Example: Configuring Service Chaining Using a Custom Bridge
This example shows how to configure service chaining using a custom bridge.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
NFX150 running Junos OS Release 18.1R1
Overview
The default system bridge is OVS. The OVS bridge is a VLAN-aware system bridge, which acts as the NFV backplane to which the VNFs and FPCs connect. However, you can choose to create a custom bridge based on your requirement. This example explains how to configure service chaining using a custom bridge.
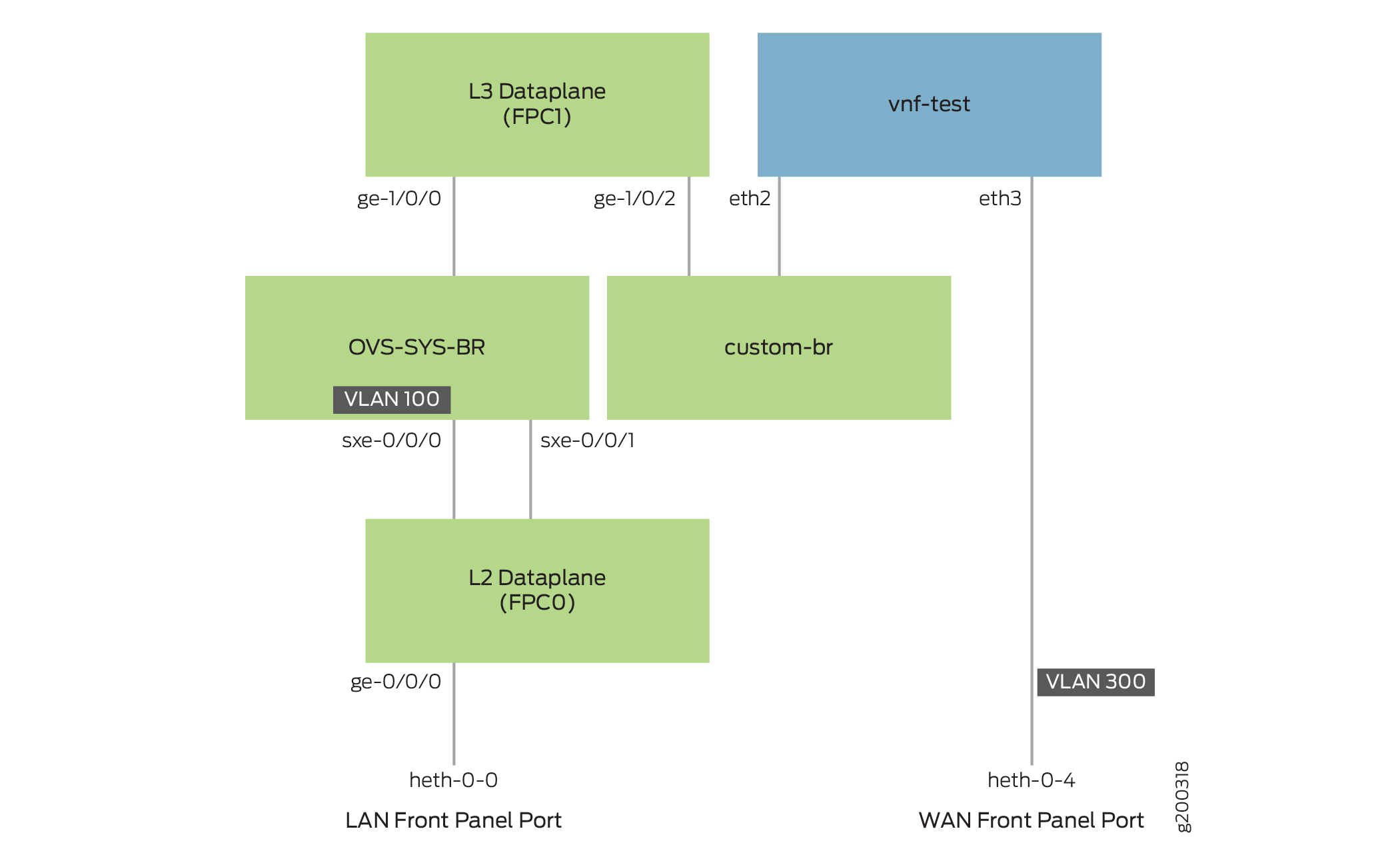
Topology
This example uses the topology shown in Figure 1.
