmit period: 30 seconds
Mac Radius: Disabled
Mac Radius Restrict: Disabled
Reauthentication: Enabled
Configured Reauthentication interval: 3600 seconds
Supplicant timeout: 30 seconds
Server timeout: 30 seconds
Maximum EAPOL requests: 2
Guest VLAN member: <not configured>
Number of connected supplicants: 1
Supplicant: user101, 00:04:0f:fd:ac:fe
Operational state: Authenticated
Authentication method: Radius
Authenticated VLAN: vo11
Dynamic Filter: match source-dot1q-tag 10 action deny
Session Reauth interval: 60 seconds
Reauthentication due in 50 seconds
Meaning
The field Role shows that the ge-0/0/2.0 interface is in the authenticator state. The Supplicant field shows that the interface is configured in multiple supplicant mode, permitting multiple supplicants to be authenticated on this interface. The MAC addresses of the supplicants currently connected are displayed at the bottom of the output.
Verifying the VLAN Association with the Interface
Purpose
Display the interface state and VLAN membership.
Action
user@switch> show ethernet-switching interfaces
Ethernet-switching table: 0 entries, 0 learned
user@switch> show ethernet-switching interfaces
Interface State VLAN members Blocking
ge-0/0/0.0 down default unblocked
ge-0/0/1.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/5.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/3.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/8.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/10.0 down default unblocked
ge-0/0/11.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/23.0 down default unblocked
ge-0/0/2.0 up voice-vlan unblocked
data-vlan unblockedMeaning
The field VLAN members shows that the ge-0/0/2.0 interface supports both the data-vlan VLAN and voice-vlan VLAN. The State field shows that the interface is up.
Example: Configuring VoIP on an EX Series Switch Without Including LLDP-MED Support
You can configure voice over IP (VoIP) on an EX Series switch to support IP telephones. The Link Layer Discovery Protocol–Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED) protocol is sometimes used with IP phones to forward VoIP parameters from the switch to the phone. However, not all IP phones support LLDP-MED.
This example describes how to configure VoIP on an EX Series switch without using LLDP-MED:
- Requirements
- Overview
- Configuring VoIP Without LLDP-MED by Using a Voice VLAN on an Access Port
- Configuring VoIP Without LLDP-MED by Using a Trunk Port with Native VLAN Option
- Verification
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
One EX Series switch with support for ELS acting as an authenticator port access entity (PAE). The interfaces on the authenticator PAE form a control gate that blocks all traffic to and from supplicants until they are authenticated.
An IP phone that does not support LLDP-MED.
Junos OS Release 13.2X50 or later for EX Series switches.
Before you configure VoIP, be sure you have:
Performed basic bridging and VLAN configuration on the switch. See Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN for an EX Series Switch with ELS Support .
Configured the IP phone as a member of the voice VLAN.
(Optional) Configured interface ge-0/0/2 for Power over Ethernet (PoE). The PoE configuration is not necessary if the VoIP supplicant is using a power adapter. See Configuring PoE Interfaces on EX Series Switches.
Overview
Instead of using a regular telephone, you connect an IP telephone directly to the switch. An IP phone has all the hardware and software needed to handle VoIP. You can also power an IP telephone by connecting it to one of the Power over Ethernet (PoE) interfaces on the switch.
EX Series switches can accommodate an IP telephone and end host connected to a single switch port. In such a scenario, voice and data traffic must be separated into different broadcast domains, or VLANs. One method for accomplishing this is by configuring a voice VLAN, which enables access ports to accept untagged data traffic as well as tagged voice traffic from IP phones, and associate each type of traffic with separate and distinct VLANs. Voice traffic (tagged) can then be treated differently, generally with a higher priority than data traffic (untagged).
The voice VLAN delivers the greatest benefit when used with IP phones that support LLDP-MED, but it is flexible enough that IP phones that do not support LLDP-MED can also use it effectively. However, in the absence of LLDP-MED, the voice VLAN ID must be set manually on the IP phone because LLDP-MED is not available to accomplish this dynamically. For information about setting up a voice VLAN for IP phones that support LLDP-MED, see Example: Setting Up VoIP with 802.1X and LLDP-MED on an EX Series Switch with ELS Support.
Another method to separate voice (tagged) and data (untagged) traffic into different VLANs is to use a trunk port with the native VLAN ID option. The trunk port is added as a member of the voice VLAN, and processes only tagged voice traffic from that VLAN. The trunk port must also be configured with the native VLAN ID for the data VLAN so that it can process untagged data traffic from the data VLAN. This configuration also requires that the voice VLAN ID be set manually on the IP phone.
This example illustrates both methods. In this example, the interface ge-0/0/2 on the switch is connected to a non-LLDP-MED IP phone.
The implementation of a voice VLAN on an IP telephone is vendor-specific. Consult the documentation that came with your IP telephone for instructions on configuring a voice VLAN. For example, on an Avaya phone, you can ensure that the phone gets the correct VoIP VLAN ID even in the absence of LLDP-MED by enabling DHCP option 176.
Topology
Configuring VoIP Without LLDP-MED by Using a Voice VLAN on an Access Port
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure VoIP, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit] set vlans data-vlan vlan-id 77 set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 99 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode access set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members data-vlan set switch-options voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 vlan voice-vlan set switch-options voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 forwarding-class assured-forwarding
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure two VLANs: one for data traffic and one for voice traffic:
[edit vlans] user@switch# set data-vlan vlan-id 77 user@switch# set voice-vlan vlan-id 99
Note:The voice VLAN ID must be set manually on the IP phone.
