ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring Service Chaining Using VLANs on NFX150 Network Services Platform
This example shows how to configure service chaining using VLANs on the host bridge.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
NFX150 running Junos OS Release 18.1R1
Before you configure service chaining, be sure you have:
Installed and launched the relevant VNFs, assigned the corresponding interfaces, and configured the resources.
Overview
Service chaining on a device running the disaggregated Junos OS allows multiple services, or virtual network functions (VNFs), to be applied to traffic as it flows through the device. This example explains how to configure the various layers of the device to enable traffic to enter the device, flow through two service VNFs, and exit the device.
Topology
This example uses a single device running the disaggregated Junos OS, as shown in Figure 1.
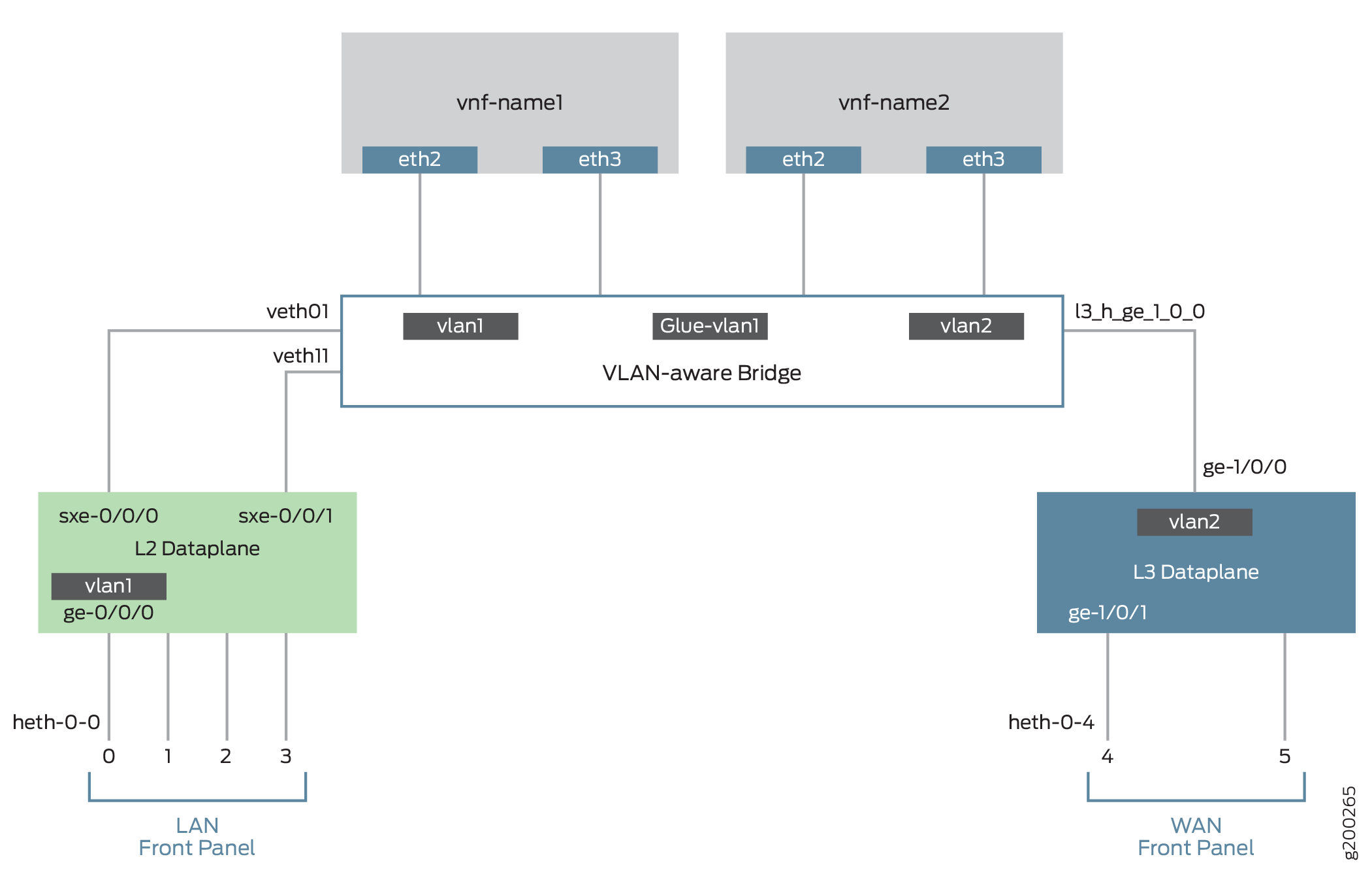
The key configuration elements include:
The front panel ports.
