IPsec VPN Traffic Flow in Single MX Series Router (CSDS Traffic Orchestrator) and Scaled-Out SRX Series Firewalls
In this topic, you’ll see how IPsec traffic flows in a single MX Series router with CSDS Traffic Orchestrator and SRX Series Firewalls.
See Figure 1 for the topology. In this topology:
- Configure a single MX Series router with two interfaces, one each for the IPSEC VR and INTERNET routing instances. MX Series CSDS Traffic Orchestrator (CSDS-TO) performs health check on all the scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls and builds the next hop for traffic load balancing.
- Use BGP to connect all the scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls to the MX Series router.
-
Configure the MX Series router with CSDS-TO on the IPSEC VR routing instance to load-balance the data traffic coming from client-side gateway router toward the scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls.
-
Configure a unique IKE proposal, IKE policy, IPsec proposal, and IPsec policy per each MNHA pair.
-
Configure a unique IP address for each of the scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls connected to the MX Series router. The TLB uses these addresses to perform the health check and build the selector table in the Packet Forwarding Engine. The Packet Forwarding Engine uses this selector table to load-balance the packet across the available next hops. The health check packets are reachable through the BGP connection. The anycast IP address used for the IKE endpoint is reachable through this unique IP address on each of the SRX Series Firewalls.
- Configure all the scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls for AutoVPN with the same anycast IP address as the IKE endpoint. All SRX Series Firewalls are in IPsec VPN responder-only mode.
- The IPsec VPN clients initiated behind the MX Series router use the same SRX Series Firewall’s IKE endpoint with unique traffic selectors. The SRX Series Firewalls use the traffic selector to install unique Auto Route Insertion (ARI) routes to invite the data return traffic to the right IPsec VPN tunnel from the server.
-
Configure the MX Series router with CSDS-TO on the IPSEC VR routing instance to load-balance the IKE traffic coming from the MX Series router toward the scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls.
Figure 1 illustrates the step-by-step traffic flow.
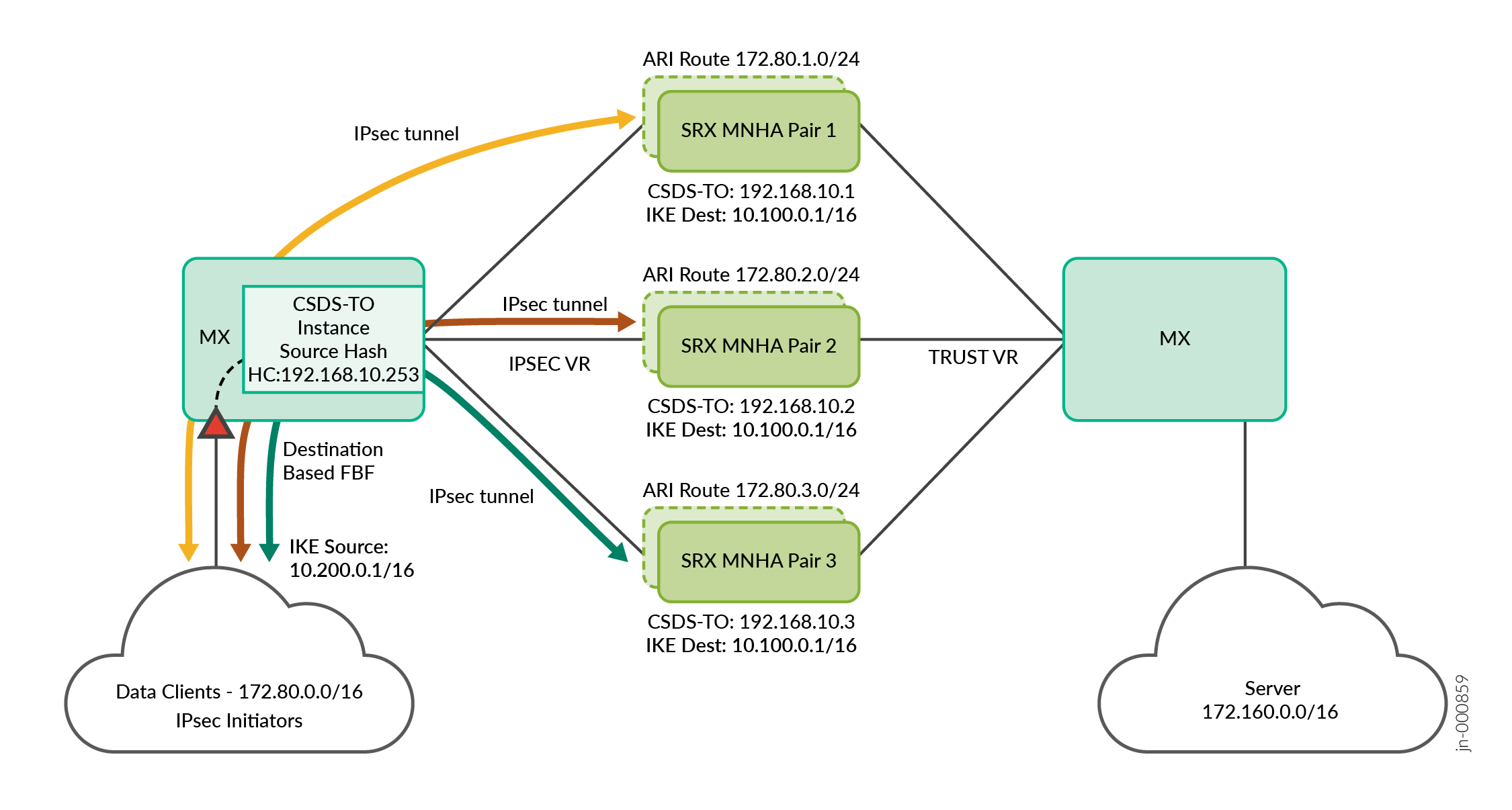
The MX Series router is a single device configured with multiple logical interfaces toward scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls on the IPSEC VR and Internet directions.
Filter-based forwarding (FBF) based on IKE destination IP address match is used in MX Series router to push IPsec VPN traffic to the CSDS-TO IPsec forwarding instance. CSDS-TO forwarding instance includes a default route with next-hop as list of SRX Series Firewalls. CSDS-TO installs this default route when the health check passes for at least one SRX Series Firewalls.
CSDS-TO performs source-based hash load balancing across all the available SRX Series Firewall next-hop devices.
Load-balanced IPsec VPN tunnel sessions anchor on any available SRX Series Firewalls and installs the ARI route.
The SRX Series Firewall decrypts the packets, routes the cleartext packets to the server over the Internet routing instance.
Unique ARI routes handle return traffic from the server to the client on the MX Series Internet routing instance. These routes ensure the traffic returns to the same SRX Series Firewalls anchoring the IPsec VPN tunnel.
The SRX Series Firewalls use the same IPsec VPN tunnel session to encrypt the packet and route the IPsec VPN traffic toward MX Series router on the IPSEC VR direction.
The MX Series routes the IPsec VPN traffic back to IPsec VPN Initiators.
For more information, see Scale-Out IPsec Solution for Enterprises — Juniper Validated Design (JVD), and Scale-Out IPsec Solution for Mobile Service Providers — Juniper Validated Design (JVD).