Associate the VLAN
data-vlanwith the interface ge-0/0/2:[edit vlans] user@switch# set data-vlan switch-options interface ge-0/0/2.0
Configure the interface ge-0/0/2 as an access port belonging to the data VLAN:
[edit interfaces] user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode access user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan member data-vlan
Configure VoIP on the interface ge-0/0/2 and add this interface to the voice VLAN:
[edit switch-options] user@switch# set voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 vlan voice-vlan
Specify the assured-forwarding forwarding class to provide the most dependable class of service:
[edit switch-options] user@switch# set voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 forwarding-class assured-forwarding
Results
Display the results of the configuration:
[edit]
user@switch> show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode access;
vlan {
members data-vlan;
}
}
}
}
}
vlans {
data-vlan {
vlan-id 77;
interface {
ge-0/0/2.0;
}
}
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 99;
}
}
ethernet-switching options {
voip {
interface ge-0/0/2.0 {
vlan voice-vlan;
forwarding-class assured-forwarding;
}
}
}
Configuring VoIP Without LLDP-MED by Using a Trunk Port with Native VLAN Option
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure VoIP, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit] set vlans data-vlan vlan-id 77 set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 99 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members voice-vlan set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching native-vlan-id data-vlan
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure two VLANs: one for data traffic and one for voice traffic:
[edit vlans] user@switch# set data-vlan vlan-id 77 user@switch# set voice-vlan vlan-id 99
Note:The voice VLAN ID must be set manually on the IP phone.
Configure interface ge-0/0/2 as a trunk port that includes only the voice VLAN:
[edit interfaces] user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan member voice-vlan
Configure the native VLAN ID for the data VLAN on the trunk port:
[edit interfaces] user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching native-vlan-id data-vlan
Results
Display the results of the configuration:
[edit]
user@switch> show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members voice-vlan;
}
native-vlan-id data-vlan;
}
}
}
}
vlans {
data-vlan {
vlan-id 77;
}
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 99;
}
}
Verification
To confirm that the configuration is working properly, perform the following task:
Verifying the VLAN Association With the Interface
Purpose
Display the interface state and VLAN membership.
Action
user@switch> show ethernet-switching interfaces
Ethernet-switching table: 0 entries, 0 learned
user@switch> show ethernet-switching interfaces
Interface State VLAN members Blocking
ge-0/0/0.0 down default unblocked
ge-0/0/1.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/5.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/3.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/8.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/10.0 down default unblocked
ge-0/0/11.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/23.0 down default unblocked
ge-0/0/2.0 up voice-vlan unblocked
data-vlan unblockedMeaning
The field VLAN members shows that the ge-0/0/2.0 interface supports both the data VLAN,
data-vlan, and the voice VLAN, voice-vlan. The State field shows that the interface is up.
Example: Configuring VoIP on an EX Series Switch Without Including LLDP-MED Support
You can configure voice over IP (VoIP) on an EX Series switch to support IP telephones. The Link Layer Discovery Protocol–Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED) protocol is sometimes used with IP phones to forward VoIP parameters from the switch to the phone. However, not all IP phones support LLDP-MED.
This example describes how to configure VoIP on an EX Series switch without using LLDP-MED:
- Requirements
- Overview
- Configuring VoIP Without LLDP-MED by Using a Voice VLAN on an Access Port
- Configuring VoIP Without LLDP-MED by Using a Trunk Port with Native VLAN Option
- Verification
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
One EX4200 switch acting as an authenticator port access entity (PAE). The interfaces on the authenticator PAE form a control gate that blocks all traffic to and from supplicants until they are authenticated.
An IP phone that does not support LLDP-MED.
Junos OS Release 9.1 or later for EX Series switches.
Before you configure VoIP, be sure you have:
Performed basic bridging and VLAN configuration on the switch. See Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN for an EX Series Switch.
Configured the IP phone as a member of the voice VLAN.
(Optional) Configured interface ge-0/0/2 for Power over Ethernet (PoE). The PoE configuration is not necessary if the VoIP supplicant is using a power adapter. See Configuring PoE Interfaces on EX Series Switches.
Overview
Instead of using a regular telephone, you connect an IP telephone directly to the switch. An IP phone has all the hardware and software needed to handle VoIP. You can also power an IP telephone by connecting it to one of the Power over Ethernet (PoE) interfaces on the switch.
EX Series switches can accommodate an IP telephone and end host connected to a single switch port. In such a scenario, voice and data traffic must be separated into different broadcast domains, or VLANs. One method for accomplishing this is by configuring a voice VLAN, which enables access ports to accept untagged data traffic as well as tagged voice traffic from IP phones, and associate each type of traffic with separate and distinct VLANs. Voice traffic (tagged) can then be treated differently, generally with a higher priority than data traffic (untagged).
The voice VLAN delivers the greatest benefit when used with IP phones that support LLDP-MED, but it is flexible enough that IP phones that do not support LLDP-MED can also use it effectively. However, in the absence of LLDP-MED, the voice VLAN ID must be set manually on the IP phone because LLDP-MED is not available to accomplish this dynamically. For information about setting up a voice VLAN for IP phones that support LLDP-MED, see Example: Setting Up VoIP with 802.1X and LLDP-MED on an EX Series Switch.
Another method to separate voice (tagged) and data (untagged) traffic into different VLANs is to use a trunk port with the native VLAN ID option. The trunk port is added as a member of the voice VLAN, and processes only tagged voice traffic from that VLAN. The trunk port must also be configured with the native VLAN ID for the data VLAN so that it can process untagged data traffic from the data VLAN. This configuration also requires that the voice VLAN ID be set manually on the IP phone.
