ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring a Four-Level Scheduler Hierarchy
This example shows how to configure a 4-level hierarchy of schedulers.
Requirements
Before you begin:
Review how to configure schedulers. See Example: Configuring Class-of-Service Schedulers on a Security Device.
Review RED drop profiles. See Understanding RED Drop Profiles.
Review how to configure and apply scheduler maps. See Example: Configuring and Applying Scheduler Maps.
Overview
The configuration parameters for this example are shown in Figure 1. The queues are shown at the top of the figure with the other three levels of the hierarchy below.
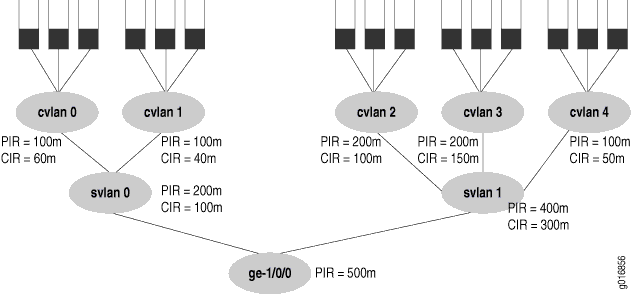
Figure 1’s PIR values will be
configured as the shaping rates, and the CIRs will be configured as
the guaranteed rate on the Ethernet interface ge-1/0/0.
The PIR can be oversubscribed (that is, the sum of the children PIRs
can exceed the parent's, as in svlan 1, where 200 + 200
+ 100 exceeds the parent rate of 400). However, the sum of the children
node level's CIRs must never exceed the parent node's CIR, as shown
in all the service VLANs (otherwise, the guaranteed rate could never
be provided in all cases).
Although a shaping rate can be applied directly to the physical interface, hierarchical schedulers must use a traffic control profile to hold the shaping rate parameter.
The keyword to configure hierarchical schedulers is at the physical interface level, as are VLAN tagging and the VLAN IDs. In this example, the interface sets are defined by logical interfaces (units) and not outer VLAN tags. All VLAN tags in this example are customer VLAN tags.
The traffic control profiles in this example are for both the service VLAN level (logical interfaces) and the customer VLAN (VLAN tag) level.
This example shows all details of the CoS configuration for
the ge-1/0/0 interface in Figure 1.
Configuration
This section contains the following topics:
- Configuring the Interfaces
- Configuring the Interface Sets
- Configuring the Forwarding Classes
- Configuring the Traffic Control Profiles
- Configuring the Schedulers
- Configuring the Drop Profiles
- Configuring the Scheduler Maps
- Applying Traffic Control Profiles
Configuring the Interfaces
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from the configuration mode.
set interfaces ge-1/0/0 hierarchical-scheduler set interfaces ge-1/0/0 vlan-tagging set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 vlan-id 100 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 1 vlan-id 101 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 2 vlan-id 102 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 3 vlan-id 103 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 4 vlan-id 104
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure the interfaces:
Create the physical interface, and enable hierarchical scheduling and VLAN tagging.
[edit interfaces ge-1/0/0] user@host# set hierarchical-scheduler user@host# set vlan-tagging
Create logical interfaces and assign VLAN IDs.
[edit interface ge-1/0/0] user@host# set unit 0 vlan-id 100 user@host# set unit 1 vlan-id 101 user@host# set unit 2 vlan-id 102 user@host# set unit 3 vlan-id 103 user@host# set unit 4 vlan-id 104
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show interface ge-1/0/0 command. If the
output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the configuration
instructions in this example to correct it.
[edit]
user@host# show interface ge-1/0/0
hierarchical-scheduler;
vlan-tagging;
unit 0 {
vlan-id 100;
}
unit 1 {
vlan-id 101;
}
unit 2 {
vlan-id 102;
}
unit 3 {
vlan-id 103;
}
unit 4 {
vlan-id 104;
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring the Interface Sets
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this section of the example,
copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any
line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration mode.
set interfaces interface-set svlan-0 interface ge-1/0/0 unit 0 set interfaces interface-set svlan-0 interface ge-1/0/0 unit 1 set interfaces interface-set svlan-1 interface ge-1/0/0 unit 2 set interfaces interface-set svlan-1 interface ge-1/0/0 unit 3 set interfaces interface-set svlan-1 interface ge-1/0/0 unit 4
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure the interface sets:
Create the first logical interface and its CoS parameters.
