Multinode High Availability in Google Cloud Platform
Understanding High Availability on Google Cloud Platform
You can configure Multinode High Availability on vSRX Virtual Firewalls deployed in the Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Marketplace. You can use the GCP Marketplace to set up your vSRX as a VM running on a Google Compute Engine instance. You can configure a pair of vSRX virtual firewalls on GCP to operate as in an active/backup Multinode high availability configuration. Participating nodes run both active control and data planes at the same time. The nodes backup each other to ensure a fast synchronized failover in case of a system or hardware failure. The interchassis link (ICL) connection between the two devices synchronizes and maintains the state information and handles device failover scenarios.
Overview
Multinode High Availability on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is designed to ensure that your network traffic and security services remain uninterrupted by enabling two instances to function as a single device in an active/backup configuration. This setup synchronizes both configuration and stateful session information between instances, ensuring seamless failover when an instance fails. When a failure occurs, the system automatically triggers a failover, redirecting traffic to the healthy node to maintain continuous service availability.
About GCP Alias Internal IP Addresses
- GCP permits each NIC interface to have a single public external IP which can be transferred between instances.
- Google Cloud alias IP ranges let you assign internal IP addresses as aliases to a VM's network interfaces. This is useful when running multiple services on a VM and needing distinct IP addresses for each. Alias IP ranges can come from a subnet's primary or secondary CIDR ranges and are routed automatically within the virtual network.
- Incoming packets don't contain the GCP alias internal IP, but it can be utilized at the egress interface for outgoing packets.
- The GCP NIC alias internal IP is used in Multinode High Availability setup for session installation, not the primary internal IP.
Following figure shows two vSRX Virtual Firewall instances form a Multinode high availability pair in the in the GCP. One vSRX Virtual Firewall instance acts as the active node and the other instance acts as the backup node. Both nodes connect to each other using an ICL to synchronize and maintain state information and to handle device failover scenarios.
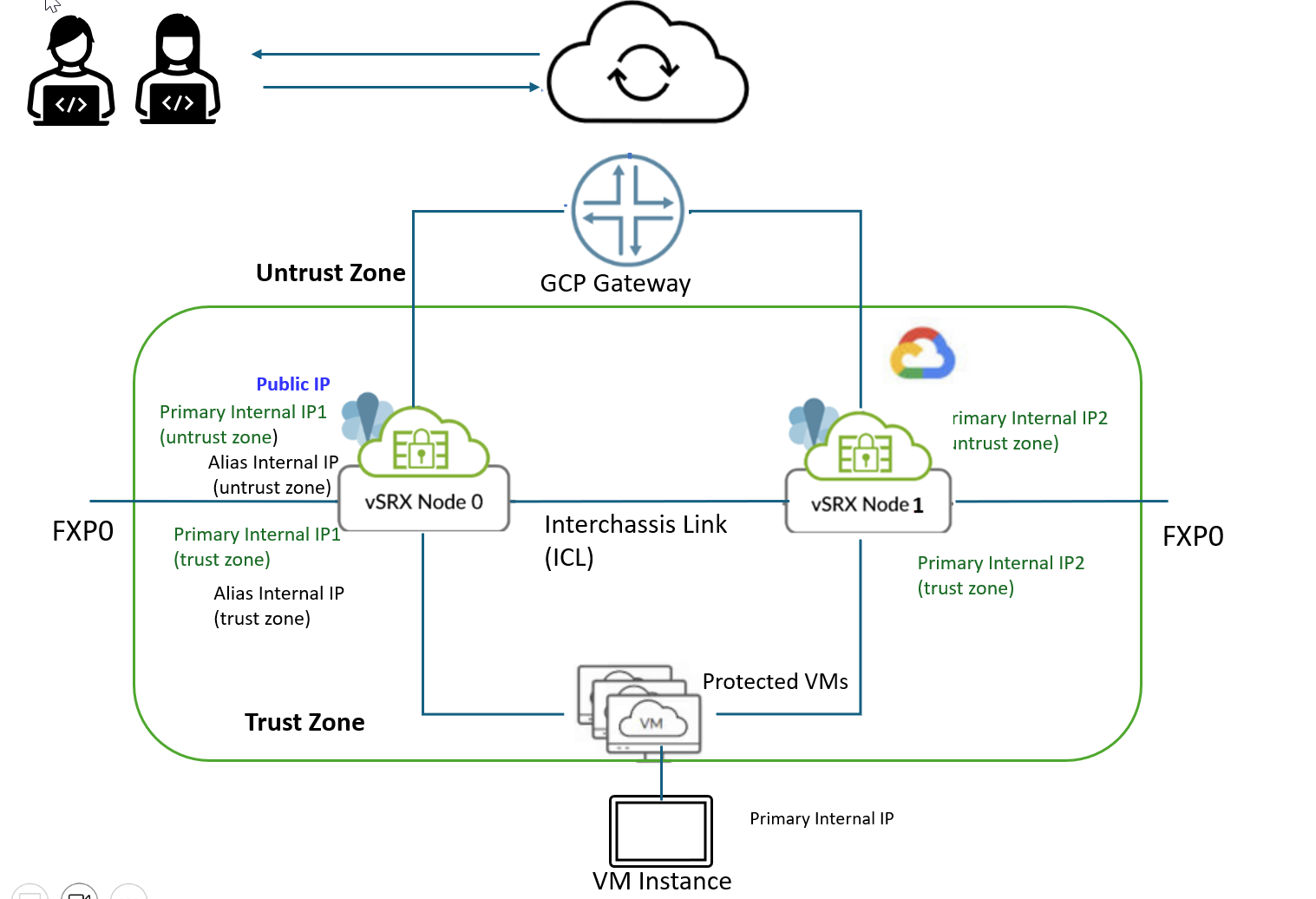
As shown in the illustration, each node has assigned one private IP address for both untrust (Internet) interface and trust (protected) interface. These IP addresses are referred as private untrust and private trust IPs in the illustration.
Active node assigns public IP address and alias internal IP address for untrust interface and assign alias internal IP address for trust interface.
When high-availability failover happens, the system moves:
- The public IP and alias internal IP of the untrust interface from one node to another node.
- The alias internal IP address of the trust interface from one node to another node.
The Cloud HA manager process and GCP SDK APIs manage the setup, synchronizing session states and configurations between two instances to provide seamless failover. The Cloud HA manager process manages state enforcement and split-brain prevention, the use of alias IPs to maintain traffic continuity, and the provision of Terraform templates to automate deployment.
IPsec VPN Support
IPsec VPN support is available for active/backup Multinode High Availability in GCP deployments. IPsec VPN tunnels are secure, encrypted connection between different networks or endpoints. In the Multinode High Availability setup, the system establishes secure tunnels between nodes in high availability setup and VPN peer devices. The IPsec VPN tunnel anchors at an active SRG1, which manages their termination and failover actions.
Limitation
Multinode High Availability doesn’t support multiple SRG configurations (active/active) in public cloud deployments. Active/backup mode supports SRG0 or SRG1.
Configuration Options
To create Multinode High Availability setup on vSRX instances in GCP, you can use CLI configuration or automate using Terraform templates.
By leveraging Terraform templates, you can automate the deployment process, significantly reducing the time and complexity involved in setting up the HA solution on GCP. These templates guide you through creating VPCs, spinning up instances, assigning IPs, and configuring HA, streamlining the deployment process.
Change History Table
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.
