CSDS Overview
Read this topic to learn about the Juniper’s Connected Security Distributed Services (CSDS) Architecture and benefits.
Juniper’s Connected Security Distributed Services (CSDS) Architecture provides a scalable, distributed security architecture design that decouples the forwarding and security services layers. The distributed framework enables existing Juniper Networks® MX Series routers to operate as intelligent forwarding engines and load balancers with path redundancy capability.
Figure 1: CSDS Architecture
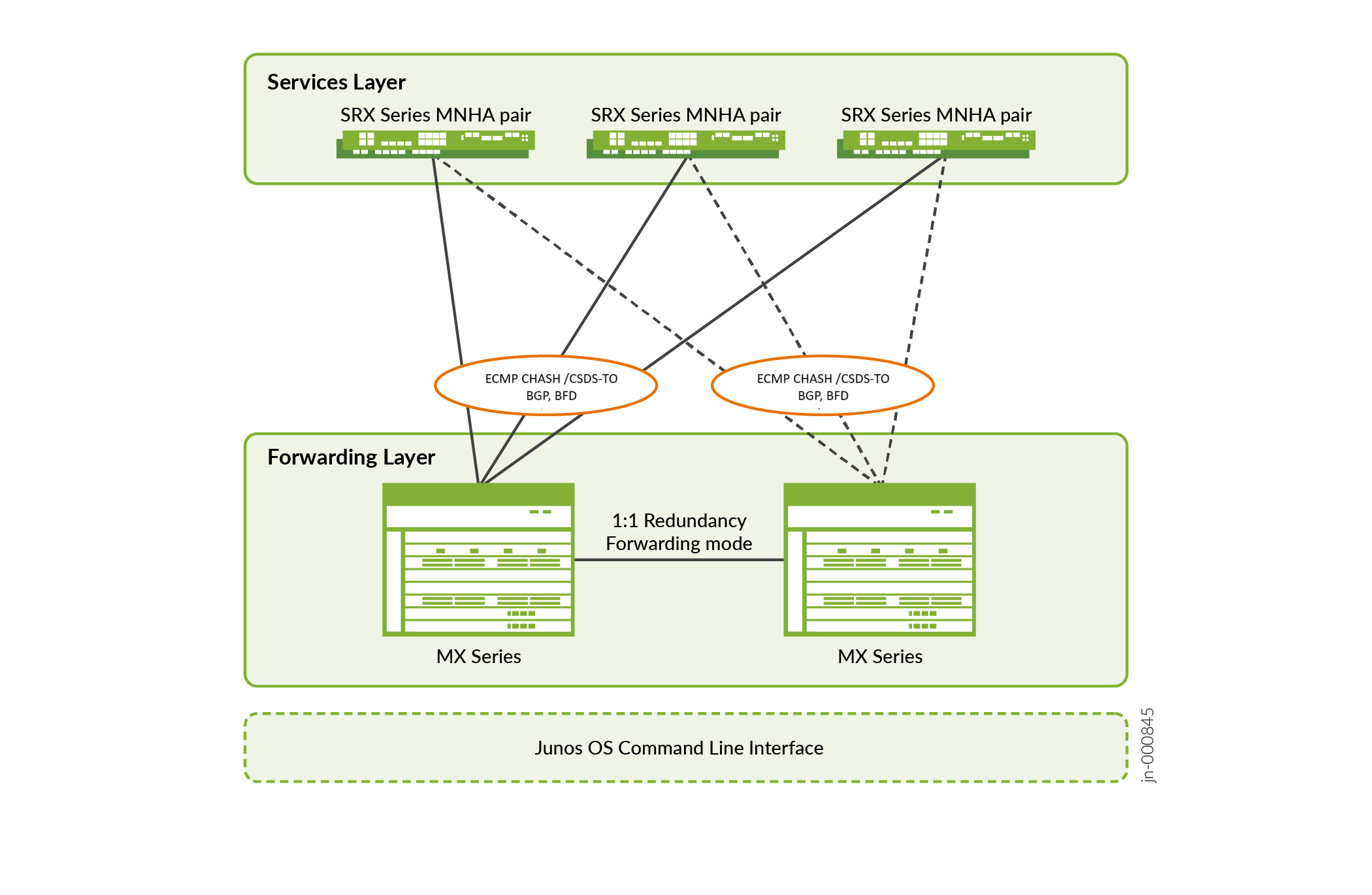

Benefits
- Scalability: Scale the topology horizontally and elastically as needed, without being constrained by chassis limitations. All distributed firewalls function together as a fabric, enabling automated resiliency with multipath redundancy. If one of the devices fail, others automatically load-balance the service.
- Simplicity: Manage all distributed firewall engines as a single logical element, regardless of the firewall count. Deployment is simple and similar to adding virtual service cards to a chassis, allowing for easy integration at each site.
- Flexibility: Decouple forwarding and services layers, enabling the two layers to scale independently. With this modular approach, you can adjust the size of the security solution depending on your deployment and combine different form factors. Additionally, you can continue to use the existing SRX Series Firewalls in the new architecture, ensuring that the processes and policies remain intact.