[edit interfaces] user@host# set interface-set svlan-0 interface ge-1/0/0 unit 0 user@host# set interface-set svlan-0 interface ge-1/0/0 unit 1
Create the second logical interface and its CoS parameters.
[edit interfaces] user@host# set interface-set svlan-1 interface ge-1/0/0 unit 2 user@host# set interface-set svlan-1 interface ge-1/0/0 unit 3 user@host# set interface-set svlan-1 interface ge-1/0/0 unit 4
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show interfaces command. If the output
does not display the intended configuration, repeat the configuration
instructions in this example to correct it.
[edit]
user@host# show interfaces
interface-set svlan-0 {
interface ge-1/0/0 {
unit 0;
unit 1;
}
}
interface-set svlan-1 {
interface ge-1/0/0 {
unit 2;
unit 3;
unit 4;
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring the Forwarding Classes
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this section of the example,
copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any
line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration mode.
set class-of-service forwarding-classes queue 1 data set class-of-service forwarding-classes queue 2 video set class-of-service forwarding-classes queue 3 voice
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure the forwarding classes:
Specify a queue number and map it to a class name.
[edit class-of-service forwarding-classes] user@host# set queue 1 data user@host# set queue 2 video user@host# set queue 3 voice
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show class-of-service forwarding-classes command. If the output does not display the intended configuration,
repeat the configuration instructions in this example to correct it.
[edit]
user@host# show class-of-service forwarding-classes
queue 1 data;
queue 2 video;
queue 3 voice;
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring the Traffic Control Profiles
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this section of the example,
copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any
line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration mode.
set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-500m-shaping-rate shaping-rate 500m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-svlan0 shaping-rate 200m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-svlan0 guaranteed-rate 100m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-svlan0 delay-buffer-rate 300m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-svlan1 shaping-rate 400m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-svlan1 guaranteed-rate 300m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-svlan1 delay-buffer-rate 100m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan0 shaping-rate 100m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan0 guaranteed-rate 60m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan0 scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlan0 set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan1 shaping-rate 100m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan1 guaranteed-rate 40m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan1 scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlan1 set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan2 shaping-rate 200m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan2 guaranteed-rate 100m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan2 scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlanx set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan3 shaping-rate 200m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan3 guaranteed-rate 150m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan3 scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlanx set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan4 shaping-rate 100m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan4 guaranteed-rate 50m set class-of-service traffic-control-profiles tcp-cvlan4 scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlanx
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure the traffic control profiles:
Create the traffic control profile for the physical interface.
[edit class-of-service traffic-control-profiles] user@host# tcp-500m-shaping-rate shaping-rate 500m
Create the traffic control profiles and parameters for the S-VLAN (logical interfaces) level.
[edit class-of-service traffic-control-profiles] user@host# set tcp-svlan0 shaping-rate 200m user@host# set tcp-svlan0 guaranteed-rate 100m user@host# set tcp-svlan0 delay-buffer-rate 300m user@host# set tcp-svlan1 shaping-rate 400m user@host# set tcp-svlan1 guaranteed-rate 300m user@host# set tcp-svlan1 delay-buffer-rate 100m
Create the traffic control profiles and parameters for the C-VLAN (VLAN tags) level.
[edit class-of-service traffic-control-profiles] user@host# set tcp-cvlan0 shaping-rate 100m user@host# set tcp-cvlan0 guaranteed-rate 60m user@host# set tcp-cvlan0 scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlan0 user@host# set tcp-cvlan1 shaping-rate 100m user@host# set tcp-cvlan1 guaranteed-rate 40m user@host# set tcp-cvlan1 scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlan1 user@host# set tcp-cvlan2 shaping-rate 200m user@host# set tcp-cvlan2 guaranteed-rate 100m user@host# set tcp-cvlan2 scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlanx user@host# set tcp-cvlan3 shaping-rate 200m user@host# set tcp-cvlan3 guaranteed-rate 150m user@host# set tcp-cvlan3 scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlanx user@host# set tcp-cvlan4 shaping-rate 100m user@host# set tcp-cvlan4 guaranteed-rate 50m user@host# set tcp-cvlan4 scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlanx
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show class-of-service traffic-control-profiles command. If the output does not display the intended configuration,
repeat the configuration instructions in this example to correct it.
