Dual Stack for PPPoE Access Networks Using NDRA
Configuring a Static PPPoE Logical Interface for NDRA
To configure a static PPPoE logical interface for static Neighbor Discovery Router Advertisement (NDRA) configurations:
See Also
Configuring an Address-Assignment Pool Used for Router Advertisements
If you are using local address-assignment pools to be used for router advertisement, create a pool and add IPv6 prefixes to the pool.
You must configure separate pools for DHCPv6 prefix delegation, DHCPv6 IA_NA, and router advertisement.
To configure an NDRA address-assignment pool.
See Also
Configuring Duplicate IPv6 Prefix Protection for Router Advertisement
If you are using AAA to supply IPv6 prefixes for router advertisement, you can enable duplicate prefix protection to prevent prefixes from being used more than once. If enabled, the following attributes received from external servers are checked:
Framed-IPv6-Prefix
Framed-IPv6-Pool
The router then takes one of the following actions:
If a prefix matches a prefix in an address pool, the prefix is taken from the pool if it is available.
If the prefix is already in use, it is rejected as unavailable.
If the prefix length requested from the external server does not match the pool’s prefix length exactly, the authentication request is denied. If configured, the Acct-Stop message will include a termination cause.
To configure duplicate prefix protection:
See Also
Configuring the IPv6 Link-Local Address for Dynamic Demux Interfaces over Static Demux VLAN Interfaces
When you are using Router Advertisement for IPv6 subscribers on dynamic demux interfaces that run over underlying static demux interfaces, both interfaces should use the same link-local address.
The link local address should be assigned using a unique 64-Bit IPv6 interface identifier (EUI-64), which is obtained based on the MAC address of the underlying interface.
To cause the system to implement the link-local address based on the MAC address of the underlying interface and to comply with the 64-bit Extended Unique Identifier (EUI-64):
Example: Configuring a Dual Stack That Uses ND/RA Over PPPoE
This example shows a dual stack configuration for a residential subscriber with a single PC. It uses ND/RA to provide a prefix used to obtain a global IPv6 address for the PC.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
MX Series 3D Universal Edge Router
Junos OS Release 11.4 or later
Overview
This design uses ND/RA in your subscriber access network as follows:
The access network is PPPoE.
ND/RA is used to assign a global IPv6 address on the WAN link. The prefixes used in router advertisements come from a local pool that is specified using AAA RADIUS.
Topology
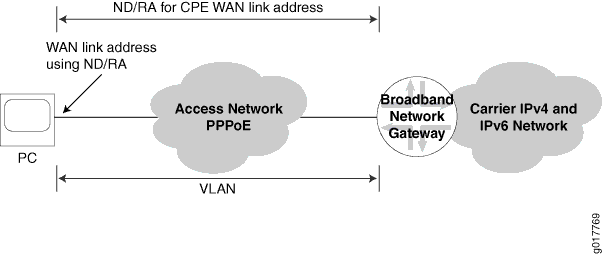
Table 1 describes the configuration components used in this example.
Configuration Component |
Component Name |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
Dynamic Profiles |
DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ndra |
Profile that creates a PPPoE logical interface when the subscriber logs in. |
Interfaces |
ge-3/3/0 |
Underlying Ethernet interface. |
lo0 |
Loopback interface for use in the access network. The loopback interface is automatically used for unnumbered interfaces. |
|
Address-Assignment Pools |
default-ipv4-pool-2 |
Pool that provides IPv4 addresses for the subscriber LAN. |
ndra-2010 |
Pool that provides IPv6 prefixes used in router advertisements. These prefixes are used to create a global IPv6 address that is assigned to the CPE WAN link. |
Configuration
To configure this example, perform these tasks:
- CLI Quick Configuration
- Configuring a Dynamic Profile for the PPPoE Logical Interface
- Configuring a Loopback Interface
- Configuring a Static Underlying Ethernet Interface for Dynamic PPPoE Subscriber Interfaces
- Specifying the BNG IP Address
- Configuring RADIUS Server Access
- Configuring RADIUS Server Access Profile
- Specifying the RADIUS Server Access Profile to Use
- Configuring Local Address-Assignment Pools
CLI Quick Configuration
The following is the complete configuration for this example:
dynamic-profiles {
DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra {
interfaces {
pp0 {
unit "$junos-interface-unit" {
ppp-options {
chap;
pap;
}
pppoe-options {
underlying-interface "$junos-underlying-interface";
server;
}
keepalives interval 30;
family inet {
unnumbered-address lo0.0;
}
family inet6 {
address $junos-ipv6-address;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
router-advertisement {
interface "$junos-interface-name" {
prefix $junos-ipv6-ndra-prefix;
}
}
}
}
}
system {
services {
dhcp-local-server {
dhcpv6 {
group DHCPv6-over-pppoe {
interface pp0.0;
}
}
}
}
}
access-profile Access-Profile;
interfaces {
ge-3/3/0 {
unit 1004 {
description "dynamic ipv4v6 dual stack, ndra, dhcpv6 pd";
encapsulation ppp-over-ether;
vlan-id 1004;
pppoe-underlying-options {
duplicate-protection;
dynamic-profile DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra;
}
}
}
lo0 {
description "dynamic ipv4v6 dual stack, ndra, dhcpv6 pd";
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.0.2.77/32 {
primary;
}
}
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:2030:0:0:0::1/64 {
primary;
}
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
router-id 203.0.113.0;
}
access {
radius-server {
203.0.113.99 {
secret "$ABC123$ABC123ABC123"; ## SECRET-DATA
timeout 45;
retry 4;
source-address 203.0.113.1;
}
}
profile Access-Profile {
authentication-order radius;
radius {
authentication-server 203.0.113.99;
accounting-server 203.0.113.99;
}
accounting {
order [ radius none ];
update-interval 120;
statistics volume-time;
}
}
address-assignment {
neighbor-discovery-router-advertisement ndra-2010;
pool default-ipv4-pool-2 {
family inet {
network 203.0.113.10/16;
range r5 {
low 203.0.113.11;
high 203.0.113.150;
}
}
}
pool ndra-2010 {
family inet6 {
prefix 2001:db8:2010:0:0:0::/48;
range L prefix-length 64;
}
}
}
address-protection;
}
Configuring a Dynamic Profile for the PPPoE Logical Interface
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra edit interfaces pp0 unit $junos-interface-unit set family inet unnumbered-address lo0.0 set family inet6 address $junos-ipv6-address set pppoe-options underlying-interface "$junos-underlying-interface" set pppoe-options server set ppp-options pap set ppp-options chap set keepalives interval 30 up 3 edit protocols router-advertisement edit interface $junos-interface-name set prefix $junos-ipv6-ndra-prefix
Step-by-Step Procedure
Create a dynamic profile for the PPPoE logical interface. This dynamic profile supports both IPv4 and IPv6 sessions on the same logical interface.
