NAT Traffic Flow in Single MX Series (CSDS Traffic Orchestrator) and Scaled-Out SRX Series Firewalls
In this topic, you’ll see how NAT traffic flows in a single MX Series with CSDS Traffic Orchestrator and SRX Series Firewalls.
See Figure 1 for the topology. In this topology for NAT traffic:
- Configure a single MX Series router with two interfaces logical interfaces (IFL) for TRUST and UNTRUST routing instances. The MX Series CSDS Traffic Orchestrator (CSDS-TO) performs health check on all the scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls and builds the next-hop for load balancing the traffic.
- Connect all the scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls to the MX Series router with BGP connections.
-
Configure the MX Series router with CSDS-TO on the TRUST routing instance. CSDS-TO performs the load balancing of data traffic coming from client-side gateway router toward the scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls.
-
Each scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls must have a unique NAT pool range, advertised toward the MX Series UNTRUST direction.
-
Configure unique IP addresses for all the scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls connected to MX Series router. CSDS-TO uses the IP addresses to perform the health check and build the selector table in the Packet Forwarding Engine. The Packet Forwarding Engine uses this selector table to load-balance the packet across the available next-hops. This health check is reachable through the BGP connection.
-
The filter-based forwarding (FBF) on source IP address match is used in the MX Series router to push the NAT specific traffic to the CSDS-TO TRUST forwarding instance.
-
The CSDS-TO forwarding instance has a default route with next-hop as list of SRX Series Firewalls. CSDS-TO installs this default route when its health check passes with at least one SRX Series Firewalls.
-
CSDS-TO does source-based hash load balancing across all the available SRX Series Firewall next-hop devices.
-
Any available SRX Series Firewall anchors load-balanced NAT data sessions and creates the NAT flow. Then the MX Series router forwards traffic through the UNTRUST routing instance to reach the server.
-
For the return traffic coming from server to client direction on the MX Series UNTRUST routing instance, unique NAT pool routes are used to route the traffic to the same SRX Series Firewalls.
-
The SRX Series Firewalls use same NAT flow to process the return traffic and route the packet toward MX Series router on the TRUST direction. The MX Series routes the packet back to the client.
Figure 1 illustrates the step-by-step traffic flow.
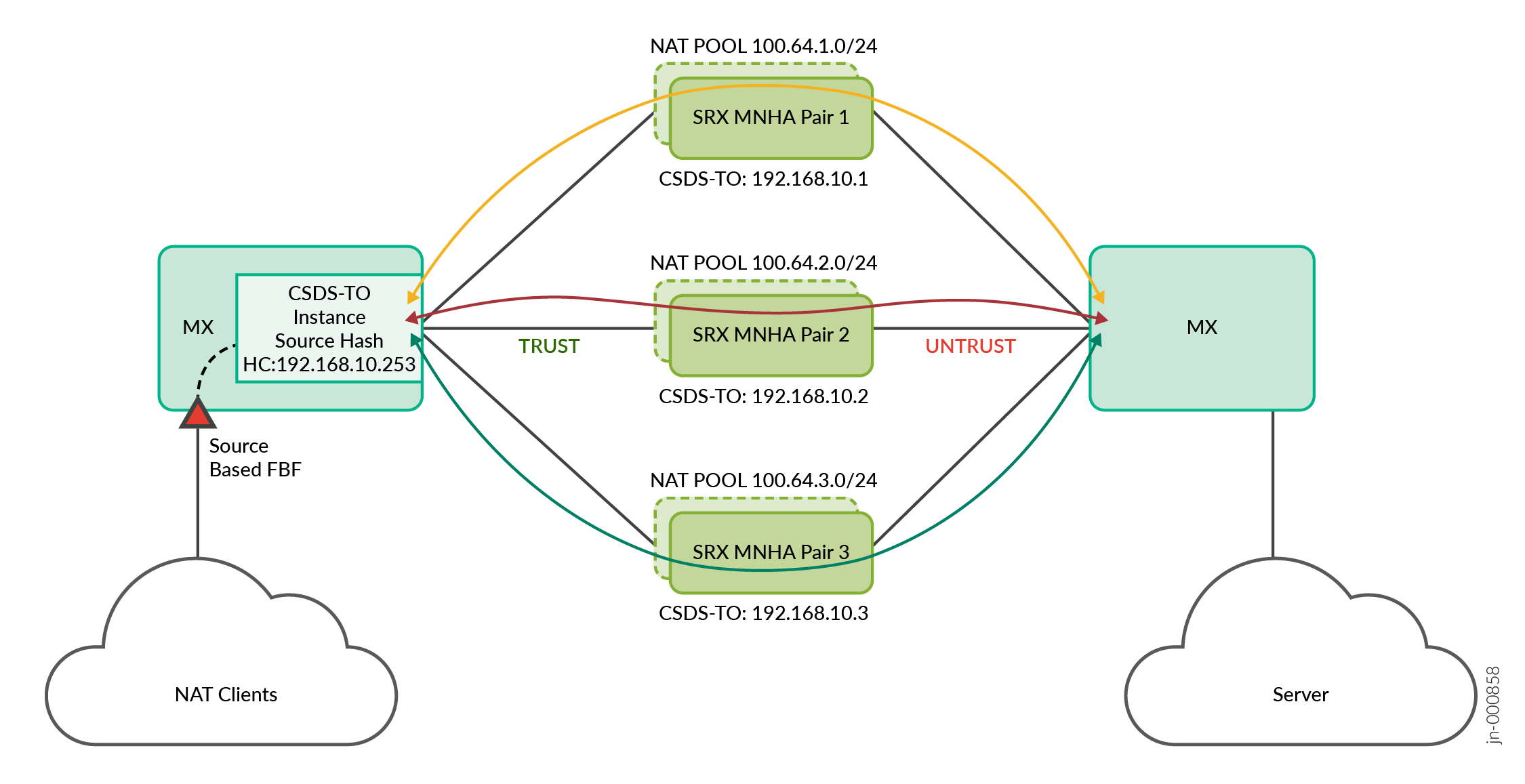
The MX Series is a single router configured with multiple logical interfaces toward scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls on the TRUST VR and UNTRUST VR direction.
For the forward traffic coming from client to server, the MX Series router uses FBF based on the source IP address match. Thr router matches the source IP address to push the NAT traffic to the CSDS-TO TRUST forwarding instance. The CSDS-TO forwarding instance includes a default route with next-hop as the list of SRX Series Firewalls. The CSDS-TO installs this default route when the health check passes for at least one SRX Series Firewalls.
The CSDS-TO performs source-based hash load balancing across all the available SRX Series Firewall next-hop devices.
Any available SRX Series Firewall anchors load balanced NAT data sessions and creates a NAT flow.
The MX Series router directs the traffic through the UNTRUST routing instance to reach the server.
For the return traffic coming from server-to-client on the MX Series UNTRUST routing instance, unique NAT pool routes are used to route the traffic to same SRX Series Firewalls.
SRX Series Firewalls use the same NAT flow to process the return traffic and routes the packet toward MX Series on the TRUST direction.
MX Series routes the packet back to the client.
For more information, see Juniper Scale-Out Stateful Firewall and Source NAT for Enterprise —JVD, and Juniper Scale-Out Stateful Firewall and CGNAT for SP Edge — JVD.