[edit]
user@host# show class-of-service traffic-control-profiles
tcp-500m-shaping-rate {
shaping-rate 500m;
}
tcp-svlan0 {
shaping-rate 200m;
guaranteed-rate 100m;
delay-buffer-rate 300m; # This parameter is not shown in the figure
}
tcp-svlan1 {
shaping-rate 400m;
guaranteed-rate 300m;
delay-buffer-rate 100m; # This parameter is not shown in the figure
}
tcp-cvlan0 {
shaping-rate 100m;
guaranteed-rate 60m;
scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlan0; # This example applies scheduler maps to customer VLANs
}
tcp-cvlan1 {
shaping-rate 100m;
guaranteed-rate 40m;
scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlan1; # This example applies scheduler maps to customer VLANs
}
tcp-cvlan2 {
shaping-rate 200m;
guaranteed-rate 100m;
scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlanx; # This example applies scheduler maps to customer VLANs
}
tcp-cvlan3 {
shaping-rate 200m;
guaranteed-rate 150m;
scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlanx; # This example applies scheduler maps to customer VLANs
}
tcp-cvlan4 {
shaping-rate 100m;
guaranteed-rate 50m;
scheduler-map tcp-map-cvlanx; # This example applies scheduler maps to customer VLANs
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring the Schedulers
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this section of the example,
copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any
line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration mode.
set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlan0-qx transmit-rate 20m set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlan0-qx buffer-size temporal 100k set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlan0-qx priority low set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlan0-qx drop-profile-map loss-priority low protocol any drop-profile dp-low set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlan0-qx drop-profile-map loss-priority high protocol any drop-profile dp-high set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlan1-q0 transmit-rate 20m set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlan1-q0 buffer-size percent 40 set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlan1-q0 priority high set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlan1-q0 drop-profile-map loss-priority low protocol any drop-profile dp-low set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlan1-q0 drop-profile-map loss-priority high protocol any drop-profile dp-high set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlanx-qx transmit-rate percent 30 set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlanx-qx buffer-size percent 30 set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlanx-qx drop-profile-map loss-priority low protocol any drop-profile dp-low set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlanx-qx drop-profile-map loss-priority high protocol any drop-profile dp-high set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlan1-qx transmit-rate 10m set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlan1-qx buffer-size temporal 100k set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlan1-qx drop-profile-map loss-priority low protocol any drop-profile dp-low set class-of-service schedulers sched-cvlan1-qx drop-profile-map loss-priority high protocol any drop-profile dp-high
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure the schedulers:
Create the schedulers and their parameters.
[edit class-of-service schedulers] user@host# set sched-cvlan0-qx priority low transmit-rate 20m user@host# set sched-cvlan0-qx buffer-size temporal 100k user@host# set sched-cvlan0-qx priority low user@host# set sched-cvlan0-qx drop-profile-map loss-priority low protocol any drop-profile dp-low user@host# set sched-cvlan0-qx drop-profile-map loss-priority high protocol any drop-profile dp-high user@host# set sched-cvlan1-q0 priority high transmit-rate 20m user@host# set sched-cvlan1-q0 buffer-size percent 40 user@host# set sched-cvlan1-q0 priority high user@host# set sched-cvlan1-q0 drop-profile-map loss-priority low protocol any drop-profile dp-low user@host# set sched-cvlan1-q0 drop-profile-map loss-priority high protocol any drop-profile dp-high user@host# set sched-cvlanx-qx transmit-rate percent 30 user@host# set sched-cvlanx-qx buffer-size percent 30 user@host# set sched-cvlanx-qx drop-profile-map loss-priority low protocol any drop-profile dp-low user@host# set sched-cvlanx-qx drop-profile-map loss-priority high protocol any drop-profile dp-high user@host# set sched-cvlan1-qx transmit-rate 10m user@host# set sched-cvlan1-qx buffer-size temporal 100k user@host# set sched-cvlan1-qx drop-profile-map loss-priority low protocol any drop-profile dp-low user@host# set sched-cvlan1-qx drop-profile-map loss-priority high protocol any drop-profile dp-high
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show class-of-service schedulers command.