Configuration
- Create VLANs and the Custom Bridge
- Map the Interfaces
- Configure the Layer 2 Datapath
- Configure the Layer 3 Datapath
- Configure the VNF
Create VLANs and the Custom Bridge
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure VLANs for the LAN-side interfaces.
user@host# set vlans vlan100 vlan-id 100
Create a custom bridge:
user@host# set vmhost vlans custom-br vlan-id none
Map the Interfaces
Step-by-Step Procedure
Map the heth-0-0 physical port to the FPC0 interface.
user@host# set vmhost virtualization-options interfaces ge-0/0/0 mapping interface heth-0-0
Map the FPC1 interface ge-1/0/2 to the custom bridge.
user@host# set vmhost virtualization-options interfaces ge-1/0/2 mapping vlan custom-br
Configure the Layer 2 Datapath
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure the LAN-side front panel ports and add them to the LAN-side VLAN.
user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members vlan100
Configure the internal-facing interfaces as trunk ports and add them to the LAN-side VLAN. The internal-facing interfaces are typically trunk ports, as they must support traffic from multiple front panel ports and VLANs.
user@host# set interfaces sxe-0/0/0 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk user@host# set interfaces sxe-0/0/0 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members vlan100
Configure the Layer 3 Datapath
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure VLAN tagging on ge-1/0/0:
user@host# set interfaces ge-1/0/0 vlan-tagging user@host# set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 vlan-id 100 user@host# set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.2.1/24
Configure VLAN tagging on ge-1/0/2:
user@host# set interfaces ge-1/0/2 vlan-tagging user@host# set interfaces ge-1/0/2 unit 0 vlan-id 200 user@host# set interfaces ge-1/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 203.0.113.2/24
Configure the VNF
Step-by-Step Procedure
Launch the VNF:
user@host# set virtual-network-functions vnf-test image /var/public/centos.img user@host# set virtual-network-functions vnf-test image image-type raw
Specify the number of CPUs required for the VNF:
user@host# set virtual-network-functions vnf-test virtual-cpu count 1
Pin a virtual CPU to a physical CPU:
user@host# set virtual-network-functions vnf-test virtual-cpu 0 physical-cpu 2
Create a VNF interface on the custom OVS bridge:
user@host# set virtual-network-functions vnf-test interfaces eth2 mapping vlan members custom-br
Attach a VNF interface to a physical interface by using the SR-IOV virtual function:
user@host# set virtual-network-functions vnf-test interfaces eth3 mapping interface heth-0-4 virtual-function vlan-id 300
Specify the memory allocation for the VNF:
user@host# set virtual-network-functions vnf-test memory size 1048576
Note:When a VNF interface is mapped to a custom bridge, you should restart the VNF for the mapping to take effect.
Verifying the Configuration
Verify the Control Plane Configuration
Purpose
Verify the control plane configuration:
Action
To verify the control plane configuration:
Verify that the VLANs and VLAN memberships are correct by using the
show vmhost vlanscommand.user@host> show vmhost vlans Routing instance VLAN name Tag Interfaces vmhost custom-br ge-1/0/2.0 vnf-test_eth2.0Verify that the VNF is operational. View the status of the VNF to ensure that the VNF is up and running.
user@host> show virtual-network-functions vnf-test ID Name State Liveliness -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 vjunos0 Running alive 2 vnf-test Running alive
The
Livelinessoutput field of the VNF indicates whether the IP address of the VNF is reachable or not reachable from Junos.To view more details of the VNF:
user@host> show virtual-network-functions vnf-test detail Virtual Network Function Information ------------------------------------ Id: 2 Name: vnf-test State: Running Liveliness: alive IP Address: 192.0.2.100 VCPUs: 1 Maximum Memory: 1048576 KiB Used Memory: 1087795 KiB Used 1G Hugepages: 0 Used 2M Hugepages: 0 Error: None
Verify the Data Plane Configuration
Purpose
Verify the data plane configuration.
