ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring an Export Policy for BGP Route Target Filtering for VPNs
This example shows how to configure an export routing policy for BGP route target filtering (also known as route target constrain, or RTC).
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
Four Juniper Networks devices that support BGP route target filtering.
Junos OS Release 12.2 or later on one or more devices configured for proxy BGP route filtering. In this example, you explicitly configure proxy BGP route filtering on the route reflectors.
Before configuring an export policy for BGP route target filtering, make sure that you are familiar with and understand the following concepts:
Overview
BGP route target filtering allows you to reduce network resource consumption by distributing route target membership (RT membership) advertisements throughout the network. BGP uses the RT membership information to send VPN routes only to the devices that need them in the network. Similar to other types of BGP reachability, you can apply a routing policy to route target filtering routes to influence the network. When route target filtering is configured, restricting the flow of route target filtering routes also restricts the VPN routes that might be attracted by this RT membership. Configuring this policy involves:
Creating a filter that defines the list of route target prefixes.
Creating a policy to select a subset of the route target filters to use for BGP route target filtering.
To define the list of route target prefixes:
You configure the
rtf-prefix-liststatement at the[edit policy-options]hierarchy level to specify the name of the route target prefix list and one or more route target prefixes to use. This configuration allows you to specify the incoming route target filtering routes that the device will use and then distribute them throughout the network.
To configure the routing policy and apply the route target prefix list to that policy, you can specify the following policy options:
-
family route-target—(Optional) The route-target family match condition specifies matching BGP route target filtering routes. You define this criteria in thefromstatement. This example shows how to create an export policy using thefamily route-targetmatch condition.Note:Juniper uses the inet.3 table to resolve the next hop address when
family route-targetis configured. protocol route-target—(Optional) The route-target protocol match condition defines the criteria that an incoming route must match. You define this criteria in thefromstatement. This statement is primarily useful for restricting the policy to locally generated route target filtering routes.Note:When you use the
show route table bgp.rtarget.0command to view proxy BGP route target filtering routes, you will see the BGP protocol for received routes and the route target protocol routes for local route target filtering routes.rtf-prefix-list name—The rtf-prefix-list statement applies the list of route target prefixes that you already configured to the policy. You define this criteria in thefromstatement.
Topology Diagram
Figure 1 shows the topology used in this example.
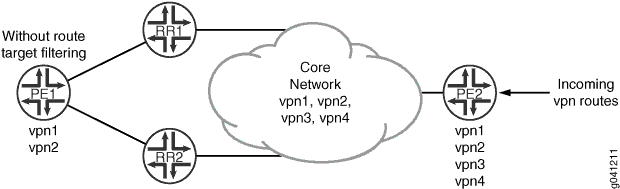
In this example, BGP route target filtering is configured on the route reflectors (Device RR1 and Device RR2) and provider edge (PE) Device PE2. The other PE, Device PE1, does not support BGP route target filtering. Proxy BGP route target filtering is also configured on the peering sessions between the route reflectors and Device PE1 to minimize the number of VPN route updates processed by Device PE1. Device PE2 has four VPNs configured (vpn1, vpn2, vpn3, and vpn4), and Device PE1 has two VPNs configured (vpn1 and vpn2). In the sample topology, all devices participate in autonomous system (AS) 203, OSPF is the configured interior gateway protocol (IGP), and LDP is the signaling protocol used by the VPNs. In this example, we use static routes in the VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) instances to generate VPN routes. This is done in place of using a PE to customer edge (CE) protocol such as OSPF or BGP.
In this example, you further control the routes being advertised
from Device PE2 to Device PE1 by configuring an export policy on Device
PE2 to prevent vpn3 routes from being advertised to Device RR1. You
create a policy that specifies the family route-target match
condition, defines the list of route target prefixes, and applies
the list of route target prefixes by defining the rtf-prefix-list criteria.
