ON THIS PAGE
Configure EVPN-VXLAN Data Center Stitching Through Interconnected EVPN-MPLS WAN Gateways
You can seamlessly stitch Ethernet VPN Virtual Extensible LAN (EVPN-VXLAN) data centers through WAN gateway devices running EVPN-MPLS.
Topology
The following diagram shows two EVPN-VXLAN data centers connected through an EVPN-MPLS WAN, using the gateway model. Each gateway is configured with an EVPN MAC-VRF routing instance. Each MAC-VRF instance uses VXLAN encapsulation, and the interconnect within each MAC-VRF instance uses MPLS encapsulation.
EVPN-VLXAN through EVPN-MPLS WAN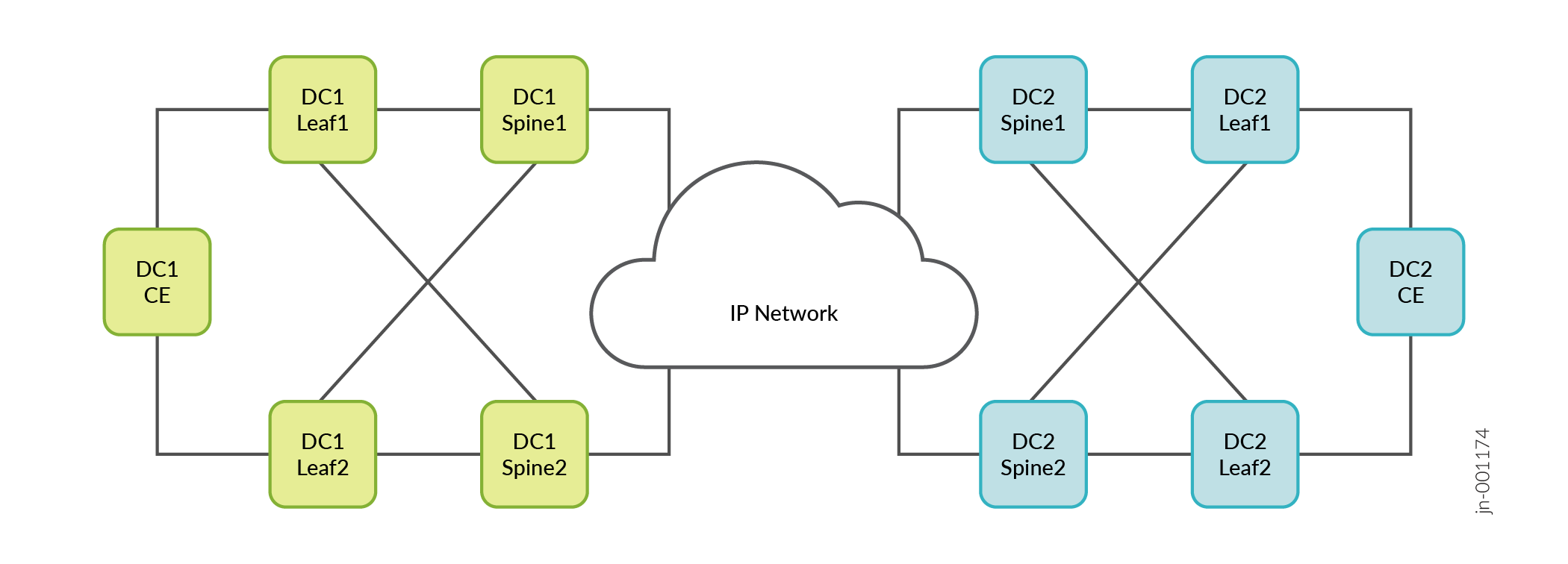
Configuration
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.