This example illustrates both methods. In this example, the interface ge-0/0/2 on the EX4200 switch is connected to a non-LLDP-MED IP phone.
The implementation of a voice VLAN on an IP telephone is vendor-specific. Consult the documentation that came with your IP telephone for instructions on configuring a voice VLAN. For example, on an Avaya phone, you can ensure that the phone gets the correct VoIP VLAN ID even in the absence of LLDP-MED by enabling DHCP option 176.
Topology
Configuring VoIP Without LLDP-MED by Using a Voice VLAN on an Access Port
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure VoIP, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit] set vlans data-vlan vlan-id 77 set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 99 set vlans data-vlan interface ge-0/0/2.0 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode access set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members data-vlan set ethernet-switching-options voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 vlan voice-vlan
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure two VLANs: one for data traffic and one for voice traffic:
[edit vlans] user@switch# set data-vlan vlan-id 77 user@switch# set voice-vlan vlan-id 99
Note:The voice VLAN ID must be set manually on the IP phone.
Configure the VLAN data-vlan on the interface ge-0/0/2:
[edit vlans] user@switch# set data-vlan interface ge-0/0/2.0
Configure the interface ge-0/0/2 as an access port belonging to the data VLAN:
[edit interfaces] user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode access user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan member data-vlan
Configure VoIP on the interface ge-0/0/2 and add this interface to the voice VLAN:
[edit ethernet-switching-options] user@switch# set voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 vlan voice-vlan
Results
Display the results of the configuration:
[edit]
user@switch> show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode access;
vlan {
members data-vlan;
}
}
}
}
}
vlans {
data-vlan {
vlan-id 77;
interface {
ge-0/0/2.0;
}
}
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 99;
}
}
ethernet-switching options {
voip {
interface ge-0/0/2.0 {
vlan voice-vlan;
}
}
}
Configuring VoIP Without LLDP-MED by Using a Trunk Port with Native VLAN Option
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure VoIP, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit] set vlans data-vlan vlan-id 77 set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 99 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members voice-vlan set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching native-vlan-id data-vlan
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure two VLANs: one for data traffic and one for voice traffic:
[edit vlans] user@switch# set data-vlan vlan-id 77 user@switch# set voice-vlan vlan-id 99
Note:The voice VLAN ID must be set manually on the IP phone.
Configure interface ge-0/0/2 as a trunk port that includes only the voice VLAN:
[edit interfaces] user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan member voice-vlan
Configure the native VLAN ID for the data VLAN on the trunk port:
[edit interfaces] user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching native-vlan-id data-vlan
Results
Display the results of the configuration:
[edit]
user@switch> show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members voice-vlan;
}
native-vlan-id data-vlan;
}
}
}
}
vlans {
data-vlan {
vlan-id 77;
}
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 99;
}
}
Verification
To confirm that the configuration is working properly, perform the following task:
Verifying the VLAN Association With the Interface
Purpose
Display the interface state and VLAN membership.
Action
user@switch> show ethernet-switching interfaces
Ethernet-switching table: 0 entries, 0 learned
user@switch> show ethernet-switching interfaces
Interface State VLAN members Blocking
ge-0/0/0.0 down default unblocked
ge-0/0/1.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/5.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/3.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/8.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/10.0 down default unblocked
ge-0/0/11.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/23.0 down default unblocked
ge-0/0/2.0 up voice-vlan unblocked
data-vlan unblockedMeaning
The field VLAN members shows that the ge-0/0/2.0 interface supports both the data VLAN,
data-vlan, and the voice VLAN, voice-vlan. The State field shows that the interface is up.
Example: Configuring VoIP on an EX Series Switch Without Including 802.1X Authentication
You can configure voice over IP (VoIP) on an EX Series switch to support IP telephones.
To configure VoIP on an EX Series switch to support an IP phone that does not support 802.1X authentication, you must either add the MAC address of the phone to the static MAC bypass list or enable MAC RADIUS authentication on the switch.
This example describes how to configure VoIP on an EX Series switch without 802.1X authentication using static MAC bypass of authentication:
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
Junos OS Release 9.1 or later for EX Series switches
An IP telephone
Before you configure VoIP, be sure you have:
Installed your EX Series switch. See the installation information for your switch.
Performed the initial switch configuration. See Connecting and Configuring an EX Series Switch (CLI Procedure).
Performed basic bridging and VLAN configuration on the switch. See Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN for an EX Series Switch.
Configured the RADIUS server for 802.1X authentication and set up the access profile. See Example: Connecting a RADIUS Server for 802.1X to an EX Series Switch.
(Optional) Configured interface
ge-0/0/2for Power over Ethernet (PoE). The PoE configuration is not necessary if the VoIP supplicant is using a power adapter. For information about configuring PoE, see Configuring PoE Interfaces on EX Series Switches.
If the IP address isn't configured on the Avaya IP phone,
the phone exchanges LLDP-MED information to get the VLAN ID for the
voice VLAN. You must configure the voip statement on the
interface to designate the interface as a VoIP interface and allow
the switch to forward the VLAN name and VLAN ID for the voice VLAN
to the IP telephone. The IP telephone then uses the voice VLAN (that
is, it references the voice VLAN’s ID) to send a DHCP discover
request and exchange information with the DHCP server (voice gateway).
