MX240 Line Card Components and Descriptions
Interface Modules—DPCs
- MX240 Dense Port Concentrator (DPC) Description
- MX240 DPC Port and Interface Numbering
- MX240 Dense Port Concentrator (DPC) LEDs
- DPCs Supported on MX240, MX480, and MX960 Routers
MX240 Dense Port Concentrator (DPC) Description
A Dense Port Concentrator (DPC) is optimized for Ethernet density and supports up to 40 Gigabit Ethernet or four 10-Gigabit Ethernet ports (see Figure 1). Other combinations of Gigabit Ethernet and 10-Gigabit ports are available in various DPC models. For more information about these models, see the MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platform Interface Module Reference.
The DPC assembly combines packet forwarding and Ethernet interfaces on a single board, with either two or four 10-Gbps Packet Forwarding Engines. Each Packet Forwarding Engine consists of one I-chip for Layer 3 processing and one Layer 2 network processor. The DPCs interface with the power supplies and Switch Control Boards (SCBs).
The router has two dedicated line card slots for DPCs, MPCs, or FPCs. DPCs install horizontally in the front of the router (see Figure 1). One multifunction slot numbered 1/0 supports either one DPC or one SCB. The DPC slots are numbered 1/0, 1, and 2, bottom to top. A DPC can be installed in any slot on the router that supports DPCs.
You can install any combination of DPC types in the router.
DPCs are hot-removable and hot-insertable. When you install a DPC in an operating router, the Routing Engine downloads the DPC software, the DPC runs its diagnostics, and the Packet Forwarding Engines housed on the DPC are enabled. Forwarding on other DPCs continues uninterrupted during this process.
If a slot is not occupied by a DPC or an SCB, a blank panel must be installed to shield the empty slot and to allow cooling air to circulate properly through the router.
Figure 1 shows typical DPCs supported on the MX240 router. For more information about DPCs, see the MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platform Interface Module Reference.


DPC Components
Each DPC consists of the following components:
-
DPC cover, which functions as a ground plane and a stiffener.
-
Fabric interfaces.
-
Two Gigabit Ethernet interfaces that allow control information, route information, and statistics to be sent between the Routing Engine and the CPU on the DPCs.
-
Two interfaces from the SCBs that enable the DPCs to be powered on and controlled.
-
Physical DPC connectors.
-
Two or four Packet Forwarding Engines.
-
Midplane connectors and power circuitry.
-
Processor subsystem, which includes a 1.2-GHz CPU, system controller, and 1 GB of SDRAM.
-
Online button—Takes the DPC online or offline when pressed.
-
LEDs on the DPC faceplate. For more information about LEDs on the DPC faceplate, see the MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platform Interface Module Reference.
Two LEDs, located on the craft interface above the DPC, display the status of the DPC and are labeled OK and FAIL.
See Also
MX240 DPC Port and Interface Numbering
Each port on a DPC corresponds to a unique interface name in the CLI.
In the syntax of an interface name, a hyphen (-)
separates the media type from the DPC number (represented as an FPC in the CLI). The DPC slot
number corresponds to the first number in the interface. The second
number in the interface corresponds to the logical PIC number. The
last number in the interface matches the port number on the DPC. Slashes
(/) separate the DPC number from the logical PIC number
and port number.
type-fpc/pic/port
-
type—Media type, which identifies the network device. For example:
-
ge—Gigabit Ethernet interface
-
so—SONET/SDH interface
-
xe—10-Gigabit Ethernet interface
For a complete list of media types, see Interface Naming Overview.
-
-
fpc—Slot in which the DPC is installed. On the MX240 router, the DPCs are represented in the CLI as
FPC 0throughFPC 2. -
pic—Logical PIC on the DPC. The number of logical PICs varies depending on the type of DPC. For example, a:
-
20-port Gigabit Ethernet DPC has two logical PICs, numbered 0 through 1.
-
40-port Gigabit Ethernet DPC has four logical PICs, numbered 0 through 3.
-
2-port 10-Gigabit Ethernet DPC has two logical PICs, numbered 0 through 1.
-
4-port 10-Gigabit Ethernet DPC has four logical PICs, numbered 0 through 3.
For more information on specific DPCs, see DPCs Supported on MX240, MX480, and MX960 Routers in the MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platform Interface Module Reference.
-
-
port—Port number.
The MX240 router supports up to three DPCs that install horizontally and are numbered from bottom to top.
Figure 3 shows a 40-port Gigabit Ethernet DPC with SFP installed in slot 2 on the MX240 router.

The DPC contains four logical PICs, numbered PIC 0 through PIC 3 in the CLI. Each logical PIC contains 10
ports numbered 0 through 9.
The show chassis hardware command output displays
a 40-port Gigabit Ethernet DPC with SFP (DPCE-R-40GE-SFP) installed in DPC slot 2. The DPC is shown
as FPC 2 and the DPC’s four logical
PICs — 10x 1GE(LAN) — are
shown as PIC 0 through PIC 3.
user@host> show chassis hardware
...
FPC 2 REV 07 750-018122 KB8222 DPCE 40x 1GE R
CPU REV 06 710-013713 KA9010 DPC PMB
PIC 0 BUILTIN BUILTIN 10x 1GE(LAN)
Xcvr 0 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2NU4 SFP-SX
Xcvr 1 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2P4R SFP-SX
Xcvr 2 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2NYL SFP-SX
Xcvr 3 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2UW6 SFP-SX
Xcvr 4 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2P4N SFP-SX
Xcvr 5 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2UME SFP-SX
Xcvr 6 REV 01 740-011613 PCE1H5P SFP-SX
Xcvr 7 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2UFG SFP-SX
Xcvr 8 REV 02 740-011613 AM0947SEYU2 SFP-SX
Xcvr 9 REV 02 740-011613 AM0947SEYTQ SFP-SX
PIC 1 BUILTIN BUILTIN 10x 1GE(LAN)
Xcvr 0 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2UYF SFP-SX
Xcvr 1 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2P4L SFP-SX
Xcvr 2 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2UCL SFP-SX
Xcvr 3 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2P4X SFP-SX
Xcvr 4 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2P1E SFP-SX
Xcvr 5 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2UD2 SFP-SX
Xcvr 6 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2PLC SFP-SX
Xcvr 7 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2UDJ SFP-SX
Xcvr 8 REV 02 740-011613 AM0947SEX7S SFP-SX
PIC 2 BUILTIN BUILTIN 10x 1GE(LAN)
Xcvr 0 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2NV7 SFP-SX
Xcvr 1 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2P6Q SFP-SX
Xcvr 2 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2NUG SFP-SX
Xcvr 3 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2P10 SFP-SX
Xcvr 9 REV 02 740-011613 AM0947SEXBT SFP-SX
PIC 3 BUILTIN BUILTIN 10x 1GE(LAN)
Xcvr 0 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2PL4 SFP-SX
Xcvr 1 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2P1K SFP-SX
Xcvr 2 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2PLM SFP-SX
Xcvr 3 REV 01 740-011782 PCH2UFF SFP-SX
Xcvr 8 REV 02 740-011613 AM1003SFV5S SFP-SX
Xcvr 9 REV 02 740-011613 AM0947SEXBX SFP-SX
... The show interfaces terse command output displays
the Gigabit Ethernet interfaces that correspond to the 40 ports located
on the DPC.
user@host> show interfaces terse ge-2* Interface Admin Link Proto Local Remote ge-2/0/0 up up ge-2/0/1 up down ge-2/0/2 up up ge-2/0/3 up up ge-2/0/4 up up ge-2/0/5 up up ge-2/0/6 up up ge-2/0/7 up up ge-2/0/8 up up ge-2/0/9 up up ge-2/1/0 up down ge-2/1/1 up down ge-2/1/2 up down ge-2/1/3 up down ge-2/1/4 up up ge-2/1/5 up up ge-2/1/6 up up ge-2/1/7 up up ge-2/1/8 up up ge-2/1/9 up down ge-2/2/0 up down ge-2/2/1 up down ge-2/2/2 up down ge-2/2/3 up down ge-2/2/4 up down ge-2/2/5 up down ge-2/2/6 up down ge-2/2/7 up down ge-2/2/8 up down ge-2/2/9 up down ge-2/3/0 up down ge-2/3/1 up down ge-2/3/2 up down ge-2/3/3 up down ge-2/3/4 up down ge-2/3/5 up down ge-2/3/6 up down ge-2/3/7 up down ge-2/3/8 up down ge-2/3/9 up down
See Also
MX240 Dense Port Concentrator (DPC) LEDs
Two LEDs, located on the craft interface above the DPC, display the status of the DPC and are labeled OK and FAIL. For more information about the DPC LEDs on the craft interface, see MX240 Component LEDs on the Craft Interface.