To configure the dynamic profile:
Create and name the dynamic profile.
[edit] user@host# edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra
Configure a PPPoE logical interface (pp0) that is used to create logical PPPoE interfaces for the IPv4 and IPv6 subscribers.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra] user@host# edit interfaces pp0
Specify
$junos-interface-unitas the predefined variable to represent the logical unit number for the pp0 interface. The variable is dynamically replaced with the actual unit number supplied by the network when the subscriber logs in.[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra interfaces pp0] user@host# edit unit $junos-interface-unit
Specify
$junos-underlying-interfaceas the predefined variable to represent the name of the underlying Ethernet interface on which the router creates the dynamic PPPoE logical interface. The variable is dynamically replaced with the actual name of the underlying interface supplied by the network when the subscriber logs in.[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra interfaces pp0 unit "$junos-interface-unit"] user@host# set pppoe-options underlying-interface $junos-underlying-interface
Configure the router to act as a PPPoE server when a PPPoE logical interface is dynamically created.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra interfaces pp0 unit "$junos-interface-unit"] user@host# set pppoe-options server
Configure the IPv4 family for the pp0 interface. Specify the unnumbered address to dynamically create loopback interfaces.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra interfaces pp0 unit "$junos-interface-unit"] user@host# set family inet unnumbered-address lo0.0
Configure the IPv6 family for the pp0 interface. Because the example uses router advertisement, assign the predefined variable
$junos-ipv6-address.[edit dynamic-profilesDS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra interfaces pp0 unit "$junos-interface-unit"] user@host# set family inet6 unnumbered-address $junos-ipv6-address
Configure one or more PPP authentication protocols for the pp0 interface.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra interfaces pp0 unit "$junos-interface-unit"] user@host# set ppp-options chap user@host# set ppp-options pap
Enable keepalives and set an interval for keepalives. We recommend an interval of 30 seconds.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra interfaces pp0 unit "$junos-interface-unit"] user@host# set keepalives interval 30
Access the router advertisement configuration.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra] user@host# edit protocols router-advertisement
Specify the interface on which the ND/RA configuration is applied.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra protocols router-advertisement] user@host# edit interface $junos-interface-name
Specify a prefix value contained in router advertisement messages sent to the CPE on interfaces created with this dynamic profile. If you specify the $junos-ipv6-ndra-prefix predefined variable, the actual value is obtained from a local pool or through AAA.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra protocols router-advertisement interface "$junos-interface-name"] user@host# set prefix $junos-ipv6-ndra-prefix
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra]
user@host# show
interfaces {
pp0 {
unit "$junos-interface-unit" {
ppp-options {
chap;
pap;
}
pppoe-options {
underlying-interface "$junos-underlying-interface";
server;
}
keepalives interval 30;
family inet {
unnumbered-address lo0.0;
}
family inet6 {
address $junos-ipv6-address;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
router-advertisement {
interface "$junos-interface-name" {
prefix $junos-ipv6-ndra-prefix;
}
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring a Loopback Interface
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit interfaces lo0 unit 0 set family inet address 192.0.2.77/32 primary set family inet6 address 2001:db8:2030:0:0::1/64 primary
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure a loopback interface:
Create the loopback interface and specify a unit number.
[edit] user@host# edit interfaces lo0 unit 0
Configure the interface for IPv4.
[edit interfaces lo0 unit 0] user@host# set family inet address 192.0.2.77/32 primary
Configure the interface for IPv6.
[edit interfaces lo0 unit 0] user@host# set family inet6 address 2001:db8:2030:0:0::1/64 primary
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit interfaces lo0]
user@host# show
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.0.2.77/32 {
primary;
}
}
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:2030:0:0::1/64 {
primary;
}
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring a Static Underlying Ethernet Interface for Dynamic PPPoE Subscriber Interfaces
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit interfaces ge-3/3/0 unit 1004 set description "dynamic ipv4v6 dual stack, ndra, dhcpv6 pd" set encapsulation ppp-over-ether set vlan-id 1004 set pppoe-underlying-options duplicate-protection set pppoe-underlying-options dynamic-profile DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure the underlying Ethernet interface:
Specify the name and logical unit number of the static underlying Ethernet interface to which you want to attach the IPv4 and IPv6 dynamic profile.
[edit] user@host# edit interfaces ge-3/3/0 unit 1004
Configure a description for the interface.
[edit interfaces ge-3/3/0 unit 1004] user@host# set description "dynamic ipv4v6 dual stack, ndra, dhcpv6 pd”
Configure PPPoE encapsulation on the underlying interface.
[edit interfaces ge-3/3/0 unit 1004] user@host# set encapsulation ppp-over-ether
Configure the VLAN Id.
[edit interfaces ge-3/3/0 unit 1004] user@host# set vlan-id 1004
Attach the dynamic profile to the underlying interface.
[edit interfaces ge-3/3/0 unit 1004] user@host# set pppoe-underlying-options dynamic-profile DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra
(Optional) Prevent multiple PPPoE sessions from being created for the same PPPoE subscriber on the same VLAN interface.
[edit interfaces ge-3/3/0 unit 1004] user@host# set pppoe-underlying-options duplicate-protection
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit interfaces]
user@host# show
ge-3/3/0 {
unit 1004 {
description "dynamic ipv4v6 dual stack, ndra, dhcpv6 pd";
encapsulation ppp-over-ether;
vlan-id 1004;
pppoe-underlying-options {
duplicate-protection;
dynamic-profile DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra;
}
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Specifying the BNG IP Address
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit routing-options set router-id 203.0.113.0
We strongly recommend that you configure the BNG IP address to avoid unpredictable behavior if the interface address on a loopback interface changes.
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure the IP address of the BNG:
Access the routing-options configuration.
[edit] user@host# edit routing-options
Specify the IP address or the BNG.
[edit routing-options] user@host# set router-id 203.0.113.0
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit routing-options] user@host# show router-id 203.0.113.0;
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring RADIUS Server Access
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit access radius-server 203.0.113.99 set secret "$ABC123$ABC123ABC123" set timeout 45 set retry 4 set source-address 203.0.113.1
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure RADIUS servers:
Create a RADIUS server configuration, and specify the address of the server.