Overview
Instead of using a regular telephone, you connect an IP telephone directly to the switch. An IP phone has all the hardware and software needed to handle VoIP. You also can power an IP telephone by connecting it to one of the Power over Ethernet (PoE) interfaces on the switch.
In this example, the access interface ge-0/0/2 on
the EX4200 switch is connected to a non-802.1X IP phone.
To configure VoIP on an EX Series switch to support an IP phone that does not support 802.1X authentication, add the MAC address of the phone as a static entry in the authenticator database and set the supplicant mode to multiple.
Configuration
To configure VoIP without 802.1X authentication:
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure VoIP, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit] set vlans data-vlan vlan-id 77 set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 99 set vlans data-vlan interface ge-0/0/2.0 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members data-vlan set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode access set ethernet-switching-options voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 vlan voice-vlan set ethernet-switching-options voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 forwarding-class assured-forwarding set protocols lldp-med interface ge-0/0/2.0 set protocols dot1x authenticator authentication-profile-name auth-profile set protocols dot1x authenticator static 00:04:f2:11:aa:a7 set protocols dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/2.0 supplicant multiple
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure VoIP without 802.1X:
Configure the VLANs for voice and data:
[edit vlans] user@switch# set data-vlan vlan-id 77 user@switch# set voice-vlan vlan-id 99
Associate the VLAN
data-vlanwith the interface:[edit vlans] user@switch# set data-vlan interface ge-0/0/2.0Configure the interface as an access interface, configure support for Ethernet switching, and add the
data-vlanVLAN:[edit interfaces] user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members data-vlan user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode access
Configure VoIP on the interface and specify the
assured-forwardingforwarding class to provide the most dependable class of service:[edit ethernet-switching-options] user@switch# set voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 vlan voice-vlan user@switch# set voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 forwarding-class assured-forwarding
Configure LLDP-MED protocol support:
[edit protocols] user@switch# set lldp-med interface ge-0/0/2.0
Set the authentication profile (see Configuring 802.1X Interface Settings (CLI Procedure) and Configuring 802.1X RADIUS Accounting (CLI Procedure)):
[edit protocols] set dot1x authenticator authentication-profile-name auth-profile
Add the MAC address of the phone to the static MAC bypass list:
[edit protocols] set dot1x authenticator static 00:04:f2:11:aa:a7
Set the supplicant mode to multiple:
[edit protocols] set dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/2.0 supplicant multiple
Results
Display the results of the configuration:
[edit]
user@switch# show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode access;
vlan {
members data-vlan;
}
}
}
}
}
protocols {
lldp-med {
interface ge-0/0/2.0;
}
dot1x {
authenticator {
authentication-profile-name auth-profile;
static {
00:04:f2:11:aa:a7;
}
}
interface {
ge-0/0/2.0 {
supplicant multiple;
}
}
}
}
vlans {
data-vlan {
vlan-id 77;
interface {
ge-0/0/2.0;
}
}
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 99;
}
}
ethernet-switching options {
voip {
interface ge-0/0/2.0 {
vlan voice-vlan;
forwarding-class assured-forwarding;
}
}
}
Verification
To confirm that the configuration is working properly, perform these tasks:
- Verifying LLDP-MED Configuration
- Verifying Authentication for the Desktop PC
- Verifying the VLAN Association with the Interface
Verifying LLDP-MED Configuration
Purpose
Verify that LLDP-MED is enabled on the interface.
Action
user@switch> show lldp detail LLDP : Enabled Advertisement interval : 30 Second(s) Transmit delay : 2 Second(s) Hold timer : 2 Second(s) Config Trap Interval : 300 Second(s) Connection Hold timer : 60 Second(s) LLDP MED : Enabled MED fast start count : 3 Packet(s) Interface LLDP LLDP-MED Neighbor count all Enabled - 0 ge-0/0/2.0 - Enabled 0 Interface VLAN-id VLAN-name ge-0/0/0.0 0 default ge-0/0/1.0 0 employee-vlan ge-0/0/2.0 0 data-vlan ge-0/0/2.0 99 voice-vlan ge-0/0/3.0 0 employee-vlan ge-0/0/8.0 0 employee-vlan ge-0/0/10.0 0 default ge-0/0/11.0 20 employee-vlan ge-0/0/23.0 0 default LLDP basic TLVs supported: Chassis identifier, Port identifier, Port description, System name, System description, System capabilities, Management address. LLDP 802 TLVs supported: Power via MDI, Link aggregation, Maximum frame size, Port VLAN tag, Port VLAN name. LLDP MED TLVs supported: LLDP MED capabilities, Network policy, Endpoint location, Extended power Via MDI.
Meaning
The show lldp detail output shows that both
LLDP and LLDP-MED are configured on the ge-0/0/2.0 interface.
The end of the output shows the list of supported LLDP basic TLVs,
802.3 TLVs, and LLDP-MED TLVs that are supported.
Verifying Authentication for the Desktop PC
Purpose
Display the 802.1X configuration for the desktop PC connected to the VoIP interface through the IP phone.
