Point-to-Multipoint RIP Networks
Configuring Point-to-Multipoint RIP Networks Overview
A point-to-multipoint RIP network consists of a device having two or more peers on a single interface. All the devices forming a point-to-multipoint connection are placed in a single broadcast domain.
In a RIP network, a device can have a single peer or multiple peers for an interface. However, the demand circuit feature implementation in a RIP network requires the use of a single RIP peer. When you configure the following statements, a RIP network with demand circuits can also be configured to have multiple peers on an interface:
Configuring the interface type to be a multipoint interface by using the
interface-type (Protocols RIP) p2mpstatement.Enabling dynamic peer discovery by using the
dynamic-peersstatement (SRX Series Firewalls only).Note:Before configuring the
dynamic-peersstatement, IPsec must be configured and IPsec tunnels must be set up by configuring IPsec parameters. Without IPsec configuration, the remote peers have to be explicitly configured at the RIP protocol level by using thepeer addressstatement. See Configuring Security Associations for IPsec on an ES PIC for more details.Configuring peers by using the
peer addressstatement.[edit] protocols { rip { group red { neighbor fe-0/1/3 { interface-type (Protocols RIP) p2mp; peer address; (or use dynamic-peers;) } } } }
The show rip statistics peer address command can be used to display
the RIP statistics at the peer level. The clear rip statistics peer address command can be used to clear the RIP statistics
for a peer. Alternatively, you can use the show rip statistics peer all and clear rip statistics peer all command to display and clear RIP statistics for all peers.
Example: Configuring Point-to-Multipoint RIP Networks
This example shows how to configure a point-to-multipoint RIP network.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
M Series routers, MX Series routers, T Series routers, or SRX Series Firewalls
Junos OS Release 12.1 or later
Overview
In a RIP network, a device can have a single peer or multiple peers for an interface. However, the demand circuit feature implementation in a RIP network requires the use of a single RIP peer.
When you include the following statements, the demand circuit implementation can have multiple peers for a given RIP neighbor.
Configuring the interface type to be a multipoint interface by using the
interface-type (Protocols RIP) p2mpstatement.Enabling dynamic peer discovery by using the dynamic-peers statement (SRX Series Firewalls only).
Note:To configure the
dynamic-peersstatement, IPsec tunnels must be set up by configuring IPsec parameters. See Configuring Security Associations for IPsec on an ES PIC for more details.Configuring peers by using the
peer addressstatement.[edit] protocols { rip { group red { neighbor fe-0/1/3 { interface-type (Protocols RIP) p2mp; peer address; (or use dynamic-peers;) } } } }
The show rip statistics peer command can be used to display the RIP statistics at
the peer level.
Topology
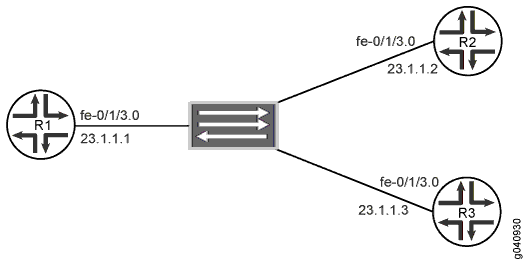
In this example, Devices R1, R2, and R3 form a point-to-multipoint
network. R1 is connected to R2 and to R3 as a point-to-multipoint
connection through a switch that places all devices in the same broadcast
domain. RIP demand circuits are configured on all three devices. The
two peers to R1 are configured statically by using the peer address statement. The dynamic-peers statement is not used here.
Figure 1 shows the topology used in this example.
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Device R1
set interfaces fe-0/1/3 unit 0 family inet address 23.1.1.1/24 set policy-options policy-statement accept-rip-routes term from-direct from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement accept-rip-routes term from-direct then accept set policy-options policy-statement accept-rip-routes term from-rip from protocol rip set policy-options policy-statement accept-rip-routes term from-rip then accept set protocols rip traceoptions file R1.log size 4m world-readable set protocols rip traceoptions flag all detail set protocols rip group red export accept-rip-routes set protocols rip group red neighbor fe-0/1/3.0 interface-type p2mp set protocols rip group red neighbor fe-0/1/3.0 peer 23.1.1.2 set protocols rip group red neighbor fe-0/1/3.0 peer 23.1.1.3 set protocols rip group red neighbor fe-0/1/3.0 demand-circuit set protocols rip group red neighbor fe-0/1/3.0 max-retrans-time 10
Similarly, configure Devices R2 and R3, omitting the peer address configuration statement.
Configuring a Point-to-Multipoint RIP Network (with Demand Circuits)
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires that you navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the CLI User Guide.
To configure the point-to-multipoint feature across a RIP network:
Configure the device interface.
[edit interfaces fe-0/1/3 unit 0] user@R1# set family inet address 23.1.1.1/24
Define a policy for exporting RIP routes from the routing table to the protocol for transmission through the network.