Each DPC also has LEDs located on the faceplate. For more information about LEDs on the DPC faceplate, see the “LEDs” section for each DPC in the MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platform Interface Module Reference.
See Also
DPCs Supported on MX240, MX480, and MX960 Routers
These DPCs have all been announced as End of Life (EOL). The End of Support (EOS) milestone dates for each model are published at https://www.juniper.net/support/eol/mseries_hw.html.
Table 1 lists the DPCs supported by the MX240, MX480, and MX960 routers.
|
DPC Name |
DPC Model Number |
Ports |
Maximum Throughput per DPC |
First Junos OS Release |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gigabit Ethernet | ||||
|
DPC-R-40GE-SFP EOL (see PSN-TSB14931 ) |
40 |
40 Gbps |
8.2 |
|
|
DPCE-R-40GE-SFP EOL (see PSN-TSB16810) |
40 |
40 Gbps |
8.4 |
|
|
DPCE-X-40GE-SFP EOL (see PSN-TSB16810) |
40 |
40 Gbps |
8.4 |
|
|
Gigabit Ethernet Enhanced Queuing Ethernet Services DPC with SFP |
DPCE-X-Q-40GE-SFP EOL (see PSN-TSB16059) |
40 |
40 Gbps |
8.5 |
|
DPCE-R-Q-20GE-SFP EOL (see PSN-TSB16059) |
20 |
20 Gbps |
9.1 |
|
|
DPCE-R-Q-40GE-SFP EOL (see PSN-TSB15618) |
40 |
40 Gbps |
8.5 |
|
|
DPC-R-4XGE-XFP EOL (see PSN-TSB14931 ) |
4 |
40 Gbps |
8.2 |
|
| 10-Gigabit Ethernet | ||||
|
DPCE-R-2XGE-XFP EOL (see PSN-TSB15618) |
2 |
20 Gbps |
9.1 |
|
|
DPCE-R-4XGE-XFP EOL (see PSN-TSB16810) |
4 |
40 Gbps |
8.4 |
|
|
DPCE-X-4XGE-XFP EOL (see PSN-TSB16810) |
4 |
40 Gbps |
8.4 |
|
|
10-Gigabit Ethernet Enhanced Queuing Ethernet Services DPC with XFP |
DPCE-X-Q-4XGE-XFP EOL (see PSN-TSB16059) |
4 |
40 Gbps |
8.5 |
|
10-Gigabit Ethernet Enhanced Queuing IP Services DPC with XFP |
DPCE-R-Q-4XGE-XFP EOL (see PSN-TSB15618) |
4 |
40 Gbps |
8.5 |
| Multi-Rate Ethernet | ||||
|
DPCE-R-20GE-2XGE EOL (see PSN-TSB15618) |
22 |
40 Gbps |
9.2 |
|
|
Multi-Rate Ethernet Enhanced Ethernet Services DPC with SFP and XFP |
DPCE-X-20GE-2XGE EOL (see PSN-TSB15618) |
22 |
40 Gbps |
9.2 |
|
Multi-Rate Ethernet Enhanced Queuing IP Services DPC with SFP and XFP |
DPCE-R-Q-20GE-2XGE EOL (see PSN-TSB16810) |
22 |
40 Gbps |
9.3 |
| Tri-Rate Ethernet | ||||
|
DPCE-R-40GE-TX EOL (see PSN-TSB16059) |
40 |
40 Gbps |
9.1 |
|
|
DPCE-X-40GE-TX EOL (see PSN – TSB15619 ) |
40 |
40 Gbps |
9.1 |
|
| Services | ||||
|
MS-DPC EOL (see PSN–TSB16812 ) |
2 (Not supported) |
– |
9.3 |
|
See Also
Interface Modules—FPCs and PICs
- MX240 Flexible PIC Concentrator (FPC) Description
- MX240 Flexible PIC Concentrator (FPC) LEDs
- FPCs Supported by MX240, MX480, and MX960 Routers
- MX240 PIC Description
- MX240 PIC Port and Interface Numbering
- MX240 PIC LEDs
- PICs Supported by MX240, MX480, and MX960 Routers
MX240 Flexible PIC Concentrator (FPC) Description
A Flexible PIC Concentrator (FPC) occupies two DPC slots on an MX Series router. The DPC slots are numbered 1/0, 1, and 2, bottom to top. One FPC can be installed horizontally in either slots 1/0 and 1, or slots 1 and 2 on the front of the router (see Figure 5). The interface corresponds to the lowest numbered DPC slot for which the FPC is installed.
Figure 4 shows typical FPCs supported on the MX240 router.

If a slot is not occupied by a DPC, an FPC, or an SCB, a blank panel must be installed to shield the empty slot and to allow cooling air to circulate properly through the router.
Each FPC supports up to two PICs. On an FPC2, one Packet Forwarding Engine receives incoming packets from the PICs installed on the FPC and forwards them through the switch planes to the appropriate destination port. On an FPC3, two Packet Forwarding Engines receive incoming packets from the PICs installed on the FPC and forwards them through the switch planes to the appropriate destination port. The FPCs interface with the power supplies and SCBs.
FPCs are hot-removable and hot-insertable, as described in MX240 Component Redundancy. When you install an FPC into a functioning router, the Routing Engine downloads the FPC software, the FPC runs its diagnostics, and the PICs, housed on the FPC, are enabled. Forwarding continues uninterrupted during this process. When you remove or install an FPC, packet forwarding between other DPCs or FPCs is not affected.

FPC Components
Each FPC consists of the following components:
-
FPC card carrier, which includes two PIC slots.
-
Up to two Packet Forwarding Engines, each consisting of one I-chip for Layer 3 processing and one Layer 2 network processor.
-
Midplane connectors and power circuitry.
-
Processor subsystem (PMB), which includes a 1.2-GHz CPU, system controller, 1 GB of SDRAM, and two Gigabit Ethernet interfaces.
-
Two LEDs, located on the craft interface above the FPC, that display the status of the FPC and are labeled OK and FAIL. For more information about the FPC LEDs located on the craft interface, see MX240 Component LEDs on the Craft Interface.
-
FPC online/offline button, located on the craft interface above the FPC
See Also
MX240 Flexible PIC Concentrator (FPC) LEDs
Two LEDs, located on the craft interface above the FPC, that display the status of the FPC and are labeled OK and FAIL. For more information about the FPC LEDs located on the craft interface, see MX240 Component LEDs on the Craft Interface.