The internal-facing ports.
The VM interfaces. VNF interfaces must use the format eth#, where # is from 0 through 9.
VLANs, to provide bridging between the sxe and VM interfaces.
Configuration
Configuring the Interfaces
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure the interfaces:
Log in to the CLI:
user@host> configure [edit] user@host#
Map the physical (heth) interfaces to the virtual (ge) interfaces.
user@host# set vmhost virtualization-options interfaces ge-0/0/0 mapping interface heth-0-0 user@host# set vmhost virtualization-options interfaces ge-1/0/1 mapping interface heth-0-4
Configure a VLAN for the LAN-side interfaces.
user@host# set vlans vlan1 vlan-id 77
Configure the LAN-side front panel port and add it to the LAN-side VLAN.
The LAN-side port is typically an access port, but could be a trunk port if appropriate.
user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/0.0 family ethernet-switching vlan members vlan1
Configure the LAN-side internal-facing interface as a trunk port and add it to the LAN-side VLAN.
The internal-facing interfaces are typically trunk ports, as they must support traffic from multiple front panel ports and VLANs.
user@host# set interfaces sxe-0/0/0.0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk user@host# set interfaces sxe-0/0/0.0 family ethernet-switching vlan members vlan1
Configure the WAN side front panel port with vlan-tagging and an IP address:
user@host# set interfaces ge-1/0/1 vlan-tagging user@host# set interfaces ge-1/0/1.0 vlan-id 1178 user@host# set interfaces ge-1/0/1.0 family inet address 203.0.113.2/30
Configure the WAN side internal-facing interface as a vlan-tagged interface and assign an IP address to it:
user@host# set interfaces ge-1/0/0 vlan-tagging user@host# set interfaces ge-1/0/0.0 vlan-id 1177 user@host# set interfaces ge-1/0/0.0 family inet address 192.0.3.1/24
Commit the configuration.
user@host# commit and-quit user@host> exit
Results
From configuration mode, check the results of your configuration by entering the following show commands:
[edit]
user@host# show interfaces ge-0/0/0
mtu 9192;
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
vlan {
members [ vlan1 ];
}
}
}
[edit]
user@host# show interfaces ge-1/0/0
vlan-tagging;
unit 0 {
vlan-id 1177;
family inet {
address 192.0.3.1/24;
}
}
[edit]
user@host# show interfaces ge-1/0/1
vlan-tagging;
unit 0 {
vlan-id 1178;
family inet {
address 203.0.113.2/30;
}
}
[edit]
user@host# show interfaces sxe-0/0/0
mtu 9192;
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [ default vlan1 ];
}
}
}
[edit]
user@host# show vlans
default {
vlan-id 1;
}
vlan1 {
vlan-id 77;
}
Configuring the VNF Interfaces and Creating the Service Chain
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure the VNF interfaces and create the service chain:
Configure the vmhost instance with either with LAN, WAN, or glue-vlan to be used for service chaining
user@host# set vmhost vlans vlan1 vlan-id 77 user@host# set vmhost vlans vlan2 vlan-id 1177 user@host# set vmhost vlans glue-vlan vlan-id 123
Bring up the VNF (vnf-name1) with one virtio interface mapped to VLAN, and another interface mapped to glue-vlan.
user@host# set virtual-network-functions vnf-name1 interfaces eth2 mapping vlan members vlan1 user@host# set virtual-network-functions vnf-name1 interfaces eth3 mapping vlan members glue-vlan
Similarly bring up the second VNF (vnf-name2) with one interface mapped to VLAN2, and the second interface mapped to the same glue-vlan.
user@host# set virtual-network-functions vnf-name2 interfaces eth2 mapping vlan members glue-vlan user@host# set virtual-network-functions vnf-name2 interfaces eth3 mapping vlan members vlan2
Finally, configure the IP addresses and static routes for each interface of the VNFs as shown in Figure 1.