Configuration
- CLI Quick Configuration
- Configuring Device PE1
- Configuring Device RR1
- Configuring Device RR2
- Configuring Device PE2
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Device PE1
set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 description PE1-to-RR1 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.49.0.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 description PE1-to-RR2 set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.49.10.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family mpls set protocols ldp interface ge-1/0/0 set protocols ldp interface ge-1/0/1 set protocols bgp group internal type internal set protocols bgp group internal local-address 10.255.163.58 set protocols bgp group internal neighbor 10.255.165.220 family inet-vpn unicast set protocols bgp group internal neighbor 10.255.165.28 family inet-vpn unicast set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/0/0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/0/1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set routing-options route-distinguisher-id 10.255.163.58 set routing-options autonomous-system 203 set routing-instances vpn1 instance-type vrf set routing-instances vpn1 vrf-target target:203:100 set routing-instances vpn1 routing-options static route 203.0.113.1/24 discard set routing-instances vpn2 instance-type vrf set routing-instances vpn2 vrf-target target:203:101 set routing-instances vpn2 routing-options static route 203.0.113.2/24 discard
Device RR1
set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 description RR1-to-PE1 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.49.0.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 description RR1-to-PE2 set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.50.0.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family mpls set protocols ldp interface ge-1/0/0 set protocols ldp interface ge-1/0/1 set protocols bgp group internal type internal set protocols bgp group internal local-address 198.51.100.0 set protocols bgp group internal cluster 198.51.100.1 set protocols bgp group internal neighbor 10.255.163.58 description vpn1-to-pe1 family inet-vpn unicast set protocols bgp group internal neighbor 10.255.163.58 family route-target proxy-generate set protocols bgp group internal neighbor 10.255.168.42 description vpn1-to-pe2 family inet-vpn unicast set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/0/0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/0/1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set routing-options route-distinguisher-id 10.255.165.220 set routing-options autonomous-system 203
Device RR2
set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 description RR2-to-PE1 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.49.10.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 description RR2-to-PE2 set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.50.10.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family mpls set protocols ldp interface ge-1/0/0 set protocols ldp interface ge-1/0/1 set protocols bgp group internal type internal set protocols bgp group internal local-address 10.255.165.28 set protocols bgp group internal cluster 198.51.100.1 set protocols bgp group internal neighbor 10.255.163.58 description vpn2-to-pe1 family inet-vpn unicast set protocols bgp group internal neighbor 10.255.163.58 family route-target proxy-generate set protocols bgp group internal neighbor 10.255.168.42 description vpn2-to-pe2 family inet-vpn unicast set protocols bgp group internal neighbor 10.255.163.58 family route-target set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/0/0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/0/1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set routing-options route-distinguisher-id 10.255.165.28 set routing-options autonomous-system 203
Device PE2
set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 description PE2-to-RR1 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.50.0.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 description PE2-to-RR2 set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.50.10.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family mpls set protocols ldp interface ge-1/0/0 set protocols ldp interface ge-1/0/1 set protocols bgp group internal type internal set protocols bgp group internal local-address 10.255.168.42 set protocols bgp group internal family inet-vpn unicast set protocols bgp group internal family route-target set protocols bgp group internal neighbor 10.255.165.220 export filter-rtc set protocols bgp group internal neighbor 10.255.165.28 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/0/0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/0/1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set policy-options rtf-prefix-list exclude-103 203:203:103/96 set policy-options policy-statement filter-rtc from family route-target set policy-options policy-statement filter-rtc from rtf-prefix-list exclude-103 set policy-options policy-statement filter-rtc then reject set routing-options route-distinguisher-id 10.255.168.42 set routing-options autonomous-system 203 set routing-instances vpn1 instance-type vrf set routing-instances vpn1 vrf-target target:203:100 set routing-instances vpn1 routing-options static route 203.0.113.1/24 discard set routing-instances vpn2 instance-type vrf set routing-instances vpn2 vrf-target target:203:101 set routing-instances vpn2 routing-options static route 203.0.113.2/24 discard set routing-instances vpn3 instance-type vrf set routing-instances vpn3 vrf-target target:203:103 set routing-instances vpn3 routing-options static route 203.0.113.3/24 discard set routing-instances vpn4 instance-type vrf set routing-instances vpn4 vrf-target target:203:104 set routing-instances vpn4 routing-options static route 203.0.113.4/24 discard
Configuring Device PE1
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode.
To configure Device PE1:
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@PE1# set ge-1/0/0 unit 0 description PE1-to-RR1 user@PE1# set ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.49.0.1/30 user@PE1# set ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family mpls user@PE1#set ge-1/0/1 unit 0 description PE1-to-RR2 user@PE1#set ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.49.10.1/30 user@PE1# set ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family mpls
Configure the route distinguisher and the AS number.
[edit routing-options] user@PE1# set route-distinguisher-id 10.255.163.58 user@PE1# set autonomous-system 203
Configure LDP as the signaling protocol used by the VPN.
[edit protocols ldp] user@PE1# set interface ge-1/0/0 user@PE1# set interface ge-1/0/1
Configure BGP.