See Also
FPCs Supported by MX240, MX480, and MX960 Routers
An FPC occupies two slots when installed in an MX240, MX480, or MX960 router. The maximum number of supported FPCs varies per router:
MX960 router—6 FPCs
MX480 router—3 FPCs
MX240 router—1 FPC
Table 2 lists FPCs supported by MX240, MX480, and MX960 routers.
FPC Type |
FPC Name |
FPC Model Number |
Maximum Number of PICs Supported |
Maximum Throughput per FPC (Full-duplex) |
First Junos OS Release |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3 |
FPC3 |
MX-FPC3 |
2 |
20 Gbps |
9.4 |
2 |
FPC2 |
MX-FPC2 |
2 |
10 Gbps |
9.5 |
See Also
MX240 PIC Description
PICs provide the physical connection to various network media types, receiving incoming packets from the network and transmitting outgoing packets to the network. During this process, each PIC performs framing and line-speed signaling for its media type. Before transmitting outgoing data packets, the PICs encapsulate the packets received from the FPCs. Each PIC is equipped with an ASIC that performs control functions specific to the media type of that PIC.
PICs are hot-removable and hot-insertable. You can install up to two PICs in the slots in each FPC. PICs used in an FPC2 have captive screws at their upper and lower corners. PICs used in a Type 3 FPC have an upper ejector handle and a lower captive screw.
See Also
MX240 PIC Port and Interface Numbering
Each port on a PIC corresponds to a unique interface name in the CLI.
In the syntax of an interface name, a hyphen (-)
separates the media type from the FPC number (represented as an FPC in the CLI). The FPC slot
number corresponds to the first number in the interface. The second
number in the interface corresponds to the PIC number. The last number
in the interface matches the port number on the PIC. Slashes (/) separate the FPC slot number from the PIC number and port
number:
type-fpc/pic/port
-
type—Media type, which identifies the network device. For example:
-
ge—Gigabit Ethernet interface
-
so—SONET/SDH interface
-
xe—10-Gigabit Ethernet interface
For a complete list of media types, see Interface Naming Overview.
-
-
fpc—Lowest slot number in which the FPC is installed. On the MX240 router, the FPC occupies two line card slots and is represented in the CLI as
FPC 0orFPC 1. -
pic—PIC number, 0 or 1 depending on the FPC slot.
For more information on specific PICs, see PICs Supported by MX240, MX480, and MX960 Routers in the MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platform Interface Module Reference.
-
port—Port number.
The FPC installs horizontally in either slots 1/0 and 1, or slots 1 and 2 and accepts up to two PICs.
Figure 6 shows a Channelized OC12/STM4 Enhanced IQ (IQE) PIC with SFP installed in PIC slot 0 of an FPC installed in slot 1 and slot 2.

The show chassis hardware command output displays
a Channelized OC12/STM4 Enhanced IQ (IQE) PIC (4x CHOC12
IQE SONET) installed in MX FPC Type 2.
user@host> show chassis hardware
...
FPC 1 REV 01 710-024386 JW9571 MX FPC Type 2
CPU REV 03 710-022351 KE2986 DPC PMB
PIC 0 REV 00 750-022630 DS1284 4x CHOC12 IQE SONET
Xcvr 0 REV 01 740-011782 PB821SG SFP-SX
Xcvr 1 REV 01 740-011782 PB829Q6 SFP-SX
Xcvr 2 REV 01 740-011613 P9F15NQ SFP-SX
Xcvr 3 REV 01 740-011782 P7N036X SFP-SX... The show interfaces terse command output displays
the channelized SONET OC12 interfaces (coc12), that correspond to the four ports located on the PIC.
user@host> show interfaces terse coc12* Interface Admin Link Proto Local Remote coc12-1/0/0 up up coc12-1/0/1 up up coc12-1/0/2 up up coc12-1/0/3 up up
See Also
MX240 PIC LEDs
Each PIC has LEDs located on the faceplate. For more information about LEDs on the PIC faceplate, see the “LEDs” section for each PIC in the MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platform Interface Module Reference.
See Also
PICs Supported by MX240, MX480, and MX960 Routers
Table 3 lists the PICs supported by MX240, MX480, and MX960 routers.
PIC Name |
PIC Model Number |
Ports |
Type |
First Junos OS Release |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Channelized IQ PICs | ||||
PB-4CHOC12-STM4-IQE-SFP |
4 |
2 |
9.5 |
|
PB-1CHOC48-STM16-IQE |
1 |
2 |
9.5 |
|
| SONET/SDH PICs | ||||
PB-4OC3-1OC12-SON2-SFP |
4 |
2 |
9.5 |
|
PB-4OC3-4OC12-SON-SFP |
4 |
2 |
9.5 |
|
PC-4OC48-STM16-IQE-SFP |
4 |
3 |
10.4R2 |
|
PB-1OC48-SON-B-SFP |
1 |
2 |
9.5 |
|
PC-4OC48-SON-SFP |
4 |
3 |
9.4 |
|
PC-1OC192-SON-VSR |
1 |
3 |
9.4 |
|
PC-1OC192-SON-XFP |
1 |
3 |
9.4 |
|
See Also
Interface Modules—MPCs and MICs
- MIC/MPC Compatibility
- MX240 Modular Interface Card (MIC) Description
- MICs Supported by MX Series Routers
- MX240 Modular Interface Card (MIC) LEDs
- MX240 MIC Port and Interface Numbering
- MX240 Modular Port Concentrator (MPC) Description
- MX240 Modular Port Concentrator (MPC) LEDs
- MPCs Supported by MX Series Routers
- MX240 Application Services Modular Line Card Description
- MX240 AS MSC LEDs
- MX240 Application Services Modular Processing Card Description
- MX240 AS MXC LEDs
MIC/MPC Compatibility
The following tables provide a compatibility matrix for the MICs currently supported by MPC1, MPC2, MPC3, MPC6, MPC8, and MPC9 on MX240, MX480, MX960, MX2008, MX2010, MX2020, and MX10003 routers. Each table lists the first Junos OS release in which the MPC supports the MIC. For example, Junos OS Release 10.2 is the first release in which the MX-MPC1-3D supports the Gigabit Ethernet MIC with SFP. An en dash indicates that the MIC is not supported.
