Understanding 802.1X and VoIP on MX Series Routers in Enhanced LAN Mode
When you use Voice over IP (VoIP), you can connect IP telephones to the router and configure IEEE 802.1X authentication for 802.1X-compatible IP telephones. 802.1X authentication provides network edge security, protecting Ethernet LANs from unauthorized user access.
VoIP is a protocol used for the transmission of voice through packet-switched networks. VoIP transmits voice calls using a network connection instead of an analog phone line.
When VoIP is used with 802.1X, the RADIUS server authenticates the phone, and Link Layer Discovery Protocol–Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED) provides the class-of-service (CoS) parameters to the phone.
You can configure 802.1X authentication to work with VoIP in multiple supplicant or single supplicant mode. In multiple-supplicant mode, the 802.1X process allows multiple supplicants to connect to the interface. Each supplicant will be authenticated individually. For an example of a VoIP multiple supplicant topology, see Figure 1.
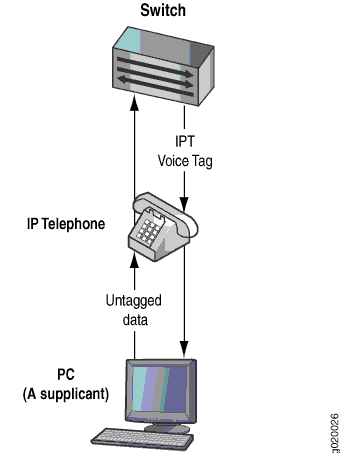
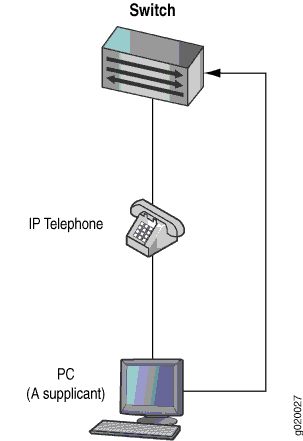
If an 802.1X-compatible IP telephone does not have an 802.1X host but has another 802.1X-compatible device connected to its data port, you can connect the phone to an interface in single-supplicant mode. In single-supplicant mode, the 802.1X process authenticates only the first supplicant. All other supplicants who connect later to the interface are allowed full access without any further authentication. They effectively “piggyback” on the first supplicant’s authentication. For an example of a VoIP single supplicant topology, see Figure 2 .
If an IP telephone does not support 802.1X, you can configure VoIP to bypass 802.1X and LLDP-MED and have the packets forwarded to a VoIP VLAN,
