Multiple Independent IGP Instances of OSPFv2
Benefits of Multi-Instance OSPFv2
- You can use multiple IGP instances of OSPFv2 and redistribute routes among independent OSPFv2 domains on a single router.
- You can construct flexible OSPFv2 hierarchies across independent IGP domains.
- Allows decoupling of multiple OSPFv2 flooding domains and therefore achieve a more scalable OSPFv2 deployment.
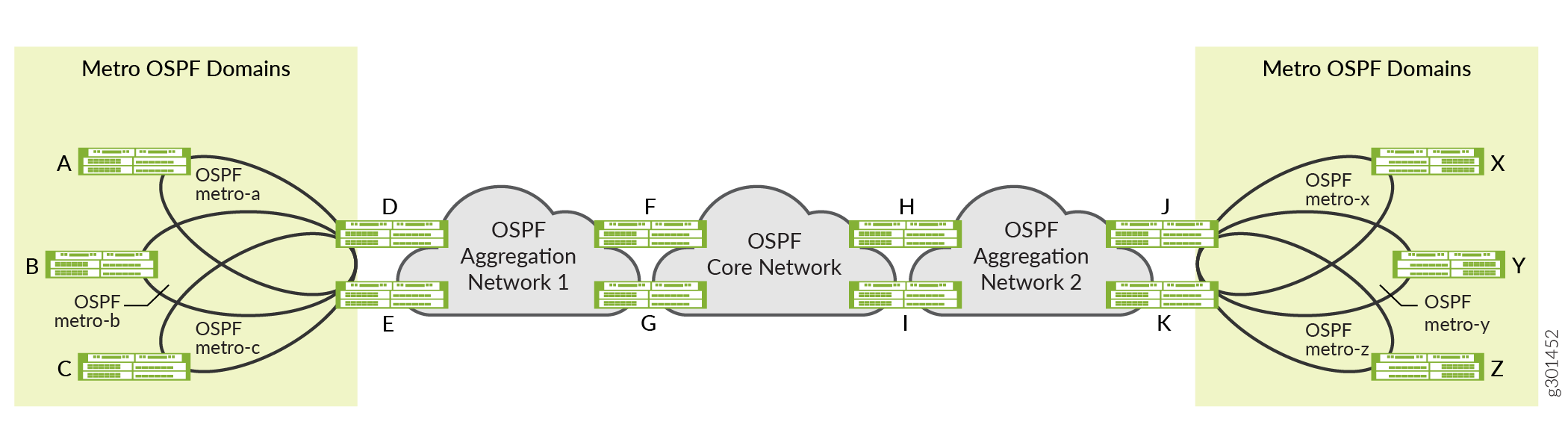
Figure 1 illustrates several benefits of configuring multiple IGP instances of OSPFv2 on the router. For example, Router F participates in two independent OSPF instances. Router F treats OSPF Aggregation Network-1 and OSPF Core Network as two independent IGP domains, while at the same time redistributing routes between those domains. Network operators can use this flexibility to construct a hierarchy of OSPF domains.
Figure 1 also illustrates the use of multiple IGP instances of OSPF to separate metro networks into independent OSPF flooding domains. In the example, routers D and E participate in the OSPF metro-a, OSPF metro-b, and OSPF metro-c networks, as well as in OSPF Aggregation Network-1. Routers D and E do not flood the different OSPF domains with OSPF advertisements. Instead they redistribute specific routes among the different OSPF domains, which allows for more scalable metro deployments.
Multi-Instance OSPF Overview
You can configure and run multiple independent IGP instances of OSPFv2 simultaneously on a router. These instances are associated with the default routing instance, and they install routes in the default routing table. Each OSPF instance can also export the routes installed in the routing table by other OSPF instances using the standard Junos OS routing policy configuration. By default, the routes installed by the different OSPF instances have the same route preference.
Junos OS does not support configuring the same logical interface in multiple IGP instances of OSPF.
In most deployment scenarios, only one OSPF instance on a router installs a route for a given prefix. Therefore, you don't need to configure different route preferences for multiple OSPF instances. However, for certain deployment scenarios where multiple OSPF instances install the routes for the same prefix in the routing table, you can set a different route preference for the routes installed by other OSPF instances. This allows the routing table to choose the routes with the best route preference and installs those routes in the forwarding table.
You can use the multiple OSPF instance feature for both hierarchical and parallel deployments. In the case of hierarchical deployments, there are well-defined borders between the groups of routers participating in different IGP instances. In parallel deployments, different IGP instances (typically not more than two or three) span entire groups of routers. You can also have mixed deployments, with some domains in a hierarchical deployment running IGP instances in parallel.
You can configure multiple independent IGP instances of OSPFv2 by including the
ospf-instance configuration statement at the [edit
protocols] hierarchy level. The configuration statements that you use at the
[edit protocols ospf-instance igp-instance-name]
hierarchy level are the same as those available at the [edit protocols
ospf] hierarchy level.
The ospf-instance configuration statement is not supported at the
[edit routing-instances routing-instance-name
protocols] hierarchy level.
You can configure and run multiple independent interior gateway protocol (IGP) instances of OSPFv2 with segment routing (SR) on a router. You can create two or more OSPF instances and apply SR-MPLS on each instance. Multiple instances of OSPF can advertise different prefix-segment identifiers (prefix-SIDs). Other instances can use these SIDs for making routing decisions.
Multi-instance OSPF combined with SR enhances network flexibility, scalability, and control over traffic engineering, especially in large and complex networks.