MIC Name |
MPC1 |
MPC1E |
MPC1 Q |
MPC1E Q |
|---|---|---|---|---|
MIC-3D-8OC3-2OC12-ATM |
— |
— |
12.1 |
12.1R4 |
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP |
10.2 |
11.2R4 |
10.2 |
11.2R4 |
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP-E |
13.2R2 |
13.2R2 |
13.2R2 |
13.2R2 |
MIC-3D-2XGE-XFP |
10.2 |
11.2R4 |
10.2 |
11.2R4 |
MIC-3D-4XGE-XFP |
— |
— |
— |
— |
MIC-3D-40GE-TX |
10.2 |
11.2R4 |
10.2 |
11.2R4 |
MIC-3D-4OC3OC12-1OC48, MIC-3D-8OC3OC12-4OC48 |
11.2 |
11.2R4 |
11.2 |
11.2R4 |
MIC-3D-4COC3-1COC12-CE (Channelized OC3/STM1 (Multi-Rate) Circuit Emulation MIC with SFP) |
— |
— |
12.2 |
12.2 |
MIC-3D-1OC192-XFP |
12.2 |
12.2 |
12.2 |
12.2 |
MIC-3D-4CHOC3-2CHOC12, MIC-3D-8CHOC3-4CHOC12 MIC-4COC3-2COC12-G, MIC-8COC3-4COC12-G |
— |
— |
11.4 |
11.4 |
MIC-3D-16CHE1-T1-CE |
13.2 Note:
Support for Non-Channelized MIC only. |
13.2 Note:
Support for Non-Channelized MIC only. |
12.3 |
12.3 |
MIC-3D-8DS3-E3, MIC-3D-8CHDS3-E3-B Note:
You cannot run Channelized DS3 (MIC-3D-8CHDS3-E3) on non-Q MPCs. Channelized DS3 is supported only on Q and EQ-based MPCs. |
11.4 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
MIC-MACSEC-20GE Gigabit Ethernet MIC with 256b-AES MACsec |
18.3R1 |
18.3R1 |
18.3R1 |
18.3R1 |
MS-MIC-16G |
13.2 |
13.2 |
13.2 |
13.2 |
MIC Name |
MPC2 |
MPC2E |
MPC2E-3D-NG |
MPC2 Q |
MPC2E Q |
MPC2 EQ |
MPC2E EQ |
MPC2E P |
MPC2E-3D-NG-Q |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MIC-3D-8OC3-2OC12-ATM |
— |
— |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
12.1 |
12.1R4 |
12.1 |
12.1R4 |
— |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP |
10.1 |
11.2R4 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
10.1 |
11.2R4 |
10.1 |
11.2R4 |
12.2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP-E |
13.2R2 |
13.2R2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
13.2R2 |
13.2R2 |
13.2R2 |
13.2R2 |
13.2R2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-2XGE-XFP |
10.2 |
11.2R4 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
10.2 |
11.2R4 |
10.2 |
11.2R4 |
12.2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-10GE-SFP-E |
— |
— |
24.2 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
24.2 |
|
MIC-3D-4XGE-XFP |
10.1 |
11.2R4 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
10.1 |
11.2R4 |
10.1 |
11.2R4 |
12.2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-40GE-TX |
10.2 |
11.2R4 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
10.2 |
11.2R4 |
10.2 |
11.2R4 |
12.2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-4OC3OC12-1OC48,MIC-3D-8OC3OC12-4OC48 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
— |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-4COC3-1COC12-CE (Channelized OC3/STM1 (Multi-Rate) Circuit Emulation MIC with SFP) |
— |
— |
— |
12.2 |
12.2 |
12.2 |
12.2 |
12.2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-1OC192-XFP |
12.2 |
12.2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
12.2 |
12.2 |
12.2 |
12.2 |
12.2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-4CHOC3-2CHOC12, MIC-3D-8CHOC3-4CHOC12 MIC-4COC3-2COC12-G, MIC-8COC3-4COC12-G |
— |
— |
15.1 with flexible queuing option |
11.4 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
— |
15.1 14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity |
|
MIC-3D-16CHE1-T1-CE |
13.2 Note:
Support for Non-Channelized MIC only. |
15.1 with flexible queuing option |
12.3 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
— |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
|
MIC-3D-8DS3-E3, MIC-3D-8CHDS3-E3-B Note:
You cannot run Channelized DS3 (MIC-3D-8CHDS3-E3) on non-Q MPCs. Channelized DS3 is supported only on Q and EQ-based MPCs. |
11.4 |
11.4 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
12.2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MS-MIC-16G Note:
Only one MS-MIC-16G can be installed into any MPC. |
13.2 |
13.2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
13.2 |
13.2 |
13.2 |
13.2 |
13.2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-MACSEC-20GE Gigabit Ethernet MIC with 256b-AES MACsec |
18.3R1 |
18.3R1 |
18.3R1 |
18.3R1 |
18.3R1 |
18.3R1 |
18.3R1 |
18.3R1 |
18.3R1 |
MIC Name |
MPC3E |
MPC3E-3D-NG |
MPC3E-3D-NG-Q |
|---|---|---|---|
|
MIC-3D-8OC3-2OC12-ATM |
— |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP |
12.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP-E |
13.2R2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC3-3D-1X100GE-CFP |
12.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-2XGE-XFP |
12.2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-4XGE-XFP |
— |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-10GE-SFP-E |
— |
24.2 |
24.2 |
|
MIC3-3D-10XGE-SFPP |
12.3 |
14.1R4, 14.2 R3 and Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC3-3D-2X40GE-QSFPP |
12.2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC3-3D-1X100GE-CXP |
12.2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC3-100G-DWDM |
15.1F515.1F617.1R1 |
15.1F515.1F617.1R1 |
15.1F515.1F617.1R1 |
|
MIC-3D-4OC3OC12-1OC48 MIC-3D-8OC3OC12-4OC48 |
13.3 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-1OC192-XFP |
13.3 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-4COC3-1COC12-CE (Channelized OC3/STM1 (Multi-Rate) Circuit Emulation MIC with SFP) |
— |
— |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-16CHE1-T1-CE |
— |
15.1 with flexible queuing option |
15.1 |
|
MS-MIC-16G Note:
On MPC3E, the installation of the Multiservices MIC (MS-MIC-16G) with MIC3-3D-2X40GE-QSFPP, MIC3-3D-10XGE-SFPP, or MIC3-3D-1X100GE-CFP does not meet the NEBS criteria. Note:
Only one MS-MIC-16G can be installed into any MPC. |
13.2R2 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-40GE-TXTri-Rate MIC |
— |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-4OC3OC12-1OC48, MIC-3D-8OC3OC12-4OC48SONET/SDH OC3/STM1 (Multi-Rate) MICs with SFP |
12.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-4CHOC3-2CHOC12, MIC-3D-8CHOC3-4CHOC12MIC-4COC3-2COC12-G, MIC-8COC3-4COC12-G Channelized SONET/SDH OC3/STM1 (Multi-Rate) MICs with SFP |
— |
15.1 with flexible queuing option |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-3D-8DS3-E3, MIC-3D-8CHDS3-E3-BDS3/E3 MIC Note:
You cannot run Channelized DS3 (MIC-3D-8CHDS3-E3) on non-Q MPCs. Channelized DS3 is supported only on Q and EQ-based MPCs. |
12.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 with Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|
MIC-MACSEC-20GE Gigabit Ethernet MIC with 256b-AES MACsec |
18.3R1 |
18.3R1 |
18.3R1 |
MIC Name |
MPC6E |
|---|---|
MIC6-10G |
13.3R2 |
MIC6-10G-OTN |
13.3R3 |
MIC6-100G-CXP |
13.3R2 |
MIC6-100G-CFP2 |
13.3R3 |
MIC Name |
MPC8E |
|---|---|
MIC-MRATE |
15.1F5 with Junos Continuity 16.1R1 |
MIC-MACSEC-MRATE |
17.4 |
MIC Name |
MPC9E |
|---|---|
MIC-MRATE |
15.1F5 with Junos Continuity 16.1R1 |
MIC-MACSEC-MRATE |
17.4 |
MIC Name |
MPC10003 |
|---|---|
JNP-MIC1 |
17.3 |
JNP-MIC1-MACSEC |
17.3R2 |
MX240 Modular Interface Card (MIC) Description
Modular Interface Cards (MICs) install into Modular Port Concentrators (MPCs) and provide the physical connections to various network media types. MICs allow different physical interfaces to be supported on a single line card. You can install MICs of different media types on the same router as long as the router supports those MICs.
MICs receive incoming packets from the network and transmit outgoing packets to the network. During this process, each MIC performs framing and high-speed signaling for its media type. Before transmitting outgoing data packets through the MIC interfaces, the MPCs encapsulate the packets received.
MICs are hot-removable and hot-insertable. You can install up to two MICs in the slots in each MPC.
See Also
MICs Supported by MX Series Routers
The following tables list the first supported Junos OS release for the MX Series.
Table 11 lists the first supported Junos OS release for MICs on MX240, MX480, MX960, and MX2008 routers.
Table 12 lists the first supported Junos OS release for MICs on MX2010 and MX2020 routers.