[edit] user@host# edit access radius-server 203.0.113.99
Configure the required secret (password) for the server. Secrets enclosed in quotation marks can contain spaces.
[edit access radius-server 203.0.113.99] user@host# set secret "$ABC123$ABC123ABC123"
Configure the source address that the BNG uses when it sends RADIUS requests to the RADIUS server.
[edit access radius-server 203.0.113.99] user@host# set source address 203.0.113.1
(Optional) Configure the number of times that the router attempts to contact a RADIUS accounting server. You can configure the router to retry from 1 through 16 times. The default setting is 3 retry attempts.
[edit access radius-server 203.0.113.99] user@host# set retry 4
(Optional) Configure the length of time that the local router or switch waits to receive a response from a RADIUS server. By default, the router or switch waits 3 seconds. You can configure the timeout to be from 1 through 90 seconds.
[edit access radius-server 203.0.113.99] user@host# set timeout 45
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit access]
user@host# show
radius-server {
203.0.113.99 {
secret "$ABC123$ABC123ABC123"; ## SECRET-DATA
timeout 45;
retry 4;
source-address 203.0.113.1;
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring RADIUS Server Access Profile
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit access profile Access-Profile set authentication-order radius set radius authentication-server 203.0.113.99 set radius accounting-server 203.0.113.99 set accounting order radius set accounting order none set accounting update-interval 120 set accounting statistics volume-time
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure a RADIUS server access profile:
Create a RADIUS server access profile.
[edit] user@host# edit access profile Access-Profile
Specify the order in which authentication methods are used.
[edit access profile Access-Profile] user@host# set authentication-order radius
Specify the address of the RADIUS server used for authentication and the server used for accounting.
[edit access profile Access-Profile] user@host# set radius authentication-server 203.0.113.99 user@host# set radius accounting-server 203.0.113.99
Configure RADIUS accounting values for the access profile.
[edit access profile Access-Profile] user@host# set accounting order [ radius none ] user@host# set accounting update-interval 120 user@host# set accounting statistics volume-time
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit access]
user@host# show
profile Access-Profile {
authentication-order radius;
radius {
authentication-server 203.0.113.99;
accounting-server 203.0.113.99;
}
accounting {
order [ radius none ];
update-interval 120;
statistics volume-time;
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Specifying the RADIUS Server Access Profile to Use
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following command and paste it into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
set access-profile Access-Profile
Step-by-Step Procedure
To specify the RADIUS server access profile to use for authentication:
Specify the access profile.
[edit] user@host# set access-profile Access-Profile
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit] user@host# show ... access-profile Access-Profile; ...
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring Local Address-Assignment Pools
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit access set address-assignment pool default-ipv4-pool-2 family inet network 203.0.113.10/16 set address-assignment pool default-ipv4-pool-2 family inet range r5 low 203.0.113.11 set address-assignment pool default-ipv4-pool-2 family inet range r5 high 203.0.113.150 set address-assignment pool ndra-2010 family inet6 prefix 2001:db8:2010:0:0:0::/48 set address-assignment pool ndra-2010 family inet6 range L prefix-length 64 set address-assignment neighbor-discovery-router-advertisement ndra-2010 set address-protection
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure three address-assignment pools for DHCPv4, DHCPv6 prefix delegation, and ND/RA.
To configure the address-assignment pools:
Configure the address-assignment pool for DHCPv4.
[edit] user@host# edit access address-assignment pool default-ipv4-pool-2 user@host# edit family inet user@host# set network 203.0.113.10/16 user@host# set range r5 low 203.0.113.11 user@host# set range r5 high 203.0.113.150
Configure the address-assignment pool for ND/RA.
[edit] user@host# edit access address-assignment pool ndra-2010 user@host# edit family inet6 user@host# set prefix 2001:db8:2010:0:0:0::/48 user@host# set range L prefix-length 64
Specify that the address-assignment pool is used for NDRA.
[edit] user@host# edit access address-assignment user@host# set neighbor-discovery-router-advertisement ndra-2010
(Optional) Enable duplicate prefix protection.
[edit access] user@host# set address-protection
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit access]
user@host# show
address-assignment {
neighbor-discovery-router-advertisement ndra-2010;
pool default-ipv4-pool-2 {
family inet {
network 203.0.113.10/16;
range r5 {
low 203.0.113.11;
high 203.0.113.150;
}
}
}
pool ndra-2010 {
family inet6 {
prefix 2001:db8:2010:0:0:0::/48;
range L prefix-length 64;
}
}
}
address-protection;
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Verifying Active Subscriber Sessions
- Verifying Both IPv4 and IPv6 Address in Correct Routing Instance
- Verifying Dynamic Subscriber Sessions
- Verifying the ND/RA Prefix Pool and Prefix Length
- Verifying the Status of the PPPoE Logical Interface
- Verifying Router Advertisements
Verifying Active Subscriber Sessions
Purpose
Verify active subscriber sessions.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show subscribers
summary command.
user@host>show subscribers summary Subscribers by State Active: 2 Total: 2 Subscribers by Client Type DHCP: 1 PPPoE: 1 Total: 2
Meaning
The fields under Subscribers by State show
the number of active subscribers.
The fields under Subscribers by Client Type show
the number of active DHCP and DHCPoE subscriber sessions.
Verifying Both IPv4 and IPv6 Address in Correct Routing Instance
Purpose
Verify that the subscriber has both an IPv4 and IPv6 address and is placed in the correct routing instance.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show subscribers command.
user@host>show subscribers Interface IP Address/VLAN ID User Name LS:RI pp0.1073741864 192.0.2.5 dual-stack-v4v6-pd default:default * 2001:db8:2010:0:0:8::/64 pp0.1073741864 2001:db8:2040:2000:2000:5::/64 default:default
Meaning
The Interface field shows that there are
two subscriber sessions running on the same interface. The IP
Address field shows that one session is assigned an IPv4 address,
and one session is assigned on IPv6 address.
The LS:RI field shows that the subscriber is placed
in the correct routing instance and that traffic can be sent and received.
Verifying Dynamic Subscriber Sessions
Purpose
Verify that the dynamic subscriber session is active, and the IPv6 prefix obtained form the ND/RA pool.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show subscribers
detail command.
user@host>show subscribers detail Type: PPPoE User Name: dual-stack-v4v6-nas IP Address: 192.0.2.4 IP Netmask: 255.255.0.0 IPv6 User Prefix: 2001:db8:2010:0:0:6::/64 Logical System: default Routing Instance: default Interface: pp0.1073741859 Interface type: Dynamic Dynamic Profile Name: DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra MAC Address: 00:00:5E:00:53:02 State: Active Radius Accounting ID: 81 Session ID: 81 Login Time: 2012-01-17 14:19:41 PST
Meaning
The IPv6 User Prefix field shows the prefix
that was obtained from the ND/RA pool. The State field
shows that the session is active.