If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat
the configuration instructions in this example to correct it.
[edit]
user@host# show class-of-service schedulers
sched-cvlan0-qx {
transmit-rate 20m;
buffer-size temporal 100k;
priority low;
drop-profile-map loss-priority low protocol any drop-profile dp-low;
drop-profile-map loss-priority high protocol any drop-profile dp-high;
}
sched-cvlan1-q0 {
transmit-rate 20m;
buffer-size percent 40;
priority high;
drop-profile-map loss-priority low protocol any drop-profile dp-low;
drop-profile-map loss-priority high protocol any drop-profile dp-high;
}
sched-cvlanx-qx {
transmit-rate percent 30;
buffer-size percent 30;
drop-profile-map loss-priority low protocol any drop-profile dp-low;
drop-profile-map loss-priority high protocol any drop-profile dp-high;
}
sched-cvlan1-qx {
transmit-rate 10m;
buffer-size temporal 100k;
drop-profile-map loss-priority low protocol any drop-profile dp-low;
drop-profile-map loss-priority high protocol any drop-profile dp-high;
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring the Drop Profiles
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this section of the example,
copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any
line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration mode.
set class-of-service drop-profiles dp-low interpolate fill-level 80 drop-probability 80 set class-of-service drop-profiles dp-low interpolate fill-level 100 drop-probability 100 set class-of-service drop-profiles dp-high interpolate fill-level 60 drop-probability 80 set class-of-service drop-profiles dp-high interpolate fill-level 80 drop-probability 100
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure the drop profiles:
Create the low drop profile.
[edit class-of-service drop-profiles] user@host# set dp-low interpolate fill-level 80 drop-probability 80 user@host# set dp-low interpolate fill-level 100 drop-probability 100
Create the high drop profile.
[edit class-of-service drop-profiles] user@host# set dp-high interpolate fill-level 60 drop-probability 80 user@host# set dp-high interpolate fill-level 80 drop-probability 100
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show class-of-service drop-profiles command.
If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat
the configuration instructions in this example to correct it.
[edit]
user@host# show class-of-service drop-profiles
dp-low {
interpolate {
fill-level [ 80 100 ];
drop-probability [ 80 100 ];
}
}
dp-high {
interpolate {
fill-level [ 60 80 ];
drop-probability [ 80 100 ];
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring the Scheduler Maps
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this section of the example,
copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any
line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration mode.
set class-of-service scheduler-maps tcp-map-cvlan0 forwarding-class voice scheduler sched-cvlan0-qx set class-of-service scheduler-maps tcp-map-cvlan0 forwarding-class video scheduler sched-cvlan0-qx set class-of-service scheduler-maps tcp-map-cvlan0 forwarding-class data scheduler sched-cvlan0-qx set class-of-service scheduler-maps tcp-map-cvlan1 forwarding-class voice scheduler sched-cvlan1-q0 set class-of-service scheduler-maps tcp-map-cvlan1 forwarding-class video scheduler sched-cvlan1-qx set class-of-service scheduler-maps tcp-map-cvlan1 forwarding-class data scheduler sched-cvlan1-qx set class-of-service scheduler-maps tcp-map-cvlanx forwarding-class voice scheduler sched-cvlanx-qx set class-of-service scheduler-maps tcp-map-cvlanx forwarding-class video scheduler sched-cvlanx-qx set class-of-service scheduler-maps tcp-map-cvlanx forwarding-class data scheduler sched-cvlanx-qx
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure three scheduler maps:
Create the first scheduler map.
