Junos Space Nodes in the Junos Space Fabric Overview
When you install and configure the Junos Space Appliance or Junos Space Virtual Appliance as a Junos Space node, Junos Space Network Management Platform automatically creates a fabric with one node. To create a fabric with multiple nodes providing the scalability and availability that your network requires, you must first configure a Junos Space Virtual Appliance as a Junos Space node using the Junos Space CLI. You can then use the Junos Space Platform GUI to add the node to the fabric.
This topic contains the following sections:
Understanding the Junos Space Node Functions in a Fabric
A fabric that consists of a single node provides complete Junos Space Platform management functionality, with the following node functions enabled for the node:
-
Load balancer—For processing HTTP requests from remote browsers and northbound interface (NBI) clients
-
Database—For processing database requests (for create, read, update, and delete operations)
-
Application logic (JBoss server)—For processing back-end business logic (Junos Space Network Management Platform service requests) and Device Mediation Layer (DML) workload (that is, any interaction between Junos Space and any device, such as device connectivity, device events, and logging events)
Figure 1 shows all functions enabled on a fabric comprising one node.
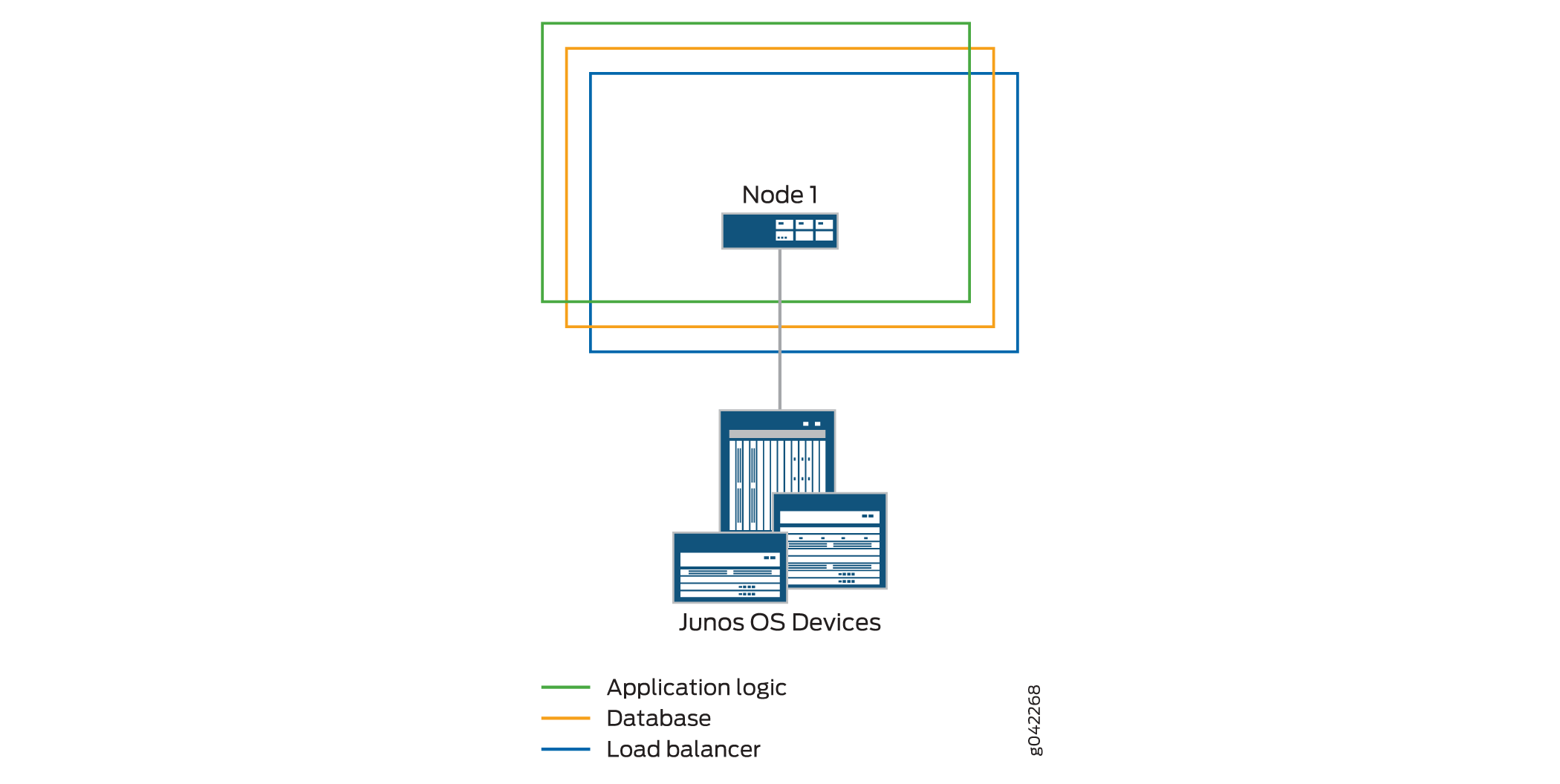
A fabric that comprises a single node provides no workload balancing and no backup if the Junos Space node goes down.
As your network expands with new devices, services, and users, you can add Junos Space nodes to handle the increased workload. For each additional Junos Space node that you configure, you must add the node to the fabric using the Junos Space Platform GUI. Each node that you add to the fabric increases the resource pool for the node functions to meet the scalability and high availability requirements of your network.