[edit protocols bgp group internal] user@PE1# set type internal user@PE1# set local-address 10.255.163.58 user@PE1# set neighbor 10.255.165.220 family inet-vpn unicast user@PE1# set neighbor 10.255.165.28 family inet-vpn unicast
Configure OSPF.
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@PE1# set interface ge-1/0/0 user@PE1# set interface ge-1/0/1 user@PE1# set interface lo0.0 passive
Configure the VPN routing instances.
[edit routing-instances vpn1] user@PE1# set instance-type vrf user@PE1# set vrf-target target:203:100 user@PE1# set routing-options static route 203.0.113.1/24 discard
[edit routing-instances vpn2] user@PE1# set instance-type vrf user@PE1# set vrf-target target:203:101 user@PE1# set routing-options static route 203.0.113.2/24 discard
If you are done configuring the device, commit the configuration.
[edit] user@PE1# commit
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering
the show interfaces, show protocols, show
routing-options, and show routing-instances commands.
If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat
the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
user@PE1# show interfaces
ge-1/0/0 {
unit 0 {
description PE1-to-RR1;
family inet {
address 10.49.0.1/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/0/1 {
unit 0 {
description PE1-to-RR2;
family inet {
address 10.49.10.1/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
user@PE1# show protocols
bgp {
group internal {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.163.58;
neighbor 10.255.165.220 {
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
}
neighbor 10.255.165.28 {
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface ge-1/0/0.0;
interface ge-1/0/1.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
ldp {
interface ge-1/0/0.0;
interface ge-1/0/1.0;
}
user@PE1# show routing-options route-distinguisher-id 10.255.14.182; autonomous-system 203;
user@PE1# show routing-instances
vpn1 {
instance-type vrf;
vrf-target target:203:100;
routing-options {
static {
route 203.0.113.1/24 discard;
}
}
}
vpn2 {
instance-type vrf;
vrf-target target:203:101;
routing-options {
static {
route 203.0.113.2/24 discard;
}
}
}
Configuring Device RR1
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode.
To configure Device RR1:
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@RR1# set ge-1/0/0 unit 0 description RR1-to-PE1 user@RR1# set ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.49.0.2/30 user@RR1# set ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family mpls user@RR1# set ge-1/0/1 unit 0 description RR1-to-PE2 user@RR1# set ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.50.0.2/30 user@RR1# set ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family mpls
Configure the route distinguisher and the AS number.
[edit routing-options] user@RR1# set route-distinguisher-id 10.255.165.220 user@RR1# set autonomous-system 203
Configure LDP as the signaling protocol used by the VPN.
[edit protocols ldp] user@RR1# set interface ge-1/0/0 user@RR1# set interface ge-1/0/1
Configure BGP.
[edit protocols bgp group internal] user@RR1# set type internal user@RR1# set local-address 10.255.165.220 user@RR1# set cluster 198.51.100.1 user@RR1# set neighbor 10.255.163.58 description vpn1-to-pe1 family inet-vpn unicast user@RR1# set neighbor 10.255.168.42 description vpn1-to-pe2 family inet-vpn unicast
Configure BGP route target filtering on the peering session with Device PE2.
[edit protocols bgp group internal] user@RR1# set neighbor 10.255.168.42 family route-target
Configure proxy BGP route target filtering on the peering session with Device PE1.
[edit protocols bgp group internal] user@RR1# set neighbor 10.255.163.58 family route-target proxy-generate
Configure OSPF.
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@RR1# set interface ge-1/0/0 user@RR1# set interface ge-1/0/1 user@RR1# set interface lo0.0 passive
If you are done configuring the device, commit the configuration.
[edit] user@RR1# commit
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering
the show interfaces, show protocols, and show routing-options commands. If the output does not display
the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example
to correct the configuration.
user@RR1# show interfaces
ge-1/0/0 {
unit 0 {
description RR1-to-PE1;
family inet {
address 10.49.0.2/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/0/1 {
unit 0 {
description RR1-to-PE2;
family inet {
address 10.50.0.2/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
user@RR1# show protocols
bgp {
group internal {
type internal;
local-address 198.51.100.0;
cluster 198.51.100.1;
neighbor 10.255.163.58 {
description vpn1-to-pe1;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
family route-target {
proxy-generate;
}
}
neighbor 10.255.168.42 {
description vpn1-to-pe2;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
family route-target;
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface ge-1/0/0.0;
interface ge-1/0/1.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
ldp {
interface ge-1/0/0.0;
interface ge-1/0/1.0;
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface ge-1/0/0.0;
interface ge-1/0/1.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
ldp {
interface ge-1/0/0.0;
interface ge-1/0/1.0;
}
user@RR1# show routing-options route-distinguisher-id 10.255.165.220; autonomous-system 203;
Configuring Device RR2
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode.
