Use BNG User Plane Maintenance
BNG User Plane Maintenance Overview
Juniper BNG CUPS in accordance with the TR 459 Multi-Service Disaggregated BNG with CUPS. Reference Architecture, Deployment Models, Interface, and Protocol specification introduces a new maintenance (hardware and software maintenance) approach for BNG User Planes. Juniper BNG CUPS enables you to perform maintenance operations on your BNG User Planes without impacting the subscribers’ traffic, therefore improving network operations and the subscribers' experience.
BNG User Plane maintenance relies on the BNG User Plane redundancy that is enabled through the BNG CUPS Controller. Instead of triggering a failure in the BNG User Plane, the BNG CUPS Controller assumes an operational procedure is occurring, which can be a maintenance repair.
BNG User Plane maintenance is applied to any session model (DHCP, IPoE, PPPoE and LNS) and assumes an access transport based on pseudowires EVPN-VPWS, with active and standby, or Ethernet with the access node controlled active and standby links to the BNG User Planes.
How to Use BNG User Plane Maintenance
Figure 1 illustrates the hitless BNG User Plane maintenance use case. It shows an example of you performing an in service maintenance on a distributed BNG User Plane (BNG-UP1 in the illustration), without disrupting any live subscriber sessions.
meaning, subscriber activity and traffic is unaffected with little or no packet loss
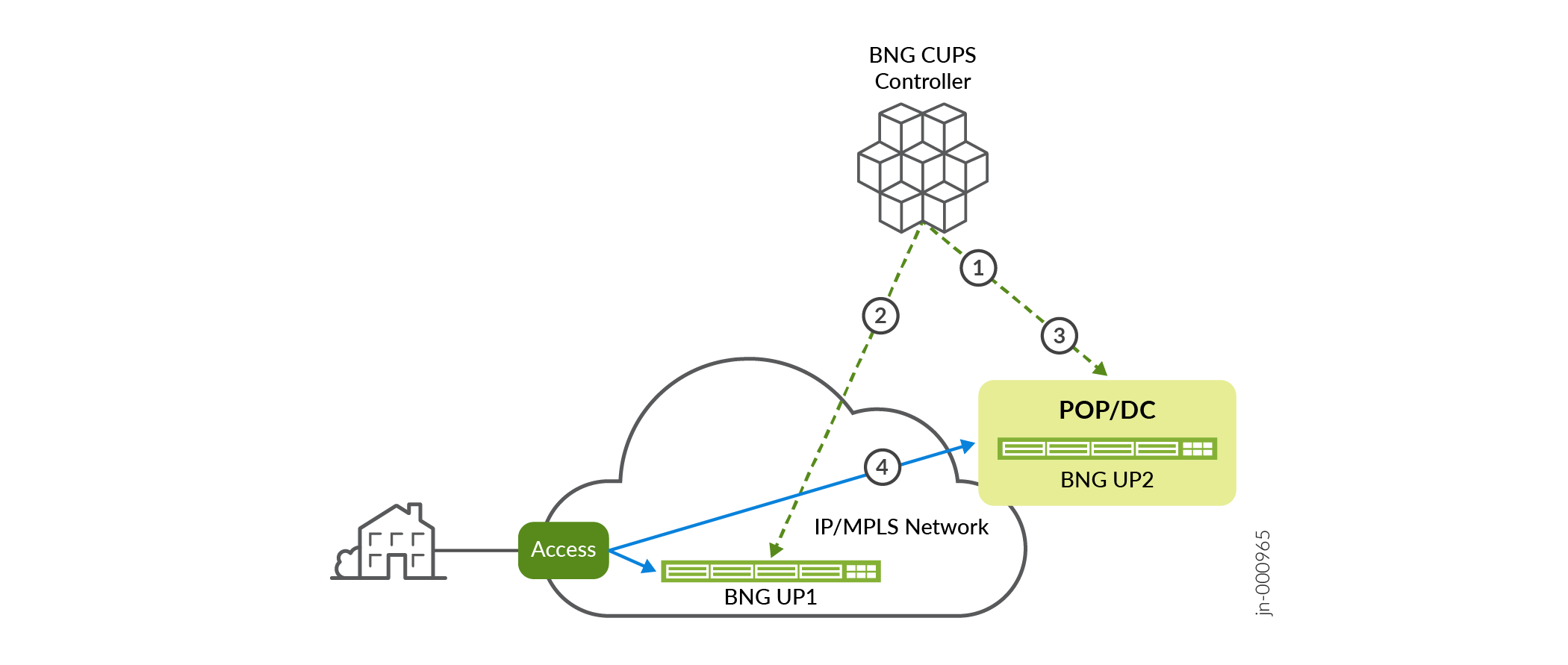
Following are the steps that occur when performing maintenance on a BNG User Plane (see Figure 1.