Table 13 list the first supported Junos OS release for MICs on MX5, MX10, and MX40 routers.
Table 14 lists the first supported Junos OS release for MICs on MX80 and MX104 routers.
Table 15 lists the first supported Junos OS release for MICs on MX10003 router.
MIC Name |
MIC Model Number |
Ports |
MX240, MX480, and MX960 Routers |
MX2008 Routers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATM | ||||
MIC-3D-8OC3-2OC12-ATM |
8 | 12.1 |
15.1F7 |
|
| DS3/E3 | ||||
MIC-3D-8DS3-E3, MIC-3D-8CHDS3-E3-B |
8 |
11.4 |
15.1F7 |
|
| Circuit Emulation | ||||
MIC-3D-16CHE1-T1-CE |
16 |
12.3 |
15.1F7 |
|
| Gigabit Ethernet | ||||
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP |
20 |
10.1 |
15.1F7 |
|
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP-E |
20 |
13.3 |
15.1F7 |
|
MIC-MACSEC-20GE |
20 |
18.3 |
— |
|
| 10-Gigabit Ethernet | ||||
MIC-3D-2XGE-XFP |
2 |
10.2 |
15.1F7 |
|
MIC-3D-4XGE-XFP |
4 |
10.1 |
15.1F7 |
|
| 1-Gigabit/10-Gigabit Ethernet MIC with SFP+ (10 Ports) |
MIC-3D-10GE-SFP-E |
10 |
24.2 |
— |
MIC3-3D-10XGE-SFPP |
10 |
12.3 |
15.1F7 |
|
MIC6-10G |
24 |
— |
15.1F7 |
|
MIC6-10G-OTN |
24 |
— |
15.1F7 |
|
| 40-Gigabit Ethernet | ||||
MIC3-3D-2X40GE-QSFPP |
2 |
12.2 |
15.1F7 |
|
| 100-Gigabit Ethernet | ||||
MIC3-3D-1X100GE-CFP |
1 |
12.1 |
15.1F7 |
|
MIC3-3D-1X100GE-CXP |
1 |
12.2 |
15.1F7 |
|
MIC6-100G-CXP |
4 |
— |
15.1F7 |
|
MIC6-100G-CFP2 |
2 |
— |
15.1F7 |
|
| 100-Gigabit DWDM OTN | ||||
MIC3-100G-DWDM |
1 |
15.1F515.1F617.1R1 |
15.1F7 |
|
| Multi-Rate | ||||
MIC-3D-4OC3OC12-1OC48 |
4 |
11.2 |
15.1F7 |
|
MIC-3D-8OC3OC12-4OC48 |
8 |
11.2 |
15.1F7 |
|
MIC-3D-4CHOC3-2CHOC12 |
4 |
11.4 |
15.1F7 |
|
MIC-3D-8CHOC3-4CHOC12 |
8 |
11.4 |
15.1F7 |
|
Channelized OC3/STM1 (Multi-Rate) Circuit Emulation MIC with SFP |
MIC-3D-4COC3-1COC12-CE |
4 |
12.2 |
15.1F7 |
MIC MRATE (12-Port Multi-Rate MIC with QSFP+) |
MIC-MRATE |
12 |
— |
15.1F7 |
Multi-Rate Ethernet MIC (12-Port Multi-Rate MACsec MIC with QSFP+) |
MIC-MACSEC-MRATE |
12 |
— |
17.4 |
| Tri-Rate | ||||
MIC-3D-40GE-TX |
40 |
10.2 |
15.1F7 |
|
| Services | ||||
MS-MIC-16G |
0 |
13.2 |
15.1F7 |
|
| SONET/SDH | ||||
MIC-3D-1OC192-XFP |
1 |
12.2 |
15.1F7 |
|
MIC Name |
MIC Model Number |
Ports |
MX2010 Routers |
MX2020 Routers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATM | ||||
MIC-3D-8OC3-2OC12-ATM |
8 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
| DS3/E3 | ||||
MIC-3D-8DS3-E3, MIC-3D-8CHDS3-E3-B |
8 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
| Circuit Emulation | ||||
MIC-3D-16CHE1-T1-CE |
16 |
— |
— |
|
| Gigabit Ethernet | ||||
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP |
20 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP-E |
20 |
13.3 |
13.3 |
|
| 10-Gigabit Ethernet | ||||
MIC-3D-2XGE-XFP |
2 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
MIC-3D-4XGE-XFP |
4 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
| 1-Gigabit/10-Gigabit Ethernet MIC with SFP+ (10 Ports) |
MIC-3D-10GE-SFP-E |
10 |
24.2 |
24.2 |
MIC3-3D-10XGE-SFPP |
10 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
MIC6-10G |
24 |
13.3R2 |
13.3R2 |
|
MIC6-10G-OTN |
24 |
13.3R3 |
13.3R3 |
|
| 40-Gigabit Ethernet | ||||
MIC3-3D-2X40GE-QSFPP |
2 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
| 100-Gigabit Ethernet | ||||
MIC3-3D-1X100GE-CFP |
1 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
MIC3-3D-1X100GE-CXP |
1 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
MIC6-100G-CXP |
4 |
13.3R2 |
13.3R2 |
|
MIC6-100G-CFP2 |
2 |
13.3R3 |
13.3R3 |
|
| 100-Gigabit DWDM OTN | ||||
MIC3-100G-DWDM |
1 |
15.1F515.1F617.1R1 |
15.1F515.1F617.1R1 |
|
| Multi-Rate | ||||
MIC-3D-4OC3OC12-1OC48 |
4 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
MIC-3D-8OC3OC12-4OC48 |
8 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
MIC-3D-4CHOC3-2CHOC12 |
4 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
MIC-3D-8CHOC3-4CHOC12 |
8 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
Channelized OC3/STM1 (Multi-Rate) Circuit Emulation MIC with SFP |
MIC-3D-4COC3-1COC12-CE |
4 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
MIC MRATE (12-Port Multi-Rate MIC with QSFP+) |
MIC-MRATE |
12 |
15.1F5 with Junos Continuity 16.1R1 and later |
15.1F5 with Junos Continuity 16.1R1 and later |
Multi-Rate Ethernet MIC (12-Port Multi-Rate MACsec MIC with QSFP+) |
MIC-MACSEC-MRATE |
12 |
17.4 |
17.4 |
| Tri-Rate | ||||
MIC-3D-40GE-TX |
40 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
| Services | ||||
MS-MIC-16G |
0 |
13.2 |
13.2 |
|
| SONET/SDH | ||||
MIC-3D-1OC192-XFP |
1 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|
MIC Name |
MIC Model Number |
Ports |
MX5 |
MX10 |
MX40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATM | |||||
MIC-3D-8OC3-2OC12-ATM |
8 |
12.1 |
12.1 |
12.1 |
|
| DS3/E3 | |||||
MIC-3D-8DS3-E3, MIC-3D-8CHDS3-E3-B |
8 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
|
| Circuit Emulation | |||||
MIC-3D-16CHE1-T1-CE |
16 |
13.2R2 |
13.2R2 |
13.2R2 |
|
MIC-3D-16CHE1-T1-CE-H |
16 |
— |
— |
— |
|
| Gigabit Ethernet | |||||
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP |
20 |
11.2R4 |
11.2R4 |
11.2R4 |
|
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP-E |
20 |
13.2R2 |
13.2R2 |
13.2R2 |
|
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP-EH |
20 |
— |
— |
— |
|
| 10-Gigabit Ethernet | |||||
MIC-3D-2XGE-XFP |
2 |
11.2R4 |
11.2R4 |
11.2R4 |
|