Action
user@switch> show dot1x interface ge/0/0/2.0 detail
ge-0/0/2.0
Role: Authenticator
Administrative state: Auto
Supplicant mode: Multiple
Number of retries: 3
Quiet period: 60 seconds
Transmit period: 30 seconds
Mac Radius: Disabled
Mac Radius Restrict: Disabled
Reauthentication: Enabled
Configured Reauthentication interval: 3600 seconds
Supplicant timeout: 30 seconds
Server timeout: 30 seconds
Maximum EAPOL requests: 2
Guest VLAN member: <not configured>
Number of connected supplicants: 1
Supplicant: user101, 00:04:0f:fd:ac:fe
Operational state: Authenticated
Authentication method: Radius
Authenticated VLAN: vo11
Dynamic Filter: match source-dot1q-tag 10 action deny
Session Reauth interval: 60 seconds
Reauthentication due in 50 seconds
Meaning
The field Role shows
that the ge-0/0/2.0 interface is in
the authenticator state. The Supplicant field shows that the interface is configured in multiple supplicant
mode, permitting multiple supplicants to be authenticated on this
interface. The MAC addresses of the supplicants currently connected
are displayed at the bottom of the output.
Verifying the VLAN Association with the Interface
Purpose
Display the interface state and VLAN membership.
Action
user@switch> show ethernet-switching interfaces
Ethernet-switching table: 0 entries, 0 learned
user@switch> show ethernet-switching interfaces
Interface State VLAN members Blocking
ge-0/0/0.0 down default unblocked
ge-0/0/1.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/5.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/3.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/8.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/10.0 down default unblocked
ge-0/0/11.0 down employee-vlan unblocked
ge-0/0/23.0 down default unblocked
ge-0/0/2.0 up voice-vlan unblocked
data-vlan unblockedMeaning
The field VLAN members shows that the ge-0/0/2.0 interface
supports both the data-vlan VLAN and voice-vlan VLAN. The State field shows that the interface is up.
Example: Setting Up VoIP with 802.1X and LLDP-MED on an EX Series Switch with ELS Support
This example uses Junos OS for EX Series switches with support for the Enhanced Layer 2 Software (ELS) configuration style. If your switch runs software that does not support ELS, see Example: Setting Up VoIP with 802.1X and LLDP-MED on an EX Series Switch. For ELS details, see Using the Enhanced Layer 2 Software CLI.
You can configure VoIP on an EX Series switch to support IP telephones. The Link Layer Discovery Protocol–Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED) protocol forwards VoIP parameters from the switch to the phone. You also configure 802.1X authentication to allow the telephone access to the LAN. Authentication is done through a backend RADIUS server.
This example describes how to configure VoIP on an EX Series switch to support an Avaya IP phone, as well as how to configure the LLDP-MED protocol and 802.1X authentication:
Requirements
This example uses the following software and hardware components:
This example also applies to QFX5100 switches.
Junos OS Release 13.2X50 or later for EX Series switches
One EX Series switch with support for ELS acting as an authenticator port access entity (PAE). The interfaces on the authenticator PAE form a control gate that blocks all traffic to and from supplicants until they are authenticated.
An Avaya IP telephone that supports LLDP-MED and 802.1X
Before you configure VoIP, be sure you have:
Installed your EX Series switch. See the installation information for your switch.
Performed the initial switch configuration. See Connecting and Configuring an EX Series Switch (CLI Procedure).
Performed basic bridging and VLAN configuration on the switch. See Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN for an EX Series Switch with ELS Support or Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN on Switches.
Configured the RADIUS server for 802.1X authentication and set up the access profile. See Example: Connecting a RADIUS Server for 802.1X to an EX Series Switch.
(Optional) Configured the interface ge-0/0/2 for Power over Ethernet (PoE). The PoE configuration is not necessary if the VoIP supplicant uses a power adapter. For information about configuring PoE, see Configuring PoE Interfaces on EX Series Switches.
If the IP address is not configured on the Avaya IP phone,
the phone exchanges LLDP-MED information to get the VLAN ID for the
voice VLAN. You must configure the voip statement on the
interface to designate the interface as a VoIP interface and allow
the switch to forward the VLAN name and VLAN ID for the voice VLAN
to the IP telephone. The IP telephone then uses the voice VLAN (that
is, it references the voice VLAN’s ID) to send a DHCP discover
request and exchange information with the DHCP server (voice gateway).
Overview and Topology
Instead of using a regular telephone, you connect an IP telephone directly to the switch. An IP phone has all the hardware and software needed to handle VoIP. You also can power an IP telephone by connecting it to one of the Power over Ethernet (PoE) interfaces on the switch.
EX Series switches can accommodate an IP telephone and end host connected to a single switch port. In such a scenario, voice and data traffic must be separated into different broadcast domains, or VLANs. One method for accomplishing this is by configuring a voice VLAN, which enables access ports to accept untagged data traffic as well as tagged voice traffic from IP phones, and associate each type of traffic with separate and distinct VLANs. Voice traffic (tagged) can then be treated differently, generally with a higher priority than data traffic (untagged).
If a MAC addresses has been learned on both the data and voice VLANs, it remains active unless it ages out of both VLANs, or both VLANs are deleted.
In this example, the access interface ge-0/0/2 on the EX Series switch is connected to an Avaya IP telephone. Avaya phones have a built-in bridge that enables you to connect a desktop PC to the phone, so the desktop and phone in a single office require only one interface on the switch. The EX Series switch is connected to a RADIUS server on the ge-0/0/10 interface (see Figure 4).
This figure also applies to QFX5100 switches.
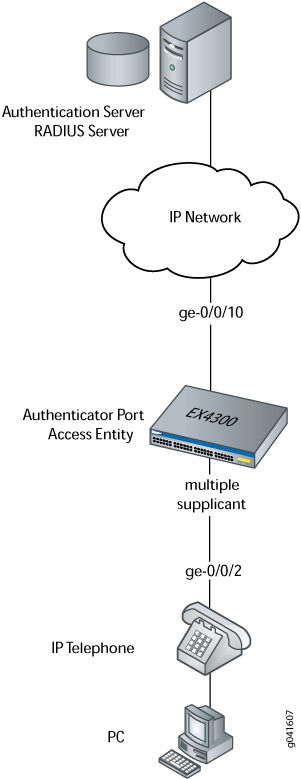
In this example, you configure VoIP parameters and specify the
forwarding class assured-forward for voice traffic to provide
the highest quality of service.
