Example: Configuring MPLS TTL Propagation for LDP-signaled LSPs
Overview
The following figure depicts a typical scenario in which the
no-propagate-ttl statement at the [edit protocol
ldp] hierarchy is beneficial.
Topology
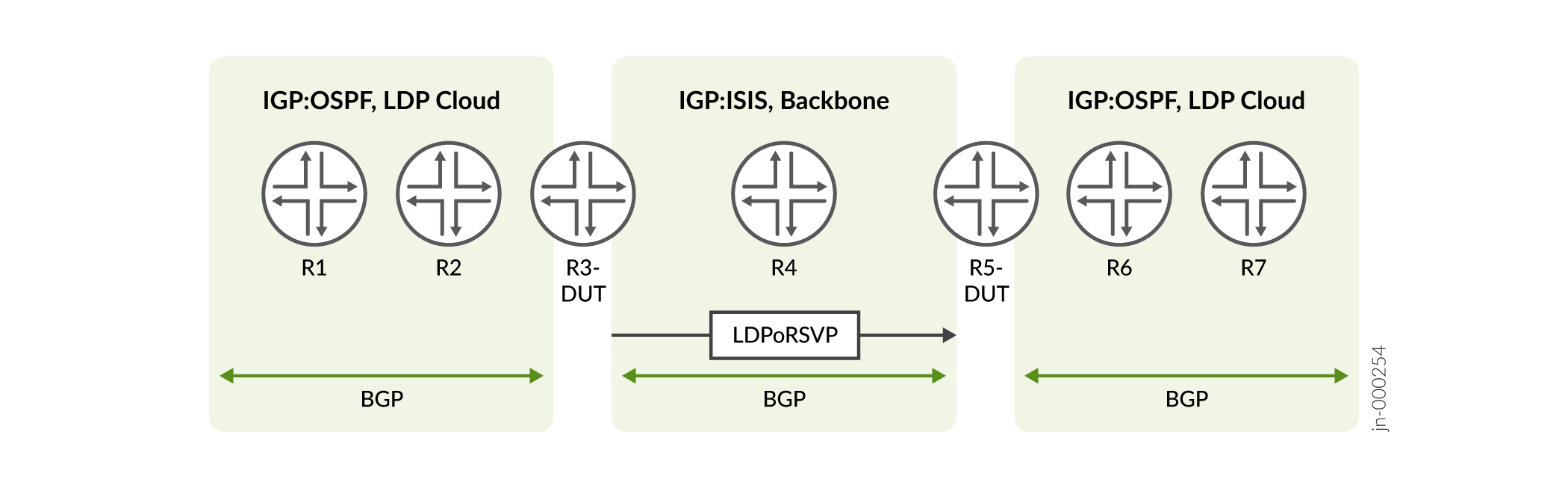
In the figure, you can see two native LDP clouds connected by a backbone with LDPoRSVP.
- From Router R1, packets are encapsulated with the LDP label and sent to the destination R7.
- On Router R3, the LDP label from a packet is stripped to an IP packet. The packet is then encapsulated with LDP over RSVP (LDPoRSVP) and sent across the backbone.
- On Router R5, the LDPoRSVP labels are stripped to an IP packet, then the packet is again encapsulated in the LDP label and sent to the destination.
Purpose
The purpose is to do the following actions:
- Hide the two LDP clouds by using no TTL propagation
- Unhide the backbone (LDPoRSVP)
When a packet is sent from Router R1 to Router R7, these actions must be performed on
two routers, R1 and R5. You cannot achieve this with the existing options. For
example, when you use the global option (set protocol mpls
no-propagate-ttl) on Router R5, it disables the TTL propagation
LDPoRSVP backbone in the reverse direction (R7-R1). This happens because the option
is applicable for both LDP and RSVP.
Use Case for the No Propagate TTL and the Propagate TTL behavior at LDP
LDP on Router R3 needs to support both no propagate TTL and the propagate TTL behavior.
From Router R3 with LDPoRSVP, in the R4 direction, the router needs to support the propagate TTL behavior. However, towards the native LDP (Router R2), the LDP needs to support the no propagate TTL behavior.
To achieve this result, we have introduced a new option,
no-propagate-ttl under LDP that you need to configure for
Router R3 and Router R5. This option disables the propagation of TTL for LDP paths.