| Multi-Rate | |||||
MIC-3D-4OC3OC12-1OC48 |
4 |
11.2R4 |
11.2R4 |
11.2R4 |
|
MIC-3D-8OC3OC12-4OC48 |
8 |
11.2R4 |
11.2R4 |
11.2R4 |
|
MIC-3D-4CHOC3-2CHOC12 |
4 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
|
MIC-3D-8CHOC3-4CHOC12 |
8 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
11.4 |
|
Channelized OC3/STM1 (Multi-Rate) Circuit Emulation MIC with SFP |
MIC-3D-4COC3-1COC12-CE |
4 |
12.2 |
12.2 |
12.2 |
Channelized OC3/STM1 (Multi-Rate) Circuit Emulation MIC with SFP (H) |
MIC-4COC3-1COC12-CE-H |
— |
— |
— |
— |
| Tri-Rate | |||||
MIC-3D-40GE-TX |
40 |
— |
11.2R4 |
11.2R4 |
|
| Services | |||||
MS-MIC-16G |
0 |
13.2 Rear slot only. |
13.2 Rear slot only. |
13.2 Rear slot only. |
|
MIC-3D-1OC192-XFP |
1 |
12.2 |
12.2 |
12.2 |
|
MIC Name |
MIC Model Number |
Ports |
MX80 |
MX104 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATM | ||||
MIC-3D-8OC3-2OC12-ATM |
8 |
12.1 |
13.3 |
|
| DS3/E3 | ||||
MIC-3D-8DS3-E3, MIC-3D-8CHDS3-E3-B |
8 |
11.4 |
13.3 |
|
| Circuit Emulation | ||||
MIC-3D-16CHE1-T1-CE |
16 |
13.2R2 |
13.2R2 |
|
MIC-3D-16CHE1-T1-CE-H |
16 |
— |
13.2R2 |
|
| Gigabit Ethernet | ||||
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP |
20 |
10.2 |
13.2R2 |
|
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP-E |
20 |
13.2R2 |
13.2R2 |
|
MIC-3D-20GE-SFP-EH |
20 |
— |
13.2R2 |
|
MIC-MACSEC-20GE |
20 |
18.3 |
18.3 |
|
MIC-3D-2XGE-XFP |
2 |
10.2 |
13.2R2 |
|
| Multi-Rate | ||||
MIC-3D-4OC3OC12-1OC48 |
4 |
11.2 |
13.3 |
|
MIC-3D-8OC3OC12-4OC48 |
8 |
11.2 |
13.3 |
|
MIC-3D-4CHOC3-2CHOC12 |
4 |
11.4 |
13.3 |
|
MIC-3D-8CHOC3-4CHOC12 |
8 |
11.4 |
13.3 |
|
Channelized OC3/STM1 (Multi-Rate) Circuit Emulation MIC with SFP |
MIC-3D-4COC3-1COC12-CE |
4 |
12.2 |
13.2R2 |
Channelized OC3/STM1 (Multi-Rate) Circuit Emulation MIC with SFP (H) |
MIC-4COC3-1COC12-CE-H |
— |
— |
13.2R2 |
| Tri-Rate | ||||
MIC-3D-40GE-TX |
40 |
10.2 |
13.2R2 |
|
| Services | ||||
MS-MIC-16G |
0 |
13.2 Rear slot only. Supported on the modular MX80 and fixed MX80-48T |
13.3R2 Note:
Starting From Junos OS 13.3R3, 14.1R2, and 14.2R1, MX104 supports only two Multiservices MICs. |
|
| SONET/SDH | ||||
MIC-3D-1OC192-XFP |
1 |
12.2 |
13.3 |
|
MIC Name |
MIC Model Number |
Ports |
MX10003 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Rate | |||
MIC MRATE (12-Port Multi-Rate MIC with QSFP+) |
JNP-MIC1 |
12 |
17.3 |
Multi-Rate Ethernet MIC (12-Port Multi-Rate MACsec MIC with QSFP+) |
JNP-MIC1-MACSEC |
12 |
17.3R2 |
See Also
MX240 Modular Interface Card (MIC) LEDs
Each MIC has LEDs located on the faceplate. For more information about LEDs on the MIC faceplate, see the “LEDs” section for each MIC in the MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platform Interface Module Reference.
See Also
MX240 MIC Port and Interface Numbering
Each port on a MIC corresponds to a unique interface name in the CLI.
Fixed configuration MPCs, that is, MPCs with built-in MICs follow the port numbering of DPCs.
In the syntax of an interface name, a hyphen (-)
separates the media type from the MPC number (represented as an FPC in the CLI). The MPC slot
number corresponds to the first number in the interface. The second
number in the interface corresponds to the logical PIC number. The
last number in the interface matches the port number on the MIC. Slashes
(/) separate the MPC number from the logical PIC number
and port number:
type-fpc/pic/port
-
type—Media type, which identifies the network device. For example:
-
ge—Gigabit Ethernet interface
-
so—SONET/SDH interface
-
xe—10-Gigabit Ethernet interface
For a complete list of media types, see Interface Naming Overview.
-
-
fpc—Slot in which the MPC is installed. On the MX240 router, the MPCs are represented in the CLI as
FPC 0throughFPC 2. -
pic—Logical PIC on the MIC, numbered 0 or 1 when installed in slot 0, and 2 or 3 when installed in slot 1. The number of logical PICs varies depending on the type of MIC. For example, a:
-
20-port Gigabit Ethernet MIC has two logical PICs, numbered 0 and 1 when installed in slot 0, or 2 and 3 when installed in slot 1.
-
4-port 10-Gigabit Ethernet MIC has two logical PICs numbered 0 and 1 when installed in slot 0, or 2 and 3 when installed in slot 1.
-
100-Gigabit Ethernet MIC with CFP has one logical PIC numbered 0 when installed in slot 0, or 2 when installed in slot 1.
For more information on specific MICs, see MICs Supported by MX Series Routers in the MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platform Interface Module Reference.
-
-
port—Port number.
The MIC number is not included in the interface name.
The MX240 router supports up to three MPCs that install horizontally and are numbered from bottom to top. Each MPC accepts up to two MICs.
Figure 7 shows
an example of a 20-port Gigabit Ethernet MIC with SFP installed in
slot 0 of an MPC in slot 2.
The 20-port Gigabit Ethernet MIC with SFP-E has a different port numbering. See Gigabit Ethernet MIC with SFP (E)

The MIC contains two logical PICs, numbered PIC 0 through PIC 1 in the CLI. Each logical PIC contains 10
ports numbered 0 through 9.
The show chassis hardware command output displays
a 20-port Gigabit Ethernet MIC with SFP — 3D 20x 1GE(LAN)
SFP — installed in slot 0 of
an MPC in slot 2. The MPC (MPC Type 2 3D
EQ) is shown as FPC 2 in
the CLI. The MIC’s two logical PICs — 10x
1GE(LAN) SFP — are shown as PIC
0 and PIC 1.
user@host> show chassis hardware
...
