Maintaining the SRX5400 Host Subsystem
Maintaining the SRX5400 Firewall Host Subsystem
Purpose
For optimum firewall performance, verify the condition of the host subsystem. The host subsystem is composed of an SCB and a Routing Engine installed into the slot in the SCB.
Action
On a regular basis:
Check the LEDs on the craft interface to view information about the status of the Routing Engines.
Check the LEDs on the SCB faceplate.
Check the LEDs on the Routing Engine faceplate.
To check the status of the Routing Engine, issue the
show chassis routing-enginecommand. The output is similar to the following:user@host> show chassis routing-engine Routing Engine status: Slot 0: Current state Master Election priority Master (default) Temperature 36 degrees C / 96 degrees F CPU temperature 33 degrees C / 91 degrees F DRAM 2048 MB Memory utilization 12 percent CPU utilization: User 1 percent Background 0 percent Kernel 4 percent Interrupt 0 percent Idle 94 percent Model RE-S-1300 Serial ID 1000697084 Start time 2008-07-11 08:31:44 PDT Uptime 3 hours, 27 minutes, 27 seconds Load averages: 1 minute 5 minute 15 minute 0.44 0.16 0.06To check the status of the SCB, issue the
show chassis environment cbcommand. The output is similar to the following:user@host> show chassis environment cb CB 0 status: State Online Master Temperature 40 degrees C / 104 degrees F Power 1 1.2 V 1208 mV 1.5 V 1521 mV 1.8 V 1807 mV 2.5 V 2507 mV 3.3 V 3319 mV 5.0 V 5033 mV 12.0 V 12142 mV 1.25 V 1243 mV 3.3 V SM3 3312 mV 5 V RE 5059 mV 12 V RE 11968 mV Power 2 11.3 V bias PEM 11253 mV 4.6 V bias MidPlane 4814 mV 11.3 V bias FPD 11234 mV 11.3 V bias POE 0 11176 mV 11.3 V bias POE 1 11292 mV Bus Revision 42 FPGA Revision 1
To check the status of a specific SCB, issue the show chassis
environment cb node slot command, for example, show chassis environment cb node 0.
For more information about using the CLI, see the CLI Explorer.
Taking the SRX5400 Firewall Host Subsystem Offline
The host subsystem is composed of an SCB with a Routing Engine installed in it. You take the host subsystem offline and bring it online as a unit. Before you replace an SCB or a Routing Engine, you must take the host subsystem offline. Taking the host subsystem offline causes the device to shut down.
To take the host subsystem offline:
Operating and Positioning the SRX5400 Firewall SCB Ejectors
When removing or inserting the SCB, ensure that the cards or blank panels in adjacent slots are fully inserted to avoid hitting them with the ejector handles. The ejector handles require that all adjacent components be completely inserted so the ejector handles do not hit them, which could result in damage.
The ejector handles must be stored toward the center of the board. Ensure the long ends of the ejectors located at both the right and left ends of the board are horizontal and pressed as far as possible toward the center of the board.
To insert or remove the SCB, slide the ejector across the SCB horizontally, rotate it, and slide it again another quarter of a turn. Turn the ejector again and repeat as necessary. Utilize the indexing feature to maximize leverage and to avoid hitting any adjacent components.
Operate both ejector handles simultaneously. The insertion force on the SCB is too great for one ejector.
Replacing the SRX5400 Firewall SCB
Before replacing the SCB, read the guidelines in Operating and Positioning the SRX5400 Firewall SCB Ejectors. To replace the SCB, perform the following procedures:
The procedure to replace an SCB applies to the SRX5K-SCB, SRX5K-SCBE, and SRX5K-SCB3.
Removing the SRX5400 Firewall SCB
To remove the SCB (see Figure 1):
The SCB and Routing Engine are removed as a unit. You can also remove the Routing Engine separately.
Before removing the SCB, ensure that you know how to operate the ejector handles properly to avoid damage to the equipment.
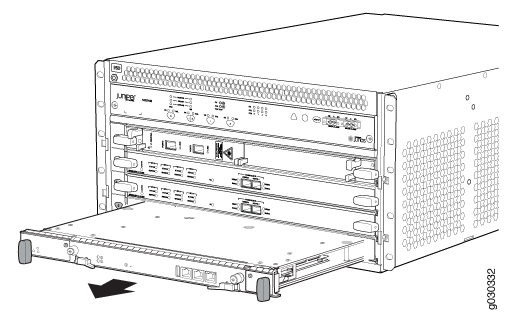
Installing an SRX5400 Firewall SCB
To install the SCB (see Figure 2):
Replacing the SRX5400 Firewall Routing Engine
To replace the Routing Engine, perform the following procedures:
The procedure to replace a Routing Engine applies to both SRX5K-RE-13-20, SRX5K-RE-1800X4, and SRX5K-RE-128G.
Removing the SRX5400 Firewall Routing Engine
Before you replace the Routing Engine, you must take the host subsystem offline.
To remove the Routing Engine (see Figure 3):
Installing the SRX5400 Firewall Routing Engine
To install the Routing Engine into the SCB (see Figure 4):
If you install only one Routing Engine in the service gateway, you must install it in SCB slot 0 of service gateway chassis.