user@device> show configuration routing-instances evpn-vxlan
instance-type mac-vrf;
protocols {
evpn {
encapsulation vxlan;
default-gateway no-gateway-community;
extended-vni-list all;
interconnect {
vrf-target target:2:2;
route-distinguisher 100:110;
esi {
00:0a:0b:0c:0d:0a:0b:0c:0d:0a;
all-active;
}
interconnected-vlan-list [ 51 52 ];
encapsulation mpls;
}
}
}
vtep-source-interface lo0.0;
service-type vlan-aware;
interface et-0/0/7.0;
interface et-0/0/9.0;
route-distinguisher 100:11;
vrf-target target:1:1;
vlans {
bd51 {
vlan-id 51;
l3-interface irb.51;
vxlan {
vni 501;
}
}
bd52 {
vlan-id 52;
l3-interface irb.52;
vxlan {
vni 502;
}
}
}user@device> show configuration routing-instances evpn-vxlan
instance-type mac-vrf;
protocols {
evpn {
encapsulation vxlan;
default-gateway no-gateway-community;
extended-vni-list all;
interconnect {
vrf-target target:2:2;
route-distinguisher 200:210;
esi {
00:aa:bb:cc:dd:aa:bb:cc:dd:aa;
all-active;
}
interconnected-vlan-list [ 51 52 ];
encapsulation mpls;
}
}
}
vtep-source-interface lo0.0;
service-type vlan-aware;
interface et-0/0/7.0;
interface et-0/0/9.0;
route-distinguisher 200:21;
vrf-target target:3:3;
vlans {
bd51 {
vlan-id 51;
l3-interface irb.51;
vxlan {
vni 501;
}
}
bd52 {
vlan-id 52;
l3-interface irb.52;
vxlan {
vni 502;
}
}
}For multihomed gateway devices, you must include the following statement at the global level:
set protocols evpn interconnect-multihoming-peer-gateways
VTEP-IP-of-each-DCI-GW-peer-in-local-DC
You can't configure the above statement within a routing instance.
Also, the statement interconnect-multihoming-peer-gateways is renamed in
Junos OS Release 24.2R1 to multihoming-peer-gateways to support
identifying multihoming peer devices in multiple use cases. Starting in Junos OS and Junos
OS Evolved Release 24.4R1, we restored the
interconnect-multihoming-peer-gateways statement name specifically for
the interconnect use case. We've implemented other statements for other feature use cases
too, and you won't see the multihoming-peer-gateways statement in the
Junos OS CLI anymore.
A full discussion of multihoming is beyond the scope of this document. For more about multihoming, see EVPN Multihoming Overview.
Verification
Confirm that routes are showing in mpls.0.
user@DC1Spine1> show route table mpls.0 protocol evpn | grep "Egress"
102 *[EVPN/7] 00:21:22, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Egress-MAC, vlan-id 51, ESI 00:aa:bb:cc:dd:aa:bb:cc:dd:aa
103 *[EVPN/7] 00:21:22, remote-pe 10.200.22.22, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Egress-MAC, vlan-id 51
104 *[EVPN/7] 00:21:22, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Egress-MAC, vlan-id 52, ESI 00:aa:bb:cc:dd:aa:bb:cc:dd:aa
105 *[EVPN/7] 00:21:22, remote-pe 10.200.22.22, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Egress-MAC, vlan-id 52
106 *[EVPN/7] 00:21:22, remote-pe 10.200.22.21, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Egress-MAC, vlan-id 51
107 *[EVPN/7] 00:21:22, remote-pe 10.200.22.21, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Egress-MAC, vlan-id 52
108 *[EVPN/7] 00:21:22, remote-pe 10.200.22.21, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Egress-IM, vlan-id 51
109 *[EVPN/7] 00:21:22, remote-pe 10.200.22.21, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Egress-IM, vlan-id 52
110 *[EVPN/7] 00:21:22, remote-pe 10.200.22.22, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Egress-IM, vlan-id 51
111 *[EVPN/7] 00:21:22, remote-pe 10.200.22.22, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Egress-IM, vlan-id 52
{master}[edit]
user@DC1Spine1> show route table mpls.0 protocol evpn | grep "Ingress"
99 *[EVPN/7] 00:21:29, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Ingress-MAC, vlan-id 51
[EVPN/7] 00:21:29, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Ingress-Aliasing, vlan-id 51
100 *[EVPN/7] 00:21:29, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Ingress-MAC, vlan-id 52
[EVPN/7] 00:21:29, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Ingress-Aliasing, vlan-id 52
112 *[EVPN/7] 00:21:28, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Ingress-IM, vlan-id 51
113 *[EVPN/7] 00:21:28, routing-instance evpn-vxlan, route-type Ingress-IM, vlan-id 52Confirm that VXLAN VNI's are populating in the EVPN database.