Verifying the ND/RA Prefix Pool and Prefix Length
Purpose
Verify the pool used for ND/RA and the prefix length used with the pool
Action
From operational mode, enter the show subscribers
extensive command.
user@host>show subscribers extensive Type: PPPoE User Name: dual-stack-v4v6-nas IP Address: 192.0.2.4 IP Netmask: 255.255.0.0 IPv6 User Prefix: 2001:db8:2010:0:0:6::/64 Logical System: default Routing Instance: default Interface: pp0.1073741859 Interface type: Dynamic Dynamic Profile Name: DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra MAC Address: 00:00:5E:00:53:02 State: Active Radius Accounting ID: 81 Session ID: 81 Login Time: 2012-01-17 14:19:41 PST IPv6 Delegated Address Pool: ndra-2010 IPv6 Delegated Network Prefix Length: 48 IPv6 Interface Address: 2001:db8:2010:0:0:6::1/64
Meaning
Under the PPPoE session, the IPv6 Delegated Address
Pool field shows the name of the pool used for ND/RA prefixes.
The IPv6 Delegated Network Prefix Length field shows the
length of the prefix used to assign the IPv6 address for this subscriber
session. The IPv6 Interface Address field shows the IPv6
address assigned to the CPE interface from the ND/RA pool.
Verifying the Status of the PPPoE Logical Interface
Purpose
Display status information about the PPPoE logical interface (pp0).
Action
From operational mode, enter the show interfaces pp0.logical command.
user@host>show interfaces pp0.1073741859
Logical interface pp0.1073741859 (Index 388) (SNMP ifIndex 674)
Flags: Point-To-Point SNMP-Traps 0x4000 Encapsulation: PPPoE
PPPoE:
State: SessionUp, Session ID: 10,
Session AC name: almach, Remote MAC address: 00:00:5E:00:53:02,
Underlying interface: ge-3/3/0.1004 (Index 354)
Bandwidth: 1000mbps
Input packets : 15
Output packets: 44
Keepalive settings: Interval 30 seconds, Up-count 1, Down-count 3
LCP state: Opened
NCP state: inet: Opened, inet6: Opened, iso: Not-configured, mpls: Not-configured
CHAP state: Closed
PAP state: Success
Protocol inet, MTU: 65531
Flags: Sendbcast-pkt-to-re
Addresses, Flags: Is-Primary
Local: 192.0.2.77
Protocol inet6, MTU: 65531
Addresses, Flags: Is-Preferred Is-Primary
Destination: 2001:db8:2010:0:0:6::/64, Local: 2001:db8:2010:0:0:6::1
Local: fe80::2a0:a50f:fc63:a842
Meaning
The Local field under Protocol inet shows the IPv4 address of the pp0 interface. This is the IPv4 address configured for the loopback interface.
The Destination field under Protocol inet6 shows the IPv6 address obtained through ND/RA. This is the value of the $junos-ipv6-ndra-prefix variable configured in the dynamic profile.
The Local field under Protocol inet6 shows the value of the $junos-ipv6-address variable configured for family inet6 in the pp0 configuration of the dynamic profile.
Verifying Router Advertisements
Purpose
Verify that router advertisements are being sent, and router solicits are being received.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show ipv6 router-advertisement command.
user@host>show ipv6 router-advertisement Interface: pp0.1073741859 Advertisements sent: 3, last sent 00:09:53 ago Solicits received: 0 Advertisements received: 0
If you have a large number of subscriber interfaces, you can display router advertisements for a specific interface.
user@host>show ipv6 router-advertisement interface pp0.1073741859 Interface: pp0.1073741859 Advertisements sent: 3, last sent 00:10:31 ago Solicits received: 0 Advertisements received: 0
Meaning
The display shows the number of advertisements that the router sent, the number of solicits and advertisements that the router received.
Example: Configuring a Dual Stack That Uses ND/RA and DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation Over PPPoE
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
MX Series 3D Universal Edge Router
Junos OS Release 11.4 or later
Overview
This design uses ND/RA and DHCPv6 prefix delegation in your subscriber access network as follows:
The access network is PPPoE.
ND/RA is used to assign a global IPv6 address on the WAN link. The prefixes used in router advertisements come from a local pool that is specified using AAA RADIUS.
DHCPv6 prefix delegation is used for subscriber LAN addressing. It used a delegated prefix from a local pool that is specified using AAA RADIUS.
DHCPv4 is used for subscriber LAN addressing.
DHCPv6 subscriber sessions are layered over an underlying PPPoE subscriber session.
Topology
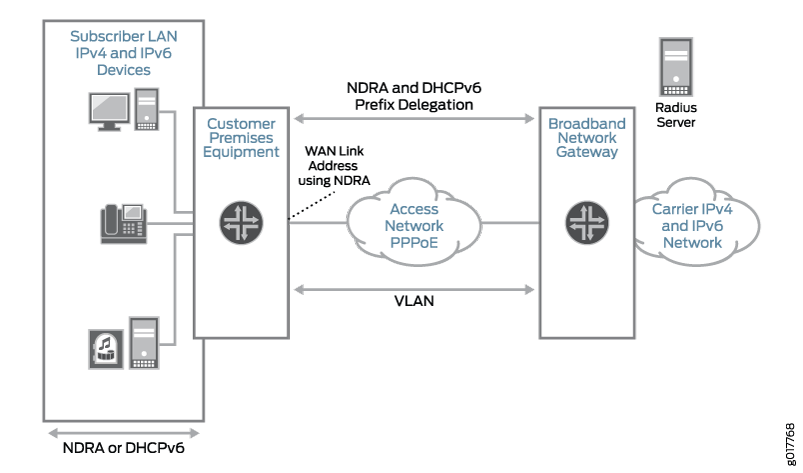
Table 2 describes the configuration components used in this example.