Replace Routing Engine in an Operating SRX5400, SRX5600, or SRX5800 Firewalls Chassis Cluster
If your Firewall is part of an operating chassis cluster, you can replace the Routung Engines; SRX5K-RE-13-20, SRX5K-RE-1800X4, and SRX5K-RE-128G by incurring a minimum downtime on your network.
To replace routung engine in a firewall that is part of a chassis cluster, it must meet the following conditions:
-
Each firewall must have at least one routing engine installed.
-
You must ensure that the Node scheduled for RE replacement is not running any services. If any services remain active on that Node, perform an RG switchover so the other Node becomes active for all RGs.
Performing the RG0 switchover prompts the firewall to flap every BGP, OSPF, and IS-IS neighborship and disrupt services. It is recommended to perform switchover during a maintenance window.
This replacement procedure guides you to replace a routing engine in a cluster with two nodes (Node 0 and Node 1). The nodes are connected with dual control links and dual fabric links. Each node contains dual routing engines (RE0 primary and RE1 secondary). This procedure is also applicable for Nodes with single RE. The procedure explains RE0 replacement in Node 0 and it is shown as online on both Nodes.
While you replace the router, you must turn off the device containing the routing engine you plan to replace.
To replace routing engine in a chassis cluster:
Low Impact Hardware Upgrade for SCB3 and IOC3
Before you begin the LICU procedure, verify that both firewalls in the cluster are running the same Junos OS release.
You can perform the hardware upgrade using the LICU process only.
You must perform the hardware upgrade at the same time as the software upgrade from Junos OS Release 12.3X48-D10 to 15.1X49-D10.
If your device is part of a chassis cluster, you can upgrade SRX5K-SCBE (SCB2) to SRX5K-SCB3 (SCB3) and SRX5K-MPC (IOC2) to IOC3 (SRX5K-MPC3-100G10G or SRX5K-MPC3-40G10G) using the low-impact hardware upgrade (LICU) procedure, with minimum downtime. You can also follow this procedure to upgrade SCB1 to SCB2, and RE1 to RE2.
In the chassis cluster, the primary device is depicted as node 0 and the secondary device as node 1.
Follow these steps to perform the LICU.
For more information about LICU, refer to KB article KB17947 from the Knowledge Base.
In-Service Hardware Upgrade for SRX5K-RE-1800X4 and SRX5K-SCBE or SRX5K-RE-1800X4 and SRX5K-SCB3 in a Chassis Cluster
Ensure that the following prerequisites are completed before you begin the ISHU procedure:
Replace all interface cards such as IOCs and Flex IOCs as specified in Table 1.
Table 1: List of Interface Cards for Upgrade Cards to Replace
Replacement Cards for Upgrade
SRX5K-40GE-SFP
SRX5K-MPC and MICs
SRX5K-4XGE-XFP
SRX5K-MPC and MICs
SRX5K-FPC-IOC
SRX5K-MPC and MICs
SRX5K-RE-13-20
SRX5K-RE-1800X4
SRX5K-SCB
SRX5K-SCBE
SRX5K-SCBE
SRX5K-SCB3
Verify that both firewalls in the cluster are running the same Junos OS versions; release 12.1X47-D15 or later for SRX5K-SCBE with SRX5K-RE-1800X4 and 15.1X49-D10 or later for SRX5K-SCB3 with SRX5K-RE-1800X4. For more information on cards supported on the firewalls see Cards Supported on SRX5400, SRX5600, and SRX5800 Firewalls.
For more information about unified in-service software upgrade (unified ISSU), see Upgrading Both Devices in a Chassis Cluster Using an ISSU.
If your device is part of a chassis cluster, using the in-service hardware upgrade (ISHU) procedure you can upgrade:
SRX5K-SCB with SRX5K-RE-13-20 to SRX5K-SCBE with SRX5K-RE-1800X4
Note:Both the firewalls must have the same Junos OS version 12.3X48.
SRX5K-SCBE with SRX5K-RE-1800X4 to SRX5K-SCB3 with SRX5K-RE-1800X4
Note:You cannot upgrade SRX5K-SCB with SRX5K-RE-13-20 directly to SRX5K-SCB3 with SRX5K-RE-1800X4.
We strongly recommend that you perform the ISHU during a maintenance window, or during the lowest possible traffic as the secondary node is not available at this time.
Ensure to upgrade the SCB and Routing Engine at the same time as the following configurations are only supported:
SRX5K-RE-13-20 and SRX5K-SCB
SRX5K-RE-1800X4 and SRX5K-SCBE
SRX5K-RE-1800X4 and SRX5K-SCB3
While performing the ISHU, in the SRX5800 firewall, the second SCB can contain a Routing Engine but the third SCB must not contain a Routing Engine. In the SRX5600 Firewall, the second SCB can contain a Routing Engine.
To perform an ISHU:
For detailed information about chassis cluster, see the Chassis Cluster User Guide for SRX Series Devices at www.juniper.net/documentation/.