In an LDPoRSVP scenario, propagation behavior depends on the RSVP no decrement TTL
(no-decrement-ttl) option.
- If you configure the
no-propagate-ttloption in the LDPoRSVP scenario, and the no decrement TTL (no-decrement-ttl) is not configured, then the TTL propagation takes place.For example:
On Router R3, in the case of the LDPoRSVP scenario, if you set the following configuration, then TTL propagation takes place.
user@host> set protocol ldp no-propagate-ttl
- If you configure the
no-decrement-ttloption over the LSP between Router R3 and Router R5, then the TTL propagation is disabled.For example, on Router R3:
user@host> set protocol ldp no-propagate-ttl user@host> set protocol mpls no-decrement-ttl
On Router R1, packets are encapsulated with the LDP label with TTL 255, as any of the
no-propagate-ttl CLI is configured.
On Router R3:
- The LDP label from a packet is stripped to an IP header, and the TTL is not copied from the LDP label to the IP header.
- The packet is encapsulated with LDPoRSVP labels and sent across the backbone.
- The new option
ldp no-propagate-ttlwithno-decrement-tlldecides whether the TTL should be propagated or not. - The
no-decrement-ttloption is not configured, so the usual TTL propagation occurs
On Router R5, the LDPoRSVP labels are stripped to the IP header. The new option is
configured to support no-propagate-ttl for LDP protocol, and the IP
packet is encapsulated with an LDP label with TTL 255 and sent across.
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network configuration, and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
set protocol ldp no-propagate-ttl
Results
We have modified the output of CLI command show ldp overview to
display the TTL configuration.
Check the results of the configuration:
user@host> show ldp overview Instance: master Reference count: 4 Router ID: 10.1.1.1 Inet LSR ID: 10.1.1.4 Inet6 LSR ID: 10.1.1.6 LDP inet: enabled LDP inet6: enabled Transport preference: Single-stack Message id: 21 Configuration sequence: 1 Deaggregate: disabled Explicit null: disabled IPv6 tunneling: disabled Strict targeted hellos: disabled Loopback if added: yes Route preference: 9 Unicast transit LSP chaining: disabled P2MP transit LSP chaining: disabled Transit LSP statistics based on route statistics: disabled LDP route acknowledgement: enabled BGP export: enabled No TTL propagate: enabled LDP mtu discovery: disabled LDP SR Mapping Client: disabled Capabilities enabled: none Egress FEC capabilities enabled: entropy-label-capability Downstream unsolicited Sessions: Operational: 2 Retention: liberal Control: ordered Auto targeted sessions: Auto targeted: disabled Dynamic tunnel session count: 0 P2MP: Recursive route: disabled No rsvp tunneling: disabled Timers: Keepalive interval: 10, Keepalive timeout: 30 Link hello interval: 5, Link hello hold time: 15 Targeted hello interval: 15, Targeted hello hold time: 45 Label withdraw delay: 60, Make before break timeout: 30 Make before break switchover delay: 3 Link protection timeout: 120 Graceful restart: Restart: enabled, Helper: enabled, Restart in process: false Reconnect time: 60000, Max neighbor reconnect time: 120000 Recovery time: 160000, Max neighbor recovery time: 240000 Traffic Engineering: Bgp igp: disabled Both ribs: disabled Mpls forwarding: disabled IGP: Tracking igp metric: disabled Sync session up delay: 10 Session protection: Session protection: disabled Session protection timeout: 0 Interface addresses advertising: 10.1.1.1 10.100.2.1 10.101.2.1 10.1.1.4 10.1.1.6 10.53.85.142 2001:db8:1000:1:2::1 2001:db8:1001:1:2::1 2001:db8:1111::1 2001:db8:abcd::128:53:85:142 fe80:1:2::1 fe80:1001:1002::1 LDP Job: Read job time quantum: 1000, Write job time quantum: 1000 Read job loop quantum: 100, Write job loop quantum: 100 Backup inbound read job time quantum: 1000, Backup outbound read job time quantum: 1000 Backup inbound read job loop quantum: 100, Backup outbound read job loop quantum: 100 Label allocation: Current number of LDP labels allocated: 4 Total number of LDP labels allocated: 7 Total number of LDP labels freed: 3 Total number of LDP label allocation failure: 0 Current number of labels allocated by all protocols: 4