Configuration Component |
Component Name |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
Dynamic Profiles |
DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ndra |
Profile that creates a PPPoE logical interface when the subscriber logs in. |
Interfaces |
ge-3/3/0 |
Underlying Ethernet interface. |
lo0 |
Loopback interface for use in the access network. The loopback interface is automatically used for unnumbered interfaces. |
|
Address-Assignment Pools |
default-ipv4-pool-2 |
Pool that provides IPv4 addresses for the subscriber LAN. |
ndra-2010 |
Pool that provides IPv6 prefixes used in router advertisements. These prefixes are used to create a global IPv6 address that is assigned to the CPE WAN link. |
|
dhcpv6-pd-pool |
Pool that provides a pool of prefixes that are delegated to the CPE and are used for assigning IPv6 global addresses on the subscriber LAN. |
Configuration
- CLI Quick Configuration
- Configuring a DHCPv6 Local Server for DHCPv6 over PPPoE
- Configuring a Dynamic Profile for the PPPoE Logical Interface
- Configuring a Loopback Interface
- Configuring a Static Underlying Ethernet Interface for Dynamic PPPoE Subscriber Interfaces
- Specifying the BNG IP Address
- Configuring RADIUS Server Access
- Configuring RADIUS Server Access Profile
- Specifying the RADIUS Server Access Profile to Use
- Configuring Local Address-Assignment Pools
- Specifying the Address-Assignment Pool to Be Used for DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation
CLI Quick Configuration
The following is the complete configuration for this example:
dynamic-profiles {
DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra {
interfaces {
pp0 {
unit "$junos-interface-unit" {
ppp-options {
chap;
pap;
}
pppoe-options {
underlying-interface "$junos-underlying-interface";
server;
}
keepalives interval 30;
family inet {
unnumbered-address lo0.0;
}
family inet6 {
address $junos-ipv6-address;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
router-advertisement {
interface "$junos-interface-name" {
prefix $junos-ipv6-ndra-prefix;
}
}
}
}
}
system {
services {
dhcp-local-server {
dhcpv6 {
overrides {
delegated-pool dhcpv6-pd-pool;
}
group DHCPv6-over-pppoe {
interface pp0.0;
}
}
}
}
}
access-profile Access-Profile;
interfaces {
ge-3/3/0 {
unit 1109 {
description "dynamic ipv4v6 dual stack, ndra, dhcpv6 pd";
encapsulation ppp-over-ether;
vlan-id 1109;
pppoe-underlying-options {
duplicate-protection;
dynamic-profile DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra;
}
}
}
lo0 {
description "dynamic ipv4v6 dual stack, ndra, dhcpv6 pd";
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.0.2.77/32 {
primary;
}
}
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:2030:0:0::1/64 {
primary;
}
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
router-id 203.0.113.0;
}
access {
radius-server {
203.0.113.99 {
secret "$ABC123$ABC123ABC123"; ## SECRET-DATA
timeout 45;
retry 4;
source-address 203.0.113.1;
}
}
profile Access-Profile {
authentication-order radius;
radius {
authentication-server 203.0.113.99;
accounting-server 203.0.113.99;
}
accounting {
order [ radius none ];
update-interval 120;
statistics volume-time;
}
}
address-assignment {
pool default-ipv4-pool-2 {
family inet {
network 203.0.113.10/16;
range r5 {
low 203.0.113.11;
high 203.0.113.150;
}
}
}
pool dhcpv6-pd-pool {
family inet6 {
prefix 2001:db8:2040:2000:2000::/48;
range r1 prefix-length 64;
}
}
pool ndra-2010 {
family inet6 {
prefix 2001:db8:2010:0:0:0::/48;
range L prefix-length 64;
}
}
}
address-protection;
}
Configuring a DHCPv6 Local Server for DHCPv6 over PPPoE
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit system services dhcp-local-server dhcpv6 edit group DHCPv6-over-pppoe set interface pp0.0
Step-by-Step Procedure
To layer DHCPv6 above the PPPoE IPv6 family (inet6), associate DHCPv6 with the PPPoE interfaces by adding the PPPoE interfaces to the DHCPv6 local server configuration. Because this example uses a dynamic PPPoE interface, we are using the pp0.0 (PPPoE) logical interface as a wildcard to indicate that a DHCPv6 binding can be made on top of a PPPoE interface.
To configure a DHCPv6 local server:
Access the DHCPv6 local server configuration.
[edit] user@host# edit system services dhcp-local-server dhcpv6
Create a group for dynamic PPPoE interfaces and assign a name.
The group feature groups a set of interfaces and then applies a common DHCP configuration to the named interface group.
[edit system services dhcp-local-server dhcpv6] user@host# edit group DHCPv6-over-pppoe
Add an interface for dynamic PPPoE logical interfaces.
[edit system services dhcp-local-server dhcpv6 group DHCPv6-over-pppoe] user@host# set interface pp0.0
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit]
user@host# show
system {
services {
dhcp-local-server {
dhcpv6 {
group DHCPv6-over-pppoe {
interface pp0.0;
}
}
}
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring a Dynamic Profile for the PPPoE Logical Interface
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra edit interfaces pp0 unit $junos-interface-unit set family inet unnumbered-address lo0.0 set family inet6 address $junos-ipv6-address set pppoe-options underlying-interface "$junos-underlying-interface" set pppoe-options server set ppp-options pap set ppp-options chap set keepalives interval 30 up 3 edit protocols router-advertisement edit interface $junos-interface-name set prefix $junos-ipv6-ndra-prefix
Step-by-Step Procedure
Create a dynamic profile for the PPPoE logical interface. This dynamic profile supports both IPv4 and IPv6 sessions on the same logical interface.
To configure the dynamic profile:
Create and name the dynamic profile.