user@DC1Spine1> show evpn database mac-address 00:00:11:11:51:01 extensive
Instance: evpn-vxlan
VN Identifier: 501, MAC address: 00:00:11:11:51:01
State: 0x0
Source: 00:11:12:11:11:11:11:11:11:11, Rank: 1, Status: Active
Remote origin: 10.11.1.11
Remote state: <Mac-Only-Adv>
Remote origin: 10.11.1.12
Remote state: <Mac-Only-Adv>
Mobility sequence number: 0 (minimum origin address 10.11.1.11)
Timestamp: Jun 28 22:51:12.147619 (0x649c6c08)
State: <Remote-To-Local-Adv-Done>
MAC advertisement route status: Not created (no local state present)
Interconn advertisement route status: DCI route created
IP address: 10.100.51.1
Remote origin: 10.11.1.11
Remote state: <Sent-to-l2ald>
Remote origin: 10.11.1.12
Remote state: <Sent-to-l2ald>
Interconn advertisement route status: DCI route created
History db:
Time Event
Jun 28 22:51:09.533 2023 00:11:12:11:11:11:11:11:11:11 : Created
Jun 28 22:51:09.541 2023 00:11:12:11:11:11:11:11:11:11 : Remote peer 10.11.1.12 created
Jun 28 22:51:09.546 2023 Updating output state (change flags 0x1 <ESI-Added>)
Jun 28 22:51:09.546 2023 Active ESI changing (not assigned -> 00:11:12:11:11:11:11:11:11:11)
Jun 28 22:51:09.547 2023 00:11:12:11:11:11:11:11:11:11 : 10.100.51.1 Selected IRB interface nexthop
Jun 28 22:51:09.547 2023 00:11:12:11:11:11:11:11:11:11 : 10.100.51.1 Reject remote ip host route 10.100.51.1 in L3 context VRF-100 since no remote-ip-host-routes configured
Jun 28 22:51:09.733 2023 00:11:12:11:11:11:11:11:11:11 : 10.100.51.1 Selected IRB interface nexthop
Jun 28 22:51:09.733 2023 00:11:12:11:11:11:11:11:11:11 : 10.100.51.1 Reject remote ip host route 10.100.51.1 in L3 context VRF-100 since no remote-ip-host-routes configured
Jun 28 22:56:46.300 2023 00:11:12:11:11:11:11:11:11:11 : 10.100.51.1 Selected IRB interface nexthop
Jun 28 22:56:46.300 2023 00:11:12:11:11:11:11:11:11:11 : 10.100.51.1 Reject remote ip host route 10.100.51.1 in L3 context VRF-100 since no remote-ip-host-routes configured
Confirm MAC table entries for an IRB.
user@DC1Spine1> show ethernet-switching table 00:00:11:11:51:01
MAC flags (S - static MAC, D - dynamic MAC, L - locally learned, P - Persistent static
SE - statistics enabled, NM - non configured MAC, R - remote PE MAC, O - ovsdb MAC,
B - Blocked MAC)
Ethernet switching table : 33 entries, 33 learned
Routing instance : evpn-vxlan
Vlan MAC MAC GBP Logical SVLBNH/ Active
name address flags tag interface VENH Index source
bd51 00:00:11:11:51:01 DR esi.11802 00:11:12:11:11:11:11:11:11:11user@DC1Spine1> show ethernet-switching mac-ip-table 00:00:11:11:51:01
MAC IP flags (S - Static, D - Dynamic, L - Local , R - Remote, Lp - Local Proxy,
Rp - Remote Proxy, K - Kernel, RT - Dest Route, (N)AD - (Not) Advt to remote,
RE - Re-ARP/ND, RO - Router, OV - Override, Ur - Unresolved,
RTS - Dest Route Skipped, RGw - Remote Gateway, GBP - Group Based Policy,
RTF - Dest Route Forced, SC - Static Config, P - Probe, NLC - No Local Config)
Routing instance : evpn-vxlan
Bridging domain : bd51
IP MAC Flags GBP Logical Active
address address Tag Interface source
10.100.51.1 00:00:11:11:51:01 DR,K,RT esi.11802 00:11:12:11:11:11:11:11:11:11
user@DC1Spine1> show route forwarding-table destination 00:00:11:11:51:01 vpn evpn-vxlan
Routing table: evpn-vxlan.vpls
VPLS:
Destination Type RtRef Next hop Type Index NhRef Netif
00:00:11:11:51:01/48 user 0 indr 11809 1 .local..56
comp 11802 1
comp 11795 1 vtep.32773
indr 6323 1
sftw 19002 1 et-0/0/1.0
10.11.11.1 ucst 1014 1 et-0/0/1.0
comp 11796 1 vtep.32775
indr 6324 1
sftw 19004 1 et-0/0/3.0
10.12.11.1 ucst 1001 1 et-0/0/3.0user@DC1Spine1> show arp no-resolve | grep 10.100.51.1 00:00:11:11:51:12 10.100.51.12 irb.51[ et-0/0/9.0 ] permanent remote