To configure Device RR2:
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@RR2# set ge-1/0/0 unit 0 description RR2-to-PE1 user@RR2# set ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.49.10.2/30 user@RR2# set ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family mpls user@RR2# set ge-1/0/1 unit 0 description RR2-to-PE2 user@RR2# set ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.50.10.2/30 user@RR2# set ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family mpls
Configure the route distinguisher and the AS number.
[edit routing-options] user@RR2# set route-distinguisher-id 10.255.165.28 user@RR2# set autonomous-system 203
Configure LDP as the signaling protocol used by the VPN.
[edit protocols ldp] user@RR2# set interface ge-1/0/0 user@RR2# set interface ge-1/0/1
Configure BGP.
[edit protocols bgp group internal] user@RR2# set type internal user@RR2# set local-address 10.255.165.28 user@RR2# set cluster 198.51.100.1 user@RR2# set neighbor 10.255.163.58 description vpn2-to-pe1 family inet-vpn unicast user@RR2# set neighbor 10.255.168.42 description vpn2-to-pe2 family inet-vpn unicast
Configure BGP route target filtering on the peering session with Device PE2.
[edit protocols bgp group internal] user@RR2# set neighbor 10.255.168.42 family route-target
Configure proxy BGP route target filtering on the peering session with Device PE1.
[edit protocols bgp group internal] user@RR2# set neighbor 10.255.163.58 family route-target proxy-generate
Configure OSPF.
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@RR2# set interface ge-1/0/0 user@RR2# set interface ge-1/0/1 user@RR2# set interface lo0.0 passive
If you are done configuring the device, commit the configuration.
[edit] user@RR2# commit
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering
the show interfaces, show protocols, and show routing-options commands. If the output does not display
the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example
to correct the configuration.
user@RR2# show interfaces
ge-1/0/0 {
unit 0 {
description RR2-to-PE1;
family inet {
address 10.49.10.2/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/0/1 {
unit 0 {
description RR2-to-PE2;
family inet {
address 10.50.10.2/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
user@RR2# show protocols
bgp {
group internal {
local-address 10.255.165.28;
cluster 198.51.100.1;
neighbor 10.255.163.58 {
description vpn2-to-pe1;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
family route-target {
proxy-generate;
}
}
neighbor 10.255.168.42 {
description vpn2-to-pe2;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
family route-target;
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface ge-1/0/0.0;
interface ge-1/0/1.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
ldp {
interface ge-1/0/0.0;
interface ge-1/0/1.0;
}
user@RR2# show routing-options route-distinguisher-id 10.255.165.28; autonomous-system 203;
Configuring Device PE2
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode.
To configure Device PE2:
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@PE2# set ge-1/0/0 unit 0 description PE2-to-RR1 user@PE2# set ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.50.0.1/30 user@PE2# set ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family mpls user@PE2#set ge-1/0/1 unit 0 description PE2-to-RR2 user@PE2#set ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.50.10.2/30 user@PE2# set ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family mpls
Configure the route distinguisher and the AS number.
[edit routing-options] user@PE2# set route-distinguisher-id 10.255.168.42 user@PE2# set autonomous-system 203
Configure LDP as the signaling protocol used by the VPN.
[edit protocols ldp] user@PE2# set interface ge-1/0/0 user@PE2# set interface ge-1/0/1
Configure BGP.
[edit protocols bgp group internal] user@PE2# set type internal user@PE2# set local-address 10.255.168.42 user@PE2# set family inet-vpn unicast user@PE2# set family route-target user@PE2# set neighbor 10.255.165.220 user@PE2# set neighbor 10.255.165.28
Configure OSPF.
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@PE2# set interface ge-1/0/0 user@PE2# set interface ge-1/0/1 user@PE2# set interface lo0.0 passive
Configure the VPN routing instances.
[edit routing-instances vpn1] user@PE2# set instance-type vrf user@PE2# set vrf-target target:203:100 user@PE2# set routing-options static route 203.0.113.1/24 discard
[edit routing-instances vpn2] user@PE2# set instance-type vrf user@PE2# set vrf-target target:203:101 user@PE2# set routing-options static route 203.0.113.2/24 discard
[edit routing-instances vpn3] user@PE2# set instance-type vrf user@PE2# set vrf-target target:203:103 user@PE2# set routing-options static route 203.0.113.3/24 discard
[edit routing-instances vpn4] user@PE2# set instance-type vrf user@PE2# set vrf-target target:203:104 user@PE2# set routing-options static route 203.0.113.4/24 discard
Configure and apply the export routing policy.