[edit] user@host# edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra
Configure a PPPoE logical interface (pp0) that is used to create logical PPPoE interfaces for the IPv4 and IPv6 subscribers.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra] user@host# edit interfaces pp0
Specify
$junos-interface-unitas the predefined variable to represent the logical unit number for thepp0interface. The variable is dynamically replaced with the actual unit number supplied by the network when the subscriber logs in.[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra interfaces pp0] user@host# edit unit $junos-interface-unit
Specify
$junos-underlying-interfaceas the predefined variable to represent the name of the underlying Ethernet interface on which the router creates the dynamic PPPoE logical interface. The variable is dynamically replaced with the actual name of the underlying interface supplied by the network when the subscriber logs in.[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra interfaces pp0 unit "$junos-interface-unit"] user@host# set pppoe-options underlying-interface $junos-underlying-interface
Configure the router to act as a PPPoE server when a PPPoE logical interface is dynamically created.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra interfaces pp0 unit "$junos-interface-unit"] user@host# set pppoe-options server
Configure the IPv4 family for the pp0 interface. Specify the unnumbered address to dynamically create loopback interfaces.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra interfaces pp0 unit "$junos-interface-unit"] user@host# set family inet unnumbered-address lo0.0
Configure the IPv6 family for the pp0 interface. Because the example uses router advertisement, assign the predefined variable
$junos-ipv6-address.[edit dynamic-profilesDS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra interfaces pp0 unit "$junos-interface-unit"] user@host# set family inet6 unnumbered-address $junos-ipv6-address
Configure one or more PPP authentication protocols for the pp0 interface.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra interfaces pp0 unit "$junos-interface-unit"] user@host# set ppp-options chap user@host# set ppp-options pap
Enable keepalives and set an interval for keepalives. We recommend an interval of 30 seconds.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra interfaces pp0 unit "$junos-interface-unit"] user@host# set keepalives interval 30
Access the router advertisement configuration.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra] user@host# edit protocols router-advertisement
Specify the interface on which the ND/RA configuration is applied.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra protocols router-advertisement] user@host# edit interface $junos-interface-name
Specify a prefix value contained in router advertisement messages sent to the CPE on interfaces created with this dynamic profile. If you specify the $junos-ipv6-ndra-prefix predefined variable, the actual value is obtained from a local pool or through AAA.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra protocols router-advertisement interface "$junos-interface-name"] user@host# set prefix $junos-ipv6-ndra-prefix
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit dynamic-profiles DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra]
user@host# show
interfaces {
pp0 {
unit "$junos-interface-unit" {
ppp-options {
chap;
pap;
}
pppoe-options {
underlying-interface "$junos-underlying-interface";
server;
}
keepalives interval 30;
family inet {
unnumbered-address lo0.0;
}
family inet6 {
address $junos-ipv6-address;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
router-advertisement {
interface "$junos-interface-name" {
prefix $junos-ipv6-ndra-prefix;
}
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring a Loopback Interface
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit interfaces lo0 unit 0 set family inet address 192.0.2.77/32 primary set family inet6 address 2001:db8:2030:0:0::1/64 primary
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure a loopback interface:
Create the loopback interface and specify a unit number.
[edit] user@host# edit interfaces lo0 unit 0
Configure the interface for IPv4.
[edit interfaces lo0 unit 0] user@host# set family inet address 192.0.2.77/32 primary
Configure the interface for IPv6.
[edit interfaces lo0 unit 0] user@host# set family inet6 address 2001:db8:2030:0:0::1/64 primary
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit interfaces lo0]
user@host# show
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.0.2.77/32 {
primary;
}
}
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:2030:0:0::1/64 {
primary;
}
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring a Static Underlying Ethernet Interface for Dynamic PPPoE Subscriber Interfaces
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit interfaces ge-3/3/0 unit 1109 set description "dynamic ipv4v6 dual stack, ndra, dhcpv6 pd" set encapsulation ppp-over-ether set vlan-id 1109 set pppoe-underlying-options duplicate-protection set pppoe-underlying-options dynamic-profile DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure the underlying Ethernet interface:
Specify the name and logical unit number of the static underlying Ethernet interface to which you want to attach the IPv4 and IPv6 dynamic profile.
[edit] user@host# edit interfaces ge-3/3/0 unit 1109
Configure a description for the interface.
[edit interfaces ge-3/3/0 unit 1109] user@host# set description "dynamic ipv4v6 dual stack, ndra, dhcpv6 pd”
Configure PPPoE encapsulation on the underlying interface.
[edit interfaces ge-3/3/0 unit 1109] user@host# set encapsulation ppp-over-ether
Configure the VLAN Id.
[edit interfaces ge-3/3/0 unit 1109] user@host# set vlan-id 1109
Attach the dynamic profile to the underlying interface.
[edit interfaces ge-3/3/0 unit 1109] user@host# set pppoe-underlying-options dynamic-profile DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra
(Optional) Prevent multiple PPPoE sessions from being created for the same PPPoE subscriber on the same VLAN interface.
[edit interfaces ge-3/3/0 unit 1109] user@host# set pppoe-underlying-options duplicate-protection
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit interfaces]
user@host# show
ge-3/3/0 {
unit 1109 {
description "dynamic ipv4v6 dual stack, ndra, dhcpv6 pd";
encapsulation ppp-over-ether;
vlan-id 1109;
pppoe-underlying-options {
duplicate-protection;
dynamic-profile DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra;
}
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Specifying the BNG IP Address
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit routing-options set router-id 203.0.113.0
We strongly recommend that you configure the BNG IP address to avoid unpredictable behavior if the interface address on a loopback interface changes.
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure the IP address of the BNG:
Access the routing-options configuration.
[edit] user@host# edit routing-options
Specify the IP address or the BNG.
[edit routing-options] user@host# set router-id 203.0.113.0
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit routing-options] user@host# show router-id 203.0.113.0;
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring RADIUS Server Access
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit access radius-server 203.0.113.99 set secret "$ABC123$ABC123ABC123" set timeout 45 set retry 4 set source-address 203.0.113.1
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure RADIUS servers:
Create a RADIUS server configuration, and specify the address of the server.
[edit] user@host# edit access radius-server 203.0.113.99
Configure the required secret (password) for the server. Secrets enclosed in quotation marks can contain spaces.
[edit access radius-server 203.0.113.99] user@host# set secret "$ABC123$ABC123ABC123"
Configure the source address that the BNG uses when it sends RADIUS requests to the RADIUS server.
[edit access radius-server 203.0.113.99] user@host# set source address 203.0.113.1
(Optional) Configure the number of times that the router attempts to contact a RADIUS accounting server. You can configure the router to retry from 1 through 16 times. The default setting is 3 retry attempts.
[edit access radius-server 203.0.113.99] user@host# set retry 4
(Optional) Configure the length of time that the local router or switch waits to receive a response from a RADIUS server. By default, the router or switch waits 3 seconds. You can configure the timeout to be from 1 through 90 seconds.
[edit access radius-server 203.0.113.99] user@host# set timeout 45
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit access]
user@host# show
radius-server {
203.0.113.99 {
secret "$ABC123$ABC123ABC123"; ## SECRET-DATA
timeout 45;
retry 4;
source-address 203.0.113.1;
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring RADIUS Server Access Profile
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit access profile Access-Profile set authentication-order radius set radius authentication-server 203.0.113.99 set radius accounting-server 203.0.113.99 set accounting order radius set accounting order none set accounting update-interval 120 set accounting statistics volume-time top set access-profile Access-Profile
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure a RADIUS server access profile:
Create a RADIUS server access profile.
[edit] user@host# edit access profile Access-Profile
Specify the order in which authentication methods are used.