Action
To verify the data plane configuration:
Verify the status of the physical ports.
user@host> show interfaces heth-0-0 statistics Physical interface: heth-0-0, Enabled, Physical link is Up Link-level type: Ethernet, Media type: Copper, MTU: 9192, Speed: 1Gbps, Duplex: Full-duplex, Auto-negotiation: Enabled Device flags : Present Running Current address: 00:00:5e:00:53:8d, Hardware address: 00:00:5e:00:53:8d Input packets : 1522 Output packets: 1466 MAC statistics: Input bytes: 161164, Input packets: 1522, Output bytes: 155312, Output packets: 1466 VF statistics: VF Number: 0, PCI Address: 0000:06:10:1, Mapped to: ge-0/0/0 Input bytes: 161164, Input packets: 1522, Output bytes: 155312, Output packets: 1466, Multicast packets: 4 VF Number: 1, PCI Address: 0000:06:10:5, Mapped to: ge-0/0/0 Input bytes: 0, Input packets: 0, Output bytes: 0, Output packets: 0, Multicast packets: 0 VF Number: 2, PCI Address: 0000:06:11:1, Mapped to: ge-0/0/0 Input bytes: 0, Input packets: 0, Output bytes: 0, Output packets: 0, Multicast packets: 0 VF Number: 3, PCI Address: 0000:06:11:5, Mapped to: ge-0/0/0 Input bytes: 0, Input packets: 0, Output bytes: 0, Output packets: 0, Multicast packets: 0Verify the status of the Layer 2 (ge-0/0/x) and Layer 3 (ge-1/0/x) interfaces.
user@host> show interfaces interface-name statistics
For example:
user@host> show interfaces ge-0/0/0 statistics Physical interface: ge-0/0/0, Enabled, Physical link is Up Interface index: 169, SNMP ifIndex: 521 Link-level type: Ethernet, MTU: 9192, LAN-PHY mode, Speed: 1000mbps, BPDU Error: None, Loop Detect PDU Error: None, Ethernet-Switching Error: None, MAC-REWRITE Error: None, Loopback: Disabled, Source filtering: Disabled, Flow control: Enabled Device flags : Present Running Interface flags: SNMP-Traps Internal: 0x4000 Link flags : None CoS queues : 8 supported, 8 maximum usable queues Current address: 00:00:5e:00:53:43, Hardware address: 00:00:5e:00:53:43 Last flapped : 2020-07-08 09:22:06 UTC (20:46:40 ago) Statistics last cleared: Never Input rate : 792 bps (0 pps) Output rate : 792 bps (0 pps) Input errors: 0, Output errors: 0 Active alarms : None Active defects : None PCS statistics Seconds Bit errors 0 Errored blocks 0 Ethernet FEC statistics Errors FEC Corrected Errors 0 FEC Uncorrected Errors 0 FEC Corrected Errors Rate 0 FEC Uncorrected Errors Rate 0 PRBS Statistics : Disabled Interface transmit statistics: Disabled Logical interface ge-0/0/0.0 (Index 333) (SNMP ifIndex 524) Flags: Up SNMP-Traps 0x24024000 Encapsulation: Ethernet-Bridge Input packets : 1608 Output packets: 1552 Protocol eth-switch, MTU: 9192 Flags: Is-Primary, Trunk-Mode