[edit policy-options] user@PE2# set rtf-prefix-list exclude-103 203:203:103/96 [edit policy-options policy-statement filter-rtc] user@PE2# set from family route-target user@PE2# set from rtf-prefix-list exclude-103 user@PE2# set then reject [edit protocols bgp group internal] user@PE2# set neighbor 10.255.165.220 export filter-rtc
If you are done configuring the device, commit the configuration.
[edit] user@PE2# commit
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering
the show interfaces, show protocols, show
policy-options, show routing-options, and show
routing-instances commands. If the output does not display the
intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to
correct the configuration.
user@PE2# show interfaces
ge-1/0/0 {
unit 0 {
description PE2-to-RR1;
family inet {
address 10.50.0.1/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/0/1 {
unit 0 {
description PE2-to-RR2;
family inet {
address 10.50.10.2/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
user@PE2# show protocols
bgp {
group internal {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.168.42;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
family route-target;
neighbor 10.255.165.220 {
export filter-rtc;
}
neighbor 10.255.165.28;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface ge-1/0/0.0;
interface ge-1/0/1.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
ldp {
interface ge-1/0/0.0;
interface ge-1/0/1.0;
}
user@PE2# show routing-options route-distinguisher-id 10.255.168.42; autonomous-system 203;
user@PE2# show policy-options
policy-statement filter-rtc {
from {
family route-target;
rtf-prefix-list exclude-103;
}
then reject;
}
rtf-prefix-list exclude-103 {
203:203:103/96;
}
user@PE2# show routing-instances
vpn1 {
instance-type vrf;
vrf-target target:203:100;
routing-options {
static {
route 203.0.113.1/24 discard;
}
}
}
vpn2 {
instance-type vrf;
vrf-target target:203:101;
routing-options {
static {
route 203.0.113.2/24 discard;
}
}
}
vpn3 {
instance-type vrf;
vrf-target target:203:103;
routing-options {
static {
route 203.0.113.3/24 discard;
}
}
}
vpn4 {
instance-type vrf;
vrf-target target:203:104;
routing-options {
static {
route 203.0.113.4/24 discard;
}
}
}
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Verifying the Route Target Filtering Routes in the bgp.rtarget.0 Routing Table for Device RR1
- Verifying the Route Target Filtering Routes in the bgp.rtarget.0 Routing Table for Device RR2
Verifying the Route Target Filtering Routes in the bgp.rtarget.0 Routing Table for Device RR1
Purpose
Verify that the route prefix for vpn3 is not in Device RR1’s bgp.rtarget.0 table. Since an export policy on Device PE2 was applied to prevent the advertisement of vpn3 routes to Device RR1, Device RR1 should not receive those advertisements.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show route advertising-protocol
bgp 10.255.165.220 table bgp.rtarget.0 command.
user@PE2# show route advertising-protocol bgp 10.255.165.220 table bgp.rtarget.0
bgp.rtarget.0: 4 destinations, 11 routes
(4 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
Prefix Nexthop MED Lclpref AS path
203:203:100/96 * Self 100 I
203:203:101/96 * Self 100 I
203:203:104/96 * Self 100 I
Meaning
The bgp.rtartget.0 table does not display 203:203:103/96, which is the route prefix for vpn3. That means the export policy was applied correctly.
Verifying the Route Target Filtering Routes in the bgp.rtarget.0 Routing Table for Device RR2
Purpose
Verify that the route prefix for vpn3 is in Device RR2’s bgp.rtarget.0 table. Since an export policy was not applied on Device PE2 to prevent the advertisement of vpn3 routes to Device RR2, Device RR2 should receive advertisements from all of the VPNs.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show route advertising-protocol
bgp 10.255.165.28 table bgp.rtarget.0 command.
user@PE2# show route advertising-protocol bgp 10.255.165.28 table bgp.rtarget.0
bgp.rtarget.0: 4 destinations, 11 routes (4 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
(4 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
Prefix Nexthop MED Lclpref AS path
203:203:100/96 * Self 100 I
203:203:101/96 * Self 100 I
203:203:103/96 * Self 100 I
203:203:104/96 * Self 100 I
Meaning
The bgp.rtartget.0 table displays the route prefixes for all of the VPNs.
