Solution Benefits
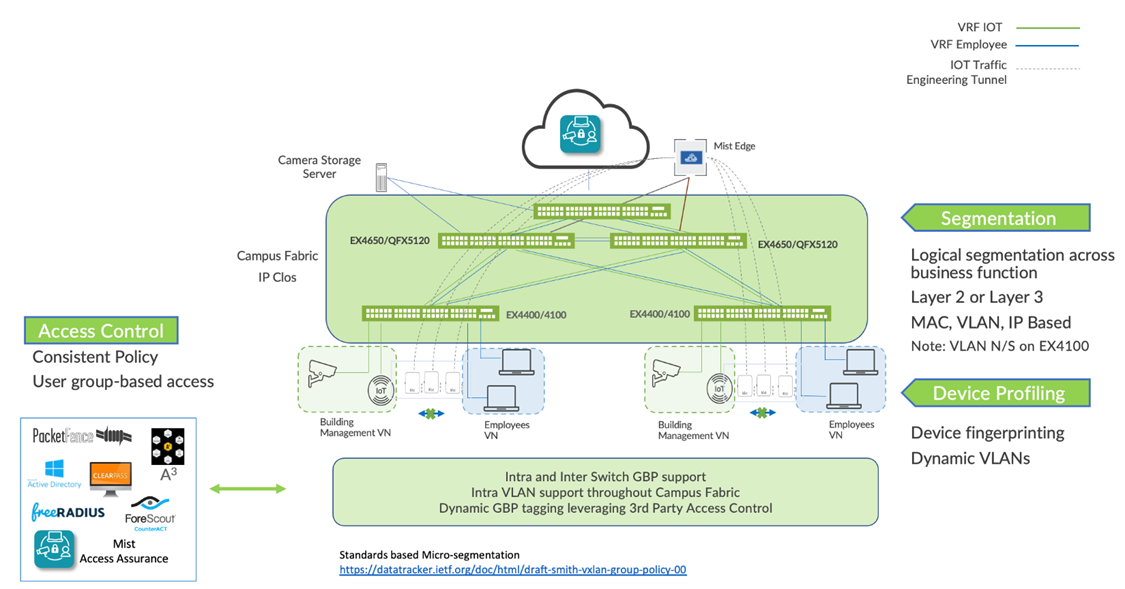
With group-based policies (GBP), you can enable microsegmentation at the access layer within a campus fabric IP Clos and leverage EVPN-VXLAN to provide traffic isolation within and between broadcast domains as well as simplify security policies across a campus fabric. See Figure 1.
There are several benefits of microsegmentation with GBP:
Standards based — https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/draft-smith-vxlan-group-policy-05
- Simplified Workflow—GBPs are administered through the Juniper Mist portal and provide a simple and well understood workflow for network wide policy control and enforcement. GBPs also simplify network configuration by avoiding the need for large numbers of firewall filters on all devices to ensure lateral threat protection.
- Consistency—GBPs provide consistent, customer-managed security policies across the enterprise through the Juniper Mist portal.
- Location-agnostic connectivity—GBPs leverage underlying VXLAN technology to provide location-agnostic endpoint access control.
- More granular control—Because GBP can be enforced as a Layer 2 method, it provides tighter control than with traditional ACL-based methods. Using VXLAN with GBP, you can block traffic to and from clients inside the same VLAN.
- Network access Control—GBPs allow for dynamic or static
tagging of wired clients.
- Dynamic GBP tagging works with industry standards-based RADIUS and network access control platforms, including the cloud-based Juniper Mist Access Assurance.
- Static GBP tagging allows you to assign GBP tags by IP prefix, MAC address, VLAN, and port on all access ports in the fabric.
Figure 1: Solution
Overview