[edit access profile Access-Profile] user@host# set authentication-order radius
Specify the address of the RADIUS server used for authentication and the server used for accounting.
[edit access profile Access-Profile] user@host# set radius authentication-server 203.0.113.99 user@host# set radius accounting-server 203.0.113.99
Configure RADIUS accounting values for the access profile.
[edit access profile Access-Profile] user@host# set accounting order [ radius none ] user@host# set accounting update-interval 120 user@host# set accounting statistics volume-time
At the top of the configuration hierarchy, enter the following command to enable the access profile.
[edit] user@host# set access-profile Access-Profile
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit access]
user@host# show
profile Access-Profile {
authentication-order radius;
radius {
authentication-server 203.0.113.99;
accounting-server 203.0.113.99;
}
accounting {
order [ radius none ];
update-interval 120;
statistics volume-time;
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Specifying the RADIUS Server Access Profile to Use
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following command and paste it into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
set access-profile Access-Profile
Step-by-Step Procedure
To specify the RADIUS server access profile to use for authentication:
Specify the access profile.
[edit] user@host# set access-profile Access-Profile
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit] user@host# show ... access-profile Access-Profile; ...
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring Local Address-Assignment Pools
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit access set address-assignment pool default-ipv4-pool-2 family inet network 203.0.113.10/16 set address-assignment pool default-ipv4-pool-2 family inet range r5 low 203.0.113.11 set address-assignment pool default-ipv4-pool-2 family inet range r5 high 203.0.113.150 set address-assignment pool dhcpv6-pd-pool family inet6 prefix 2001:db8:2040:2000:2000::/48 set address-assignment pool dhcpv6-pd-pool family inet6 range r1 prefix-length 64 set address-assignment pool ndra-2010 family inet6 prefix 2001:db8:2010:0:0:0::/48 set address-assignment pool ndra-2010 family inet6 range L prefix-length 64 set address-protection
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure three address-assignment pools for DHCPv4, DHCPv6 prefix delegation, and ND/RA.
To configure the address-assignment pools:
Configure the address-assignment pool for DHCPv4.
[edit] user@host# edit access address-assignment pool default-ipv4-pool-2 user@host# edit family inet user@host# set network 203.0.113.10/16 user@host# set range r5 low 203.0.113.11 user@host# set range r5 high 203.0.113.150
Configure the address-assignment pool for DHCPv6 prefix delegation
[edit] user@host# edit access address-assignment pool dhcpv6-pd-pool user@host# edit family inet6 user@host# set prefix 2001:db8:2040:2000:2000::/48 user@host# set range r1 prefix-length 64
Configure the address-assignment pool for ND/RA.
[edit] user@host# edit access address-assignment pool ndra-2010 user@host# edit family inet6 user@host# set prefix 2001:db8:2010:0:0:0::/48 user@host# set range L prefix-length 64
(Optional) Enable duplicate prefix protection.
[edit access] user@host# set address-protection
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit access]
user@host# show
address-assignment {
pool default-ipv4-pool-2 {
family inet {
network 203.0.113.10/16;
range r5 {
low 203.0.113.11;
high 203.0.113.150;
}
}
}
pool dhcpv6-pd-pool {
family inet6 {
prefix 2001:db8:2040:2000:2000::/48;
range r1 prefix-length 64;
}
}
pool ndra-2010 {
family inet6 {
prefix 2001:db8:2010:0:0:0::/48;
range L prefix-length 64;
}
}
}
address-protection;
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Specifying the Address-Assignment Pool to Be Used for DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
edit system services dhcp-local-server dhcpv6 set overrides delegated-pool dhcpv6-pd-pool
Step-by-Step Procedure
To specify that the dhcpv6-pd-pool is used for DHCPv6 prefix delegation:
Access the DHCPv6 local server configuration.
[edit] user@host# edit system services dhcp-local-server dhcpv6
Specify the address pool that assigns the delegated prefix.
[edit system services dhcp-local-server dhcpv6] user@host# set overrides delegated-pool dhcpv6-pd-pool
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show command.
[edit system]
user@host# show
services {
dhcp-local-server {
dhcpv6 {
overrides {
delegated-pool dhcpv6-pd-pool;
}
}
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Verifying Active Subscriber Sessions
- Verifying Both IPv4 and IPv6 Address in Correct Routing Instance
- Verifying Dynamic Subscriber Sessions
- Verifying DHCPv6 Address Pools Used for NDRA and DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation
- Verifying DHCPv6 Address Bindings
- Verifying Router Advertisements
- Verifying the Status of the PPPoE Logical Interface
Verifying Active Subscriber Sessions
Purpose
Verify active subscriber sessions.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show subscribers
summary command.
user@host>show subscribers summary Subscribers by State Active: 2 Total: 2 Subscribers by Client Type DHCP: 1 PPPoE: 1 Total: 2
Meaning
The fields under Subscribers by State show
the number of active subscribers.
The fields under Subscribers by Client Type show
the number of active DHCP and DHCPoE subscriber sessions.
Verifying Both IPv4 and IPv6 Address in Correct Routing Instance
Purpose
Verify that the subscriber has both an IPv4 and IPv6 address and is placed in the correct routing instance.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show subscribers command.
user@host>show subscribers Interface IP Address/VLAN ID User Name LS:RI pp0.1073741864 203.0.113.5 dual-stack-v4v6-pd default:default * 2001:db8:2010:0:0:8::/64 pp0.1073741864 2001:db8:2040:2000:2000:5::/64 default:default
Meaning
The Interface field shows that there are
two subscriber sessions running on the same interface. The IP
Address field shows that one session is assigned an IPv4 address,
and one session is assigned on IPv6 address.
The LS:RI field shows that the subscriber is placed
in the correct routing instance and that traffic can be sent and received.