FPC 2 REV 28 750-031090 YH8181 MPC Type 2 3D EQ
CPU REV 06 711-030884 YH9437 MPC PMB 2G
MIC 0 REV 22 750-028392 YD0439 3D 20x 1GE(LAN) SFP
PIC 0 BUILTIN BUILTIN 10x 1GE(LAN) SFP
Xcvr 0 REV 01 740-011613 PCE14D5 SFP-SX
Xcvr 1 REV 01 740-011782 P9C280T SFP-SX
Xcvr 2 REV 01 740-011782 P9C2512 SFP-SX
Xcvr 3 REV 02 740-011613 AM0951SFF3Z SFP-SX
Xcvr 4 REV 02 740-011613 AM0951SFF33 SFP-SX
Xcvr 5 REV 02 740-011613 AM0951SFF3Y SFP-SX
Xcvr 6 REV 02 740-011613 AM0951SFF4B SFP-SX
Xcvr 7 REV 01 740-011613 E08H01273 SFP-SX
Xcvr 8 REV 02 740-011613 AM0951SFFWK SFP-SX
PIC 1 BUILTIN BUILTIN 10x 1GE(LAN) SFP
Xcvr 0 REV 01 740-011613 E08H00516 SFP-SX
Xcvr 1 REV 01 740-011613 E08G03648 SFP-SX
Xcvr 2 REV 01 740-011613 E08H00514 SFP-SX
... The show interfaces terse command output displays
the Gigabit Ethernet interfaces that correspond to the 20 ports located
on the MIC.
user@host> show interfaces terse ge-2* Interface Admin Link Proto Local Remote ge-2/0/0 up down ge-2/0/1 up down ge-2/0/2 up down ge-2/0/3 up up ge-2/0/4 up up ge-2/0/5 up up ge-2/0/6 up up ge-2/0/7 up up ge-2/0/8 up up ge-2/0/9 up down ge-2/1/0 up up ge-2/1/1 up up ge-2/1/2 up up ge-2/1/3 up down ge-2/1/4 up down ge-2/1/5 up down ge-2/1/6 up down ge-2/1/7 up down ge-2/1/8 up down ge-2/1/9 up down
See Also
MX240 Modular Port Concentrator (MPC) Description
Modular Port Concentrators (MPCs) provide packet forwarding services. The MPCs are inserted into a slot in a router. Modular Interface Cards (MICs) provide the physical interfaces and install into the MPCs. You can install up to two MICs of different media types on the same router as long as the router supports those MICs.
A specialized fixed configuration MPC provides higher port density over MICs and combines packet forwarding and Ethernet interfaces onto a single line card. The fixed configuration MPC is inserted into a slot in a router and contains no slots for MICs.
MICs receive incoming packets from the network and transmit outgoing packets to the network. During this process, each MIC performs framing and high-speed signaling for its media type. Before transmitting outgoing data packets through the MIC interfaces, the MPCs encapsulate the packets received. Each MPC is equipped with up to four Junos Trio chipsets, which perform control functions tailored to the MPC’s media type. The MPCs interface with the power supplies and Switch Control Boards (SCBs). You must install redundant SCBs to support full line-rate.
The MX240 router supports up to three MPCs. You must install a high-capacity fan tray to use an MPC. For power requirements, see Calculating Power Requirements for MX240 Routers.
The router has two dedicated line card slots for DPCs, MPCs, or FPCs. MPCs install horizontally in the front of the router (see Figure 8). One multifunction slot numbered 1/0 supports either one line card or one SCB. The line card slots are numbered 1/0, 1, and 2, bottom to top. An MPC can be installed in any slot on the router that supports MPCs. You can install any combination of line card types in the router.
When a slot is not occupied by an MPC or other line card, you must insert a blank DPC panel to fill the empty slot and ensure proper cooling of the system.
MPCs are hot-removable and hot-insertable. When you install an MPC in an operating router, the Routing Engine downloads the MPC software, the MPC runs its diagnostics, and the Packet Forwarding Engines housed on the MPC are enabled. Forwarding on other MPCs continues uninterrupted during this process.
Figure 8 shows a typical MPC supported on the MX240 router. Figure 9 shows an MPC installed horizontally in the MX240 Router. For more information about MPCs, see the MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platform Interface Module Reference.

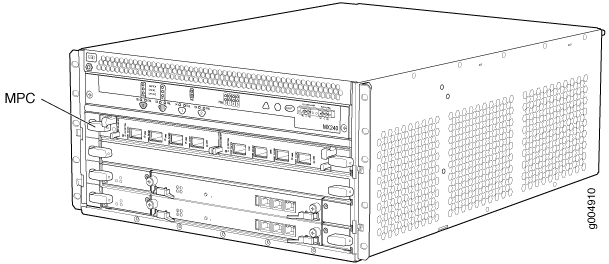
MPC Components
Each MPC consists of the following components:
MPC card carrier, which includes two MIC slots (excludes the fixed configuration MPC).
Fabric interfaces.
Two Gigabit Ethernet interfaces that allow control information, route information, and statistics to be sent between the Routing Engine and the CPU on the MPCs.
Two interfaces from the SCBs that enable the MPCs to be powered on and controlled.
Physical MPC connectors.
Up to four Junos Trio chipsets, which perform control functions tailored to the MPC’s media type.
Midplane connectors and power circuitry.
Processor subsystem, which includes a 1.5-GHz CPU, system controller, and 1 GB of SDRAM.
Online button which takes the MPC online or offline when pressed.
OK/Fail LED on the MPC faceplate. For more information about LEDs on the MPC faceplate, see the MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platform Interface Module Reference.
Two LEDs, located on the craft interface above the MPC, display the status of the line cards and are labeled OK and FAIL.
See Also
MX240 Modular Port Concentrator (MPC) LEDs
Two LEDs, located on the craft interface above the MPC, display the status of the line cards and are labeled OK and FAIL. For more information about the line card LEDs on the craft interface, see MX240 Component LEDs on the Craft Interface.
Each MPC also has LEDs located on the faceplate. For more information about LEDs on the MPC faceplate, see the “LEDs” section for each MPC in the MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platform Interface Module Reference.
See Also
MPCs Supported by MX Series Routers
MPCs Supported by MX240, MX480, MX960, MX10003, MX10004, MX10016, MX2008, MX2010, and MX2020 Routers lists the MPCs and their first supported Junos OS release on MX240, MX480, MX960, MX10003, MX10004, and MX10016, MX2008, MX2010, and MX2020 routers.
