Paragon Planner Equal Cost Multiple-Paths Overview
This chapter describes several Equal Cost Multiple-Paths (ECMP) features and walks through a scenario where it is useful. You will be able to display all the equal cost multiple-paths in the network as well as view any equal cost paths between two given nodes in detail. You can also split flows into sub-flows. Note that parallel links between two nodes do not count towards ECMPs.
When modelling ECMP routing, you set a point-to-point demand to type ECMP. When set to ECMP, the demand is split into a number of sub-flows and routed independently and the sub-flows which end up having the same path are recombined. The number of sub-flows can be either set explicitely on the main demand definition (ECMP=10), or if only tagged as ECMP (that is, you do not specify the number of sub-flows), the number of sub-flows is determined by the demand bandwidth and the settings defined for ECMP path placement (Design > Design Options > Path Placement > ECMP).
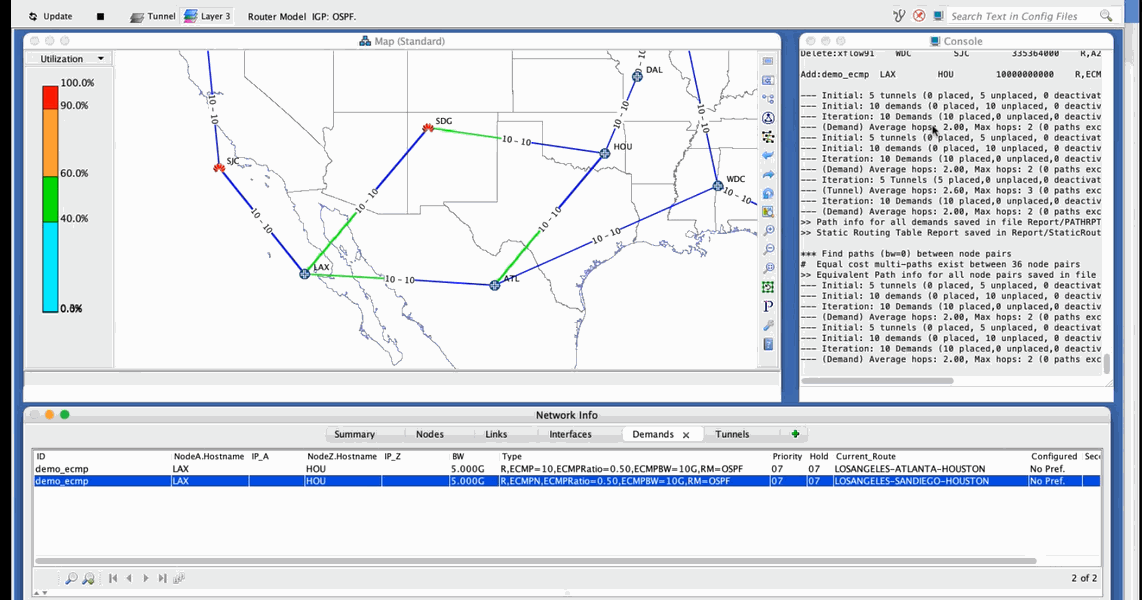
Figure shows that the demand demo_ecmp between Los Angeles and Houston is specified for ECMP routing with up to 10 sub-flows. After routing, two unique paths are found for the demand and the 10 sub-flows are recombined into the two flows—one flowing through Atlanta and the other through San Diego. ECMP=10 in the first row indicates that it is the original flow for the demand. 10 indicates that the original demand is split into 10 sub-flows. ECMPN in the second row indicates that it is a sub-flow for the demand. ECMPRatio=0.50 indicates that the original bandwidth of the demand (ECMPBW=10G) is split in the ratio of 0.5 between the two sub-flows. When you reroute the demands, It is possible that the bandwidth could be split in other ratios such as 0.6/0.4, 0.7/0.3 and so on.
The Report Manager (Report > Report Manager > Network Reports > Demand Reports > Equal Cost Multi-Path) provides a report of all the ECMPs in your network. For more information on the Report Manager, see Report Manager: Network Reports
Sometimes it is desirable to reduce the number of ECMPs in order to improve the predictability of how demands will be routed in the network. At other times it is desirable to split flows into sub-flows with ECMPs in order to perform load balancing. Paragon Planner will place these flows on routing paths that have identical costs.
For an overview of Paragon Planner or for a detailed description of each feature and the use of each window, refer to the Paragon Planner Desktop Application User Guide.