Verifying Dynamic Subscriber Sessions
Purpose
Verify dynamic PPPoE and DHCPv6 subscriber sessions. In this example configuration the DHCPv6 subscriber session should be layered over the underlying PPPoE subscriber session.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show subscribers
detail command.
user@host>show subscribers detail Type: PPPoE User Name: dual-stack-v4v6-pd IP Address: 203.0.113.5 IP Netmask: 255.255.0.0 IPv6 User Prefix: 2001:db8:2010:0:0:8::/64 Logical System: default Routing Instance: default Interface: pp0.1073741864 Interface type: Dynamic Dynamic Profile Name: DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra MAC Address: 00:00:5E:00:53:02 State: Active Radius Accounting ID: 87 Session ID: 87 Login Time: 2012-01-17 14:45:30 PST Type: DHCP IPv6 Prefix: 2001:db8:2040:2000:2000:5::/64 Logical System: default Routing Instance: default Interface: pp0.1073741864 Interface type: Static MAC Address: 00:00:5E:00:53:02 State: Active Radius Accounting ID: 88 Session ID: 88 Underlying Session ID: 87 Login Time: 2012-01-17 14:46:00 PST DHCP Options: len 42 00 08 00 02 0b b8 00 01 00 0a 00 03 00 01 00 07 64 11 07 02 00 06 00 02 00 19 00 19 00 0c 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Meaning
When a subscriber has logged in and started both an IPv4 and an IPv6 session, the output shows the active underlying PPPoE session and the active DHCPv6 session.
The Session ID field for the PPPoE session is 87.
The Underlying Session ID for the DHCP session is 87, which
shows that the PPPoE session is the underlying session.
Verifying DHCPv6 Address Pools Used for NDRA and DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation
Purpose
Verify the pool used for ND/RA, the delegated address pool used for DHCPv6 prefix delegation and the length of the IPv6 prefixes that were delegated to the CPE.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show subscribers
extensive command.
user@host>show subscribers extensive Type: PPPoE User Name: dual-stack-v4v6-pd IP Address: 203.0.113.5 IP Netmask: 255.255.0.0 IPv6 User Prefix: 2001:db8:2010:0:0:8::/64 Logical System: default Routing Instance: default Interface: pp0.1073741864 Interface type: Dynamic Dynamic Profile Name: DS-dyn-ipv4v6-ra MAC Address: 00:00:5E:00:53:02 State: Active Radius Accounting ID: 87 Session ID: 87 Login Time: 2012-01-17 14:45:30 PST IPv6 Delegated Address Pool: dhcpv6-pd-pool IPv6 Delegated Network Prefix Length: 64 IPv6 Interface Address: 2001:db8:2040:2000:2000::/48 Type: DHCP IPv6 Prefix: 2001:db8:2040:2000:2000:5::/64 Logical System: default Routing Instance: default Interface: pp0.1073741864 Interface type: Static MAC Address: 00:00:5E:00:53:02 State: Active Radius Accounting ID: 88 Session ID: 88 Underlying Session ID: 87 Login Time: 2012-01-17 14:46:00 PST DHCP Options: len 42 00 08 00 02 0b b8 00 01 00 0a 00 03 00 01 00 07 64 11 07 02 00 06 00 02 00 19 00 19 00 0c 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 IPv6 Delegated Address Pool: dhcpv6-pd-pool IPv6 Delegated Network Prefix Length: 64
Meaning
Under the PPPoE session, the IPv6 Delegated Address
Pool fields show the names of the pools used for DHCPv6 prefix
delegation and for ND/RA prefixes. The IPv6 Delegated Network
Prefix Length field shows the length of the prefix used to assign
the IPv6 address for this subscriber session. The IPv6 Interface
Address field shows the IPv6 address assigned to the CPE interface
from the ND/RA pool.
Under the DHCP session, the IPv6 Delegated Address Pool fields show the name of the pool used for DHCPv6 prefix delegation.
The IPv6 Delegated Network Prefix Length fields shows the
length of the prefix used in DHCPv6 prefix delegation.
Verifying DHCPv6 Address Bindings
Purpose
Display the address bindings in the client table on the DHCPv6 local server.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show dhcpv6 server binding command.
user@host>show dhcpv6 server binding Prefix Session Id Expires State Interface Client DUID 2001:db8:2040:2000:2000:5::/64 88 86189 BOUND pp0.1073741864 LL0x1-00:07:64:11:07:02
If you have many active subscriber sessions, you can display the server binding for a specific interface.
user@host>show dhcpv6 server binding interface pp0.1073741864 Prefix Session Id Expires State Interface Client DUID 2001:db8:2040:2000:2000:5::/64 88 86182 BOUND pp0.1073741864 LL0x1-00:07:64:11:07:02
Meaning
The Prefix field shows the DHCPv6 prefix
assigned to the subscriber session from the pool used for DHCPv6 prefix
delegation.
Verifying Router Advertisements
Purpose
Verify that router advertisements are being sent, and router solicits are being received.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show ipv6 router-advertisement command.
user@host>show ipv6 router-advertisement Interface: pp0.1073741864 Advertisements sent: 3, last sent 00:03:29 ago Solicits received: 0 Advertisements received: 0
If you have a large number of subscriber interfaces, you can display router advertisements for a specific interface.
user@host>show ipv6 router-advertisement interface pp0.1073741864 Interface: pp0.1073741864 Advertisements sent: 3, last sent 00:03:34 ago Solicits received: 0 Advertisements received: 0
Meaning
The display shows the number of advertisements that the router sent, the number of solicits and advertisements that the router received.
Verifying the Status of the PPPoE Logical Interface
Purpose
Display status information about the PPPoE logical interface (pp0).
Action
From operational mode, enter the show interfaces pp0.logical command.
user@host>show interfaces pp0.1073741864
Logical interface pp0.1073741864 (Index 388) (SNMP ifIndex 681)
Flags: Point-To-Point SNMP-Traps 0x4000 Encapsulation: PPPoE
PPPoE:
State: SessionUp, Session ID: 10,
Session AC name: almach, Remote MAC address: 00:00:5E:00:53:02,
Underlying interface: ge-3/3/0.1109 (Index 367)
Bandwidth: 1000mbps
Input packets : 22
Output packets: 50
Keepalive settings: Interval 30 seconds, Up-count 1, Down-count 3
LCP state: Opened
NCP state: inet: Opened, inet6: Opened, iso: Not-configured, mpls: Not-configured
CHAP state: Closed
PAP state: Success
Protocol inet, MTU: 65531
Flags: Sendbcast-pkt-to-re
Addresses, Flags: Is-Primary
Local: 192.0.2.77
Protocol inet6, MTU: 65531
Addresses, Flags: Is-Preferred Is-Primary
Destination: 2001:db8:2010:0:8::/64, Local: 2001:db8:2010:0:8::1
Local: fe80::2a0:a50f:fc63:a842
Meaning
The Underlying interface field shows the underlying Ethernet interface configured in the example.
The Destination field under Protocol inet6 shows the IPv6 address obtained through ND/RA. This is the value of the $junos-ipv6-ndra-prefix variable configured in the dynamic profile.
The Local field under Protocol inet6 shows the value of the $junos-ipv6-address variable configured for family inet6 in the pp0 configuration of the dynamic profile.