|
MPC Name |
MPC Model Number |
First Junos OS Release on MX240, MX480, and MX960 Routers |
First Junos OS Release on MX10003 Routers |
First Junos OS Release on MX10004 Routers |
First Junos OS Release on MX10008 Routers |
First Junos OS Release on MX10016 Routers |
First Junos OS Release on MX2008 Routers |
First Junos OS Release on MX2010 Routers |
First Junos OS Release on MX2020 Routers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Configuration MPCs | |||||||||
|
MPC-3D- 16XGE-SFP |
10.0R2 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|||
|
MS-MPC |
13.2R4 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
15.1 |
15.1 |
|||
|
MPC4E-3D- 32XGE-SFPP |
12.3R2 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
12.3R2 |
12.3R2 |
|||
|
MPC4E-3D- 2CGE-8XGE |
12.3R2 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
12.3R2 |
12.3R2 |
|||
|
MPC5E-40G10G |
13.3R2 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
13.3R2 |
13.3R2 |
|||
|
MPC5EQ-40G10G |
13.3R2 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
13.3R2 |
13.3R2 |
|||
|
MPC5E-100G10G |
13.3R3 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
13.3R3 |
13.3R3 |
|||
|
MPC5EQ-100G10G |
13.3R3 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
13.3R3 |
13.3R3 |
|||
|
MPC7E-MRATE |
|
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
|
|
|||
|
MPC7E-10G |
|
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
|
|
|||
|
MPC10E-10C-MRATE |
19.2R1 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|||
|
MPC10E-15C-MRATE |
19.1R1 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|||
|
MX2K-MPC11E |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
|||
|
MX-MPC1-3D |
10.2 |
MPCs |
15.1F7 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
||||
|
MX-MPC1E-3D |
11.2R4 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|||
|
MX-MPC1-3D-Q |
10.2 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|||
|
MX-MPC1E-3D-Q |
11.2R4 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|||
|
MX-MPC2-3D |
10.1 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|||
|
MX-MPC2E-3D |
11.2R4 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|||
|
MX-MPC2-3D-Q |
10.1 |
– |
15.1F7 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
||||
|
MX-MPC2E-3D-Q |
11.2R4 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|||
|
MX-MPC2-3D-EQ |
10.1 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|||
|
MX-MPC2E-3D-EQ |
11.2R4 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|||
|
MX-MPC2E-3D-P |
12.2 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|||
|
MX-MPC2E-3D-NG |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 and Junos Continuity 15.1 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 and Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 and Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|||
|
MX-MPC2E-3D-NG-Q |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 and Junos Continuity 15.1 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 and Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 and Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|||
|
MX-MPC3E-3D |
12.1 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
12.3 |
12.3 |
|||
|
MX-MPC3E-3D-NG |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 and Junos Continuity 15.1 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 and Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 and Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|||
|
MX-MPC3E-3D-NG-Q |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 and Junos Continuity 15.1 |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 and Junos Continuity 15.1 |
14.1R4, 14.2R3 and Junos Continuity 15.1 |
|||
|
MX2K-MPC6E |
– |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
13.3R2 |
13.3R2 |
|||
|
MX2K-MPC8E |
– |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
|
|
|||
|
MX2K-MPC9E |
– |
– |
– |
15.1F7 |
|
|
|||
|
MX10003-LC2103 |
– |
17.3R1 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|||
|
MX10003-LC2103-V2 |
– |
21.3R1 |
– |
– |
– |
||||
|
MX10K-LC2101 |
JNP10K-LC2101 |
- |
- |
22.3R1 |
18.2R1 |
19.2R1 |
- |
- |
- |
|
MX10K-LC480 |
JNP10K-LC480 |
- |
- |
22.3R1 |
21.2R1 |
21.2R1 |
- |
- |
- |
|
MX10K-LC9600 |
JNP10K-LC9600 |
- |
- |
22.3R1 |
21.4R1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
MX10K-LC4800 |
JNP10K-LC4800 |
- |
- |
24.2R1 |
24.2R1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
MX10K-LC4802 |
JNP10K-LC4802 |
25.2R1 |
25.2R1 |
||||||
| Services Processing Cards (SPCs) | |||||||||
|
MX-SPC3 Services Card |
JNP-SPC3 |
19.3R2 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
See Also
MX240 Application Services Modular Line Card Description
The Application Services Modular Line Card (AS MLC) is an X86-based card for MX960, MX480, and MX240 routers to deliver integrated application service solutions. See Figure 10. The first application that network operators can take advantage of is the Junos Content Encore system, a high-throughput, solid state storage platform for media rich content delivery. Additionally, the AS MLC can serve as the platform for Juniper Networks JunosV App Engine, powering a host of network applications directly embedded into your MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platforms.
AS MLC is modular and decouples CPU and storage in individual field-upgradeable units. The AS MLCs are designed to enable application throughput up to 50 Gbps and a storage capacity of 400 gigabytes (GB) of NAND Flash.

- MX240 AS MLC Function
- AS MLC Components
- MX240 SCB, Power Supply, and Cooling System Requirements for AS MLC
MX240 AS MLC Function
The AS MLC provides modular processing and modular storage. Installed on the AS MLC, the Junos Content Encore system operates as a caching application, in either HTTP reverse proxy mode or HTTP transparent proxy mode, to manage client requests for content and the distribution of the content to clients from origin servers. In the future, AS MLC will run other Juniper Networks router services and applications as well as serve as a virtualized platform for third-party applications. AS MLC provides Ethernet switching and high-speed fabric interface to MX routers. Graceful Routing Engine switchover is also supported on the AS MLC.
Integrated with application forwarding on MX Series routers, the AS MLC provides increased service flexibility with reduced power and space requirements for the network infrastructure.
AS MLC Components
Each AS MLC consists of the following components:
AS MLC Modular Carrier Card (AS MCC), which fits horizontally in front of the MX240 router, includes two slots for the Application Services Modular Storage Card (AS MSC) and Application Services Modular Processing Card (AS MXC)
AS MXC with 64 GB RAM for processing
AS MSC with 400 GB NAND Flash capacity for modular storage
Note:The AS MCC, AS MXC, and AS MSC are hot-removable and hot-insertable
Switch fabric interfaces to the chassis
XM ASIC chip, which owns and manages the packet data memory built from external DDR3 memory chips, the fabric queuing system, a portion of the WAN queuing system, and the host queuing system
LU ASIC chip, which performs all functions relating to header processing including input processing, route lookup, classification, filtering, policing, accounting, encapsulation, and statistics
Midplane connectors and power circuitry
Processor Mezzanine Board (PMB), which contains the host processor and supporting peripherals.
LED on the AS MCC, which displays the status of the AS MLC
MX240 SCB, Power Supply, and Cooling System Requirements for AS MLC
Each MX240 router requires specific SCB, power supply, and cooling system models to run the AS MLC:
SCB—Enhanced MX Switch Control Board (SCBE-MX). See MX240 SCBE-MX Description for details
Power supply:
2520W AC power supply—Model PWR-MX480-2520-AC
2400W DC power supply—Model PWR-MX480-2400-DC
Power requirement for AS MLC:
AS MCC—191W
AS MXC—259W
AS MSC—50W
Cooling system—Required fans and fan tray models:
Fans:
For AC power supply: PWR-FAN-MX240-ACH-HC-U and PWR-MX240-ACL-HC-U
For DC power supply: PWR-FAN-MX2400-DC-HC-U
Fan tray—FFANTRAY-MX240-HC
See Also
MX240 AS MSC LEDs
Two LEDs (CPU and AP) indicate the status of the AS MSC and are located on the AS MSC. Table 17 describes the functions of the AS MSC LEDs.
Label |
Color |
State |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
CPU |
Green |
On steadily |
AS MSC operates normally. |
Red |
On steadily |
AS MSC has an error or has failed. |
|
– |
Off |
AS MSC is offline. |
|
AP |
Green |
On steadily |
AS MSC storage operation is normal. |
Red |
On steadily |
AS MSC storage operation has an error. |
|
– |
Off |
AS MSC storage operation is not activated. |
See Also
MX240 Application Services Modular Processing Card Description
The Application Services Modular Processing Card (AS MXC) is a pluggable X86-based card that can be inserted into the lower slot of the Application Services Modular Line Card (AS MLC). The AS MXC serves as the processing card for the Junos Content Encore system and contains the two X86, Intel 8-core processors with interface ability greater than 80 Gbps. The AS MXC (see Figure 11) is equivalent to a PIC or MIC (Modular Interface Card).
AS MXCs are hot-removable and hot-insertable. One MXC can be installed in the lower slot of each AS MLC. Each MXC has these components:
Two 8-core Intel processors—Contains eight execution cores with Ring Interconnect architecture. Each core supports two threads, up to 16 threads per socket.
64 GB DRAM—On DIMM sockets.
LEDs—Two LEDs on the faceplate display the CPU and application status.

See Also
MX240 AS MXC LEDs
Two LEDs (CPU and AP) indicate the status of the AS MXC and are located on the AS MXC. Table 18 describes the functions of the AS MXC LEDs.
Label |
Color |
State |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
CPU |
Green |
On steadily |
AS MXC operates normally. |
Red |
On steadily |
AS MXC has an error or has failed. |
|
– |
Off |
AS MXC is offline. |
|
AP |
Green |
On steadily |
AS MXC applications operation is normal. |
Red |
On steadily |
AS MXC applications operation has an error. |
|
– |
Off |
AS MXC applications are not activated. |