Prepare for performing maintenance on your BNG User Plane. You use the BNG CUPS Controller to program an alternate BNG User Plane (BNG-UP2) with subscriber state information from BNG User Plane BNG-UP1.
The BNG CUPS Controller activates BNG User Plane BNG-UP2.
You enable the access network to start forwarding traffic from the access node to BNG User Plane BNG-UP2 and the core network.
As the hot standby BNG User Plane, BNG User Plane BNG-UP2 is now preprogrammed with the subscriber state information from BNG User Plane BNG-UP1. As subscriber traffic arrives on BNG User Plane BNG-UP2, it forwards the subscriber traffic. Once maintenance is complete, you perform the same work flow in reverse to revert traffic back to BNG User Plane BNG-UP1.
BNG User Plane Maintenance Process
This section describes the process that is required when you perform a maintenance operation on a BNG User Plane. The procedure refers to Figure 1.
Create a backup for BNG User Plane BNG-UP1 on BNG User Plane BNG-UP2.
At this step you must first associate the active BNG User Plane BNG-UP1 ports with the backup BNG User Plane BNG-UP2 port. Then synchronize the ports, existing subscribers, and the address domain state from the active BNG User Plane BNG-UP1 to the backup BNG User Plane BNG-UP2. Subscribers that are on BNG User Plane BNG-UP1 are now also programmed on the backup BNG User Plane BNG-UP2's logical ports together with the address domain (prefixes, tags, routing-instances, and so on are also programmed on BNG-UP2).user@host# request user-plane maintenance associate serviced-user-plane BNG-UP1 serviced-port port1 backup-user-plane BNG-UP2 backup-port port2
Setup network to route traffic to the chosen backup BNG User Plane (BNG-UP2). This step is provider and operator specific and the actions taken at this step vary greatly with the various access and core network topologies deployed.
For example, at this step the operator could setup the core network for attracting subscriber traffic to the backup BNG User Plane by setting the routing policy to import these prefixes. Also, it is expected that at this step the operator is done setting up the access network for the backup BNG User Plane.
Make the backup BNG User Plane BNG-UP2 the active BNG User Plane. Now subscribers are programmed on the BNG User Plane BNG-UP2 and it is ready to take over.
This step executes the switchover from BNG User Plane BNG-UP1 to BNG User Plane BNG-UP2. After completing this step, BNG User Plane BNG-UP2 is the active BNG User Plane and BNG User Plane BNG-UP1 is the backup.
user@host# request user-plane maintenance switchover serviced-user-plane BNG-UP2
Perform the require maintenance on BNG User Plane BNG-UP1. The service can be various activities, such as servicing a line card or a software upgrade.
Restore the subscribers on BNG User Plane BNG-UP1 as backup. At this step the ports, subscribers, and domain state are automatically synchronized from the active BNG User Plane BNG-UP2 to the backup BNG User Plane BNG-UP1.
Note:At this steps, BNG User Plane BNG-UP 1 is expected to be back online. You can verify this, by checking the BNG User Plane BNG-UP1's node association state on the BNG CUPS Controller, using the
show health user-planecommand.Clean up the backup BNG User Plane BNG-UP2. During this step the ports and subscribers on BNG User Plane BNG-UP2 are cleaned up. After completing this step, BNG User Plane BNG-UP2 will be placed back into its original state.
user@host# request user-plane maintenance disassociate serviced-user-plane BNG-UP1 backup-user-plane BNG-UP2 user@host# request user-plane maintenance complete serviced-user-plane BNG-UP1