Table 2 describes the components used in this VoIP configuration example.
| Property | Settings |
|---|---|
Switch hardware |
EX Series switch with support for ELS. |
VLAN names and IDs |
data-vlan, 77 voice-vlan, 99 |
Connection to Avaya phone—with integrated hub, to connect phone and desktop PC to a single interface (requires PoE) |
ge-0/0/2 |
One RADIUS server |
Provides backend database connected to the switch through interface ge-0/0/10. |
Besides configuring a VoIP for interface ge-0/0/2, you configure:
802.1X authentication. Authentication is set to
multiplesupplicant mode to support more than one supplicant's access to the LAN through interface ge-0/0/2.LLDP-MED protocol information. The switch uses LLDP-MED to forward VoIP parameters to the phone. Using LLDP-MED ensures that voice traffic gets tagged and prioritized with the correct values at the source itself. For example, 802.1p class of service and 802.1Q tag information can be sent to the IP telephone.
Note:A PoE configuration is not necessary if an IP telephone uses a power adapter.
Topology
Configuration
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure VoIP, LLDP-MED, and 802.1X, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit] set vlans data-vlan vlan-id 77 set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 99 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members data-vlan set switch-options voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 vlan voice-vlan set switch-options voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 forwarding-class assured-forwarding set protocols lldp-med interface ge-0/0/2 set protocols dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/2.0 supplicant multiple
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure VoIP with LLDP-MED and 802.1X:
Configure the VLANs for voice and data:
[edit vlans] user@switch# set data-vlan vlan-id 77 user@switch# set voice-vlan vlan-id 99
Associate the VLAN data-vlan with the interface:
[edit vlans] user@switch# set data-vlan switch-options interface ge-0/0/2.0Configure the interface as an access interface, configure support for Ethernet switching, and add the interface as a member of the data-vlan VLAN:
[edit interfaces] user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members data-vlan
Note:You must not configure both data and voice on the same VLAN. If you configure data and voice on the same VLAN, the configuration will not be accepted.
If you have enabled 802.1X authentication on your switch and:
-
The voice VLAN you have configured is the same as the data VLAN that the authentication server sends,
-
The data VLAN you have configured is the same as the voice VLAN that the authentication server sends, or
-
The data VLAN and the voice VLAN that the authentication server sends are the same
The client would move to HELD state.
-
Configure VoIP on the interface and specify the
assured-forwardingforwarding class to provide the most dependable class of service:[edit switch—options] user@switch# set voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 vlan voice-vlan user@switch# set voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 forwarding-class assured-forwarding
Configure LLDP-MED protocol support:
[edit protocols] user@switch# set lldp-med interface ge-0/0/2
To authenticate an IP phone and a PC connected to the IP phone on the interface, configure 802.1X authentication support and specify
multiplesupplicant mode:Note:If you do not want to authenticate any device, skip the 802.1X configuration on this interface.
[edit protocols] user@switch# set dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/2.0 supplicant multiple
Results
Display the results of the configuration:
[edit]
user@switch# show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode access;
vlan {
members data-vlan;
}
}
}
}
}
protocols {
lldp-med {
interface ge-0/0/2;
}
dot1x {
authenticator {
interface {
ge-0/0/2.0 {
supplicant multiple;
}
}
}
}
}
vlans {
data-vlan {
vlan-id 77;
switch-options {
interface ge-0/0/2.0;
}
}
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 99;
}
}
switch-options {
voip {
interface ge-0/0/2.0 {
vlan voice-vlan;
forwarding-class assured-forwarding;
}
}
}
Verification
To confirm that the configuration is working properly, perform these tasks:
- Verifying LLDP-MED Configuration
- Verifying 802.1X Authentication for IP Phone and Desktop PC
- Verifying the VLAN Association with the Interface
Verifying LLDP-MED Configuration
Purpose
Verify that LLDP-MED is enabled on the interface.
Action
user@switch> show lldp detail LLDP : Enabled Advertisement interval : 30 seconds Transmit delay : 2 seconds Hold timer : 120 seconds Notification interval : 0 Second(s) Config Trap Interval : 0 seconds Connection Hold timer : 300 seconds LLDP MED : Enabled MED fast start count : 3 Packets Port ID TLV subtype : locally-assigned Interface Parent Interface LLDP LLDP-MED Power Negotiation Neighbor count all - Enabled Enabled Enabled 0 ge-0/0/2 - - Enabled - 0 Interface Parent Interface Vlan-id Vlan-name ge-0/0/0 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/1 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/2 - 77 vlan-77 ge-0/0/2 - 99 vlan-99 ge-0/0/3 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/4 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/5 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/6 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/7 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/8 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/9 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/10 - 1 vlan-1 Basic Management TLVs supported: End Of LLDPDU, Chassis ID, Port ID, Time To Live, Port Description, System Name, System Description, System Capabilities, Management Address Organizationally Specific TLVs supported: MAC/PHY configuration/status, Power via MDI, Link aggregation, Maximum Frame Size, Port VLAN tag, Port VLAN name.
Meaning
The show lldp detail output shows that both LLDP and LLDP-MED are
configured on the ge-0/0/2 interface.