[edit policy-options policy-statement accept-rip-routes] user@R1# set term from-direct from protocol direct user@R1# set term from-direct then accept user@R1# set term from-rip from protocol rip user@R1# set term from-rip then accept
Configure RIP and a RIP group with the defined export policy and point-to-multipoint configuration statements.
[edit protocols rip] user@R1# set traceoptions file R1.log size 4m world-readable user@R1# set traceoptions flag all detail user@R1# set group red export accept-rip-routes user@R1# set group red neighbor fe-0/1/3.0 interface-type p2mp user@R1# set group red neighbor fe-0/1/3.0 peer 23.1.1.2 user@R1# set group red neighbor fe-0/1/3.0 peer 23.1.1.3 user@R1# set group red neighbor fe-0/1/3.0 demand-circuit user@R1# set group red neighbor fe-0/1/3.0 max-retrans-time 10
Similarly, configure Devices R2 and R3, omitting the peer address configuration statement.
Note:Configuring max-retrans-time is optional. In the absence of this configuration statement, the default retransmission time of 180 seconds is configured.
The configuration used in this example is for a RIP network with demand circuits. To configure RIP for networks without demand circuits, exclude the demand-circuit and
max-retrans-timestatements from the configuration and check the resulting output. For more information about configuring RIP demand circuits, see Example: Configuring RIP Demand Circuits.
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show interfaces, show policy-options, and show protocols rip commands. If the output does
not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in
this example to correct the configuration.
[edit]
user@R1# show interfaces
fe-0/1/3 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 23.1.1.1/24;
}
}
}
user@R1# show protocols rip
traceoptions {
file R1.log size 4m world-readable;
flag all detail;
}
group red {
export accept-rip-routes;
neighbor fe-0/1/3.0 {
interface-type p2mp;
peer 23.1.1.2;
peer 23.1.1.3;
demand-circuit;
max-retrans-time 10;
}
}
user@R1# show policy-options
policy-statement accept-rip-routes {
term from-direct {
from protocol direct;
then accept;
}
term from-rip {
from protocol rip;
then accept;
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
Verifying the Point-to-Multipoint RIP Network
Purpose
Verify that the RIP network is functional with the point-to-multipoint feature configured.
Action
From operational mode, run the show rip neighbor command.
user@R1> show rip neighbor
Local Source Destination Send Receive In
Neighbor State Address Address Mode Mode Met
-------- ----- ------- ----------- ---- ------- ---
fe-0/1/3.0(DC) Up 23.1.1.1 23.1.1.2 unicast unicast 1
fe-0/1/3.0(DC) Up 23.1.1.1 23.1.1.3 unicast unicast 1
From operational mode, run the show rip statistics
peer address command.
user@R1> show rip statistics peer 23.1.1.2
RIPv2 info: port 520; holddown 120s.
rts learned rts held down rqsts dropped resps dropped
3 0 0 0
fe-0/1/3.0 Peer-Ip 23.1.1.2: 2 routes learned; 3 routes advertised; timeout 180s; update interval 0s
Counter Total Last 5 min Last minute
------- ----------- ----------- -----------
Updates Sent 0 0 0
Triggered Updates Sent 3 0 0
Responses Sent 0 0 0
Bad Messages 0 0 0
RIPv1 Updates Received 0 0 0
RIPv1 Bad Route Entries 0 0 0
RIPv1 Updates Ignored 0 0 0
RIPv2 Updates Received 2 0 0
RIPv2 Bad Route Entries 0 0 0
RIPv2 Updates Ignored 0 0 0
Authentication Failures 0 0 0
RIP Requests Received 0 0 0
RIP Requests Ignored 0 0 0
none 3 0 0
user@R1> show rip statistics peer 23.1.1.3
RIPv2 info: port 520; holddown 120s.
rts learned rts held down rqsts dropped resps dropped
3 0 0 0
fe-0/1/3.0 Peer-Ip 23.1.1.3: 2 routes learned; 3 routes advertised; timeout 180s; update interval 0s
Counter Total Last 5 min Last minute
------- ----------- ----------- -----------
Updates Sent 0 0 0
Triggered Updates Sent 3 0 0
Responses Sent 0 0 0
Bad Messages 0 0 0
RIPv1 Updates Received 0 0 0
RIPv1 Bad Route Entries 0 0 0
RIPv1 Updates Ignored 0 0 0
RIPv2 Updates Received 2 0 0
RIPv2 Bad Route Entries 0 0 0
RIPv2 Updates Ignored 0 0 0
Authentication Failures 0 0 0
RIP Requests Received 0 0 0
RIP Requests Ignored 0 0 0
none 3 0 0
Meaning
The RIP network is up and running with the point-to-multipoint feature configured.