[edit class-of-service scheduler-maps] user@host# set tcp-map-cvlan0 forwarding-class voice scheduler sched-cvlan0-qx user@host# set tcp-map-cvlan0 forwarding-class video scheduler sched-cvlan0-qx user@host# set tcp-map-cvlan0 forwarding-class data scheduler sched-cvlan0-qx
Create the second scheduler map.
[edit class-of-service scheduler-maps] user@host# set tcp-map-cvlan1 forwarding-class voice scheduler sched-cvlan1-q0 user@host# set tcp-map-cvlan1 forwarding-class video scheduler sched-cvlan1-qx user@host# set tcp-map-cvlan1 forwarding-class data scheduler sched-cvlan1-qx
Create the third scheduler map.
[edit class-of-service scheduler-maps] user@host# set tcp-map-cvlanx forwarding-class voice scheduler sched-cvlanx-qx user@host# set tcp-map-cvlanx forwarding-class video scheduler sched-cvlanx-qx user@host# set tcp-map-cvlanx forwarding-class data scheduler sched-cvlanx-qx
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show class-of-service scheduler-maps command.
If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat
the configuration instructions in this example to correct it.
[edit]
user@host# show class-of-service scheduler-maps
tcp-map-cvlan0 {
forwarding-class voice scheduler sched-cvlan0-qx;
forwarding-class video scheduler sched-cvlan0-qx;
forwarding-class data scheduler sched-cvlan0-qx;
}
tcp-map-cvlan1 {
forwarding-class voice scheduler sched-cvlan1-q0;
forwarding-class video scheduler sched-cvlan1-qx;
forwarding-class data scheduler sched-cvlan1-qx;
}
tcp-map-cvlanx {
forwarding-class voice scheduler sched-cvlanx-qx;
forwarding-class video scheduler sched-cvlanx-qx;
forwarding-class data scheduler sched-cvlanx-qx;
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Applying Traffic Control Profiles
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this section of the example,
copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any
line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration mode.
set class-of-service interfaces ge-1/0/0 output-traffic-control-profile tcp-500m-shaping-rate set class-of-service interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 output-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan0 set class-of-service interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 1 output-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan1 set class-of-service interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 2 output-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan2 set class-of-service interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 3 output-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan3 set class-of-service interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 4 output-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan4 set class-of-service interfaces interface-set svlan0 output-traffic-control-profile tcp-svlan0 set class-of-service interfaces interface-set svlan1 output-traffic-control-profile tcp-svlan1
Step-by-Step Procedure
To apply traffic control profiles:
Apply the traffic control profile for the interface.
[edit class-of-service interfaces ge-1/0/0] user@host# set output-traffic-control-profile tcp-500m-shaping-rate
Apply the traffic control profiles for the C-VLANs.
[edit class-of-service interfaces ge-1/0/0] user@host# set unit 0 output-control-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan0 user@host# set unit 1 output-control-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan1 user@host# set unit 2 output-control-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan2 user@host# set unit 3 output-control-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan3 user@host# set unit 4 output-control-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan4
Apply the traffic control profiles for the S-VLANs.
[edit class-of-service interfaces] user@host# set interface-set-svlan0 output-control-traffic-control-profile tcp-svlan0 user@host# set interface-set-svlan1 output-control-traffic-control-profile tcp-svlan1
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show class-of-service interfaces command.
If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat
the configuration instructions in this example to correct it.
[edit]
user@host# show class-of-service interfaces
ge-1/0/0 {
output-traffic-control-profile tcp-500m-shaping-rate;
unit 0 {
output-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan0;
}
unit 1 {
output-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan1;
}
unit 2 {
output-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan2;
}
unit 3 {
output-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan3;
}
unit 4 {
output-traffic-control-profile tcp-cvlan4;
}
}
interface-set svlan0 {
output-traffic-control-profile tcp-svlan0;
}
interface-set svlan1 {
output-traffic-control-profile tcp-svlan1;
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Verifying Scheduler Hierarchy Configuration
Purpose
Verify that the scheduler hierarchy is configured properly.
Action
From operational mode, enter the following commands:
show interface ge-1/0/0show class-of-service interfacesshow class-of-service traffic-control-profilesshow class-of-service schedulersshow class-of-service drop-profilesshow class-of-service scheduler-maps