The end of the output shows the list of supported LLDP basic management
TLVs and organizationally specific TLVs that are supported.
Verifying 802.1X Authentication for IP Phone and Desktop PC
Purpose
Display the 802.1X configuration to confirm that the VoIP interface has access to the LAN.
Action
user@switch> show dot1x interface ge/0/0/2.0 detail
ge-0/0/2.0
Role: Authenticator
Administrative state: Auto
Supplicant mode: Multiple
Number of retries: 3
Quiet period: 60 seconds
Transmit period: 30 seconds
Mac Radius: Disabled
Mac Radius Restrict: Disabled
Reauthentication: Enabled
Configured Reauthentication interval: 3600 seconds
Supplicant timeout: 30 seconds
Server timeout: 30 seconds
Maximum EAPOL requests: 2
Guest VLAN member: <not configured>
Number of connected supplicants: 1
Supplicant: user101, 00:04:0f:fd:ac:fe
Operational state: Authenticated
Authentication method: Radius
Authenticated VLAN: vo11
Dynamic Filter: match source-dot1q-tag 10 action deny
Session Reauth interval: 60 seconds
Reauthentication due in 50 seconds
Meaning
The field Role shows that the ge-0/0/2.0 interface is in the authenticator state.
The Supplicant mode field shows that the interface is configured
in multiple supplicant mode, permitting
multiple supplicants to be authenticated on this interface. The MAC
addresses of the supplicants currently connected are displayed at
the bottom of the output.
Verifying the VLAN Association with the Interface
Purpose
Display the interface’s VLAN membership.
Action
user@switch> show ethernet-switching interface ge-0/0/2.0
Routing Instance Name : default-switch
Logical Interface flags (DL - disable learning, AD - packet action drop,
LH - MAC limit hit, DN - interface down )
Logical Vlan TAG MAC STP Logical Tagging
interface members limit state interface flags
ge-0/0/2.0 65535 untagged
voice-vlan 99
65535 Discarding
data-vlan 77
65535 DiscardingMeaning
The field VLAN members shows that the ge-0/0/2.0 interface supports both the data-vlan VLAN and voice-vlan VLAN.
Example: Configuring VoIP on an EX Series Switch with ELS Support Without Including 802.1X Authentication
This example uses Junos OS for EX Series switches with support for the Enhanced Layer 2 Software (ELS) configuration style. If your switch runs software that does not support ELS, see Example: Configuring VoIP on an EX Series Switch Without Including 802.1X Authentication. For ELS details, see Using the Enhanced Layer 2 Software CLI.
You can configure voice over IP (VoIP) on an EX Series switch to support IP telephones.
To configure VoIP on an EX Series switch to support an IP phone that does not support 802.1X authentication, you must either add the MAC address of the phone to the static MAC bypass list or enable MAC RADIUS authentication on the switch.
This example describes how to configure VoIP on an EX Series switch without 802.1X authentication by using static MAC bypass of authentication:
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
This figure also applies to QFX5100 switches.
One EX Series switch with support for ELS
Junos OS Release 13.2 or later for EX Series switches
An Avaya IP telephone
Before you configure VoIP, be sure you have:
Installed your EX Series switch. See the installation information for your switch.
Performed the initial switch configuration. See Connecting and Configuring an EX Series Switch (CLI Procedure).
Performed basic bridging and VLAN configuration on the switch. See Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN for an EX Series Switch with ELS Support or Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN on Switches.
Configured the RADIUS server for 802.1X authentication and set up the access profile. See Example: Connecting a RADIUS Server for 802.1X to an EX Series Switch.
(Optional) Configured the interface ge-0/0/2 for Power over Ethernet (PoE). The PoE configuration is not necessary if the VoIP supplicant uses a power adapter. For information about configuring PoE, see Configuring PoE Interfaces on EX Series Switches.
If the IP address is not configured on the Avaya IP phone,
the phone exchanges LLDP-MED information to get the VLAN ID for the
voice VLAN. You must configure the voip statement on the
interface to designate the interface as a VoIP interface and allow
the switch to forward the VLAN name and VLAN ID for the voice VLAN
to the IP telephone. The IP telephone then uses the voice VLAN (that
is, it references the voice VLAN’s ID) to send a DHCP discover
request and exchange information with the DHCP server (voice gateway).
Overview
Instead of using a regular telephone, you connect an IP telephone directly to the switch. An IP phone has all the hardware and software needed to handle VoIP. You also can power an IP telephone by connecting it to one of the Power over Ethernet (PoE) interfaces on the switch.
In this example, the access interface ge-0/0/2 on the EX Series switch is connected to a non-802.1X IP phone.
To configure VoIP on an EX Series switch to support an IP phone that does not support 802.1X authentication, add the MAC address of the phone as a static entry in the authenticator database and set the supplicant mode to multiple.
Configuration
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure VoIP without using 802.1X authentication, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit] set vlans data-vlan vlan-id 77 set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 99 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members data-vlan set switch-options voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 vlan voice-vlan set switch-options voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 forwarding-class assured-forwarding set protocols lldp-med interface ge-0/0/2 set protocols dot1x authenticator authentication-profile-name auth-profile set protocols dot1x authenticator static 00:04:f2:11:aa:a7 set protocols dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/2.0 supplicant multiple
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure VoIP without 802.1X authentication:
Configure the VLANs for voice and data:
[edit vlans] user@switch# set data-vlan vlan-id 77 user@switch# set voice-vlan vlan-id 99
Configure the interface as an access interface, configure support for Ethernet switching, and add the interface as a member of the
data-vlanVLAN:[edit interfaces] user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access user@switch# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members data-vlan
Note:You must not configure both data and voice on the same VLAN. If you configure data and voice on the same VLAN, the configuration will not be accepted.
Configure VoIP on the interface and specify the
assured-forwardingforwarding class to provide the most dependable class of service:[edit switch-options] user@switch# set voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 vlan voice-vlan user@switch# set voip interface ge-0/0/2.0 forwarding-class assured-forwarding
Configure LLDP-MED protocol support:
[edit protocols] user@switch# set lldp-med interface ge-0/0/2
Set the authentication profile with the name
auth-profile(see Configuring 802.1X Interface Settings (CLI Procedure) and Configuring 802.1X RADIUS Accounting (CLI Procedure)):[edit protocols] user@switch# set dot1x authenticator authentication-profile-name auth-profile
Add the MAC address of the phone to the static MAC bypass list:
[edit protocols] user@switch# set dot1x authenticator static 00:04:f2:11:aa:a7
Set the supplicant mode to multiple:
[edit protocols] user@switch# set dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/2.0 supplicant multiple
Results
Display the results of the configuration:
[edit]
user@switch# show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode access;
vlan {
members data-vlan;
}
}
}
}
}
protocols {
lldp-med {
interface ge-0/0/2;
}
dot1x {
authenticator {
authentication-profile-name auth-profile;
static {
00:04:f2:11:aa:a7;
}
}
interface {
ge-0/0/2.0 {
supplicant multiple;
}
}
}
}
vlans {
data-vlan {
vlan-id 77;
switch-options {
interface ge-0/0/2.0;
}
}
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 99;
}
}
switch-options {
voip {
interface ge-0/0/2.0 {
vlan voice-vlan;
forwarding-class assured-forwarding;
}
}
}
Verification
To confirm that the configuration is working properly, perform these tasks:
- Verifying LLDP-MED Configuration
- Verifying Authentication for the Desktop PC
- Verifying the VLAN Association with the Interface
Verifying LLDP-MED Configuration
Purpose
Verify that LLDP-MED is enabled on the interface.
Action
user@switch> show lldp detail LLDP : Enabled Advertisement interval : 30 seconds Transmit delay : 2 seconds Hold timer : 120 seconds Notification interval : 0 Second(s) Config Trap Interval : 0 seconds Connection Hold timer : 300 seconds LLDP MED : Enabled MED fast start count : 3 Packets Port ID TLV subtype : locally-assigned Interface Parent Interface LLDP LLDP-MED Power Negotiation Neighbor count all - Enabled Enabled Enabled 0 ge-0/0/2 - - Enabled - 0 Interface Parent Interface Vlan-id Vlan-name ge-0/0/0 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/1 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/2 - 77 vlan-77 ge-0/0/2 - 99 vlan-99 ge-0/0/3 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/4 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/5 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/6 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/7 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/8 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/9 - 1 vlan-1 ge-0/0/10 - 1 vlan-1 Basic Management TLVs supported: End Of LLDPDU, Chassis ID, Port ID, Time To Live, Port Description, System Name, System Description, System Capabilities, Management Address Organizationally Specific TLVs supported: MAC/PHY configuration/status, Power via MDI, Link aggregation, Maximum Frame Size, Port VLAN tag, Port VLAN name.
Meaning
The show lldp detail command output shows
that both LLDP and LLDP-MED are configured on the ge-0/0/2 interface. The end of the output shows the list of supported LLDP
basic management TLVs and organizationally specific TLVs that are
supported.
Verifying Authentication for the Desktop PC
Purpose
Display the 802.1X configuration for the desktop PC connected to the VoIP interface through the IP phone.
Action
user@switch> show dot1x interface ge/0/0/2.0 detail
ge-0/0/2.0
Role: Authenticator
Administrative state: Auto
Supplicant mode: Multiple
Number of retries: 3
Quiet period: 60 seconds
Transmit period: 30 seconds
Mac Radius: Disabled
Mac Radius Restrict: Disabled
Reauthentication: Enabled
Configured Reauthentication interval: 3600 seconds
Supplicant timeout: 30 seconds
Server timeout: 30 seconds
Maximum EAPOL requests: 2
Guest VLAN member: <not configured>
Number of connected supplicants: 1
Supplicant: user101, 00:04:0f:fd:ac:fe
Operational state: Authenticated
Authentication method: Radius
Authenticated VLAN: vo11
Dynamic Filter: match source-dot1q-tag 10 action deny
Session Reauth interval: 60 seconds
Reauthentication due in 50 seconds
Meaning
The field Role shows that the ge-0/0/2.0 interface is in the authenticator role.
The Supplicant Mode field shows that the interface is configured
in multiple supplicant mode, permitting
multiple supplicants to be authenticated on this interface. The MAC
addresses of the supplicants currently connected are displayed at
the bottom of the output.
Verifying the VLAN Association with the Interface
Purpose
Display the interface’s VLAN membership.
Action
user@switch> show ethernet-switching interface ge-0/0/2.0
Routing Instance Name : default-switch
Logical Interface flags (DL - disable learning, AD - packet action drop,
LH - MAC limit hit, DN - interface down )
Logical Vlan TAG MAC STP Logical Tagging
interface members limit state interface flags
ge-0/0/2.0 65535 untagged
voice-vlan 99
65535 Discarding
data-vlan 77
65535 DiscardingMeaning
The Vlan members field shows that the ge-0/0/2.0 interface supports both the data-vlan VLAN and voice-vlan VLAN.