The Junos Space Platform node functions distribute the workload across operating nodes according to the following load-distribution rules:
-
Load balancer—When a node that functions as the active load-balancer server is down, all HTTP requests are automatically routed to the standby load-balancer server that is running on a separate node.
-
Database—When a node that functions as the active database server is down, all database requests (for create, read, update, and delete operations) are routed to the node that functions as the standby database server.
-
Application logic (DML and business logic)—Device connections and user requests are distributed among the nodes, and device-related operations are routed to the node to which the device is connected.
Junos Space Platform uses the following algorithm to ensure that the number of devices connected to a node does not exceed the threshold limit for each node:
Threshold Limit = [(Number of Devices in Database) / (Number of Nodes Running)] + 2
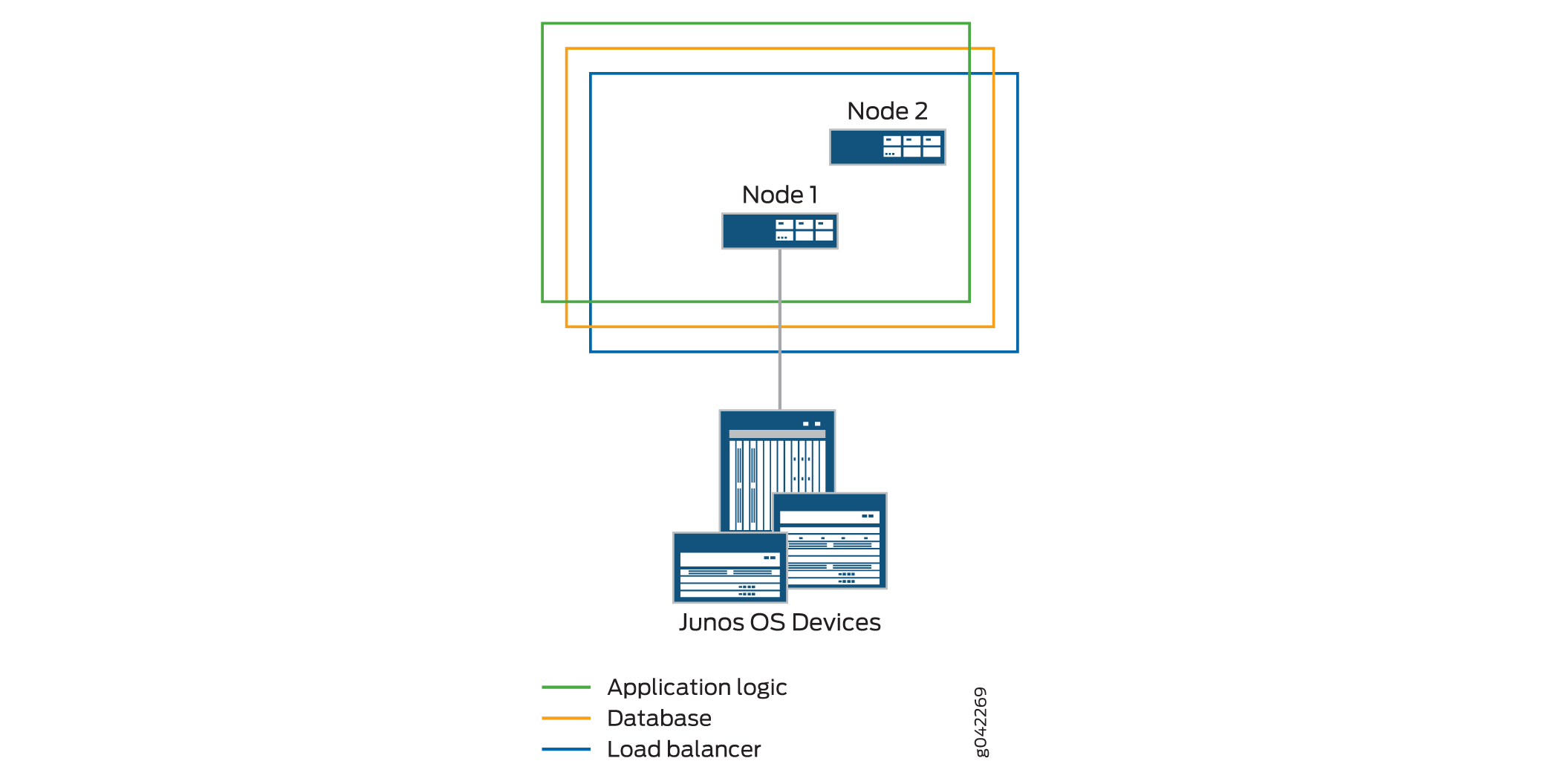
When a second Junos Space node is added to the fabric, the first node functions as the active load-balancer server and active database server, and the second node functions as the standby load-balancer server and standby database server. The load-balancer and application logic node functions provide scalability and high availability. The database node function on the second node provides high availability only.
Figure 2 shows the functions enabled on a fabric comprising two nodes.
Typically, if the fabric has three or more Junos Space Nodes, only the application logic functionality is enabled from the third node onward. The application logic functionality provides both scalability and high availability. However, high availability for application logic is not available if both the first and second nodes are down. For high availability of application logic, at least one among the first and second nodes should be up.
Figure 3 shows the functions enabled on a fabric comprising three nodes.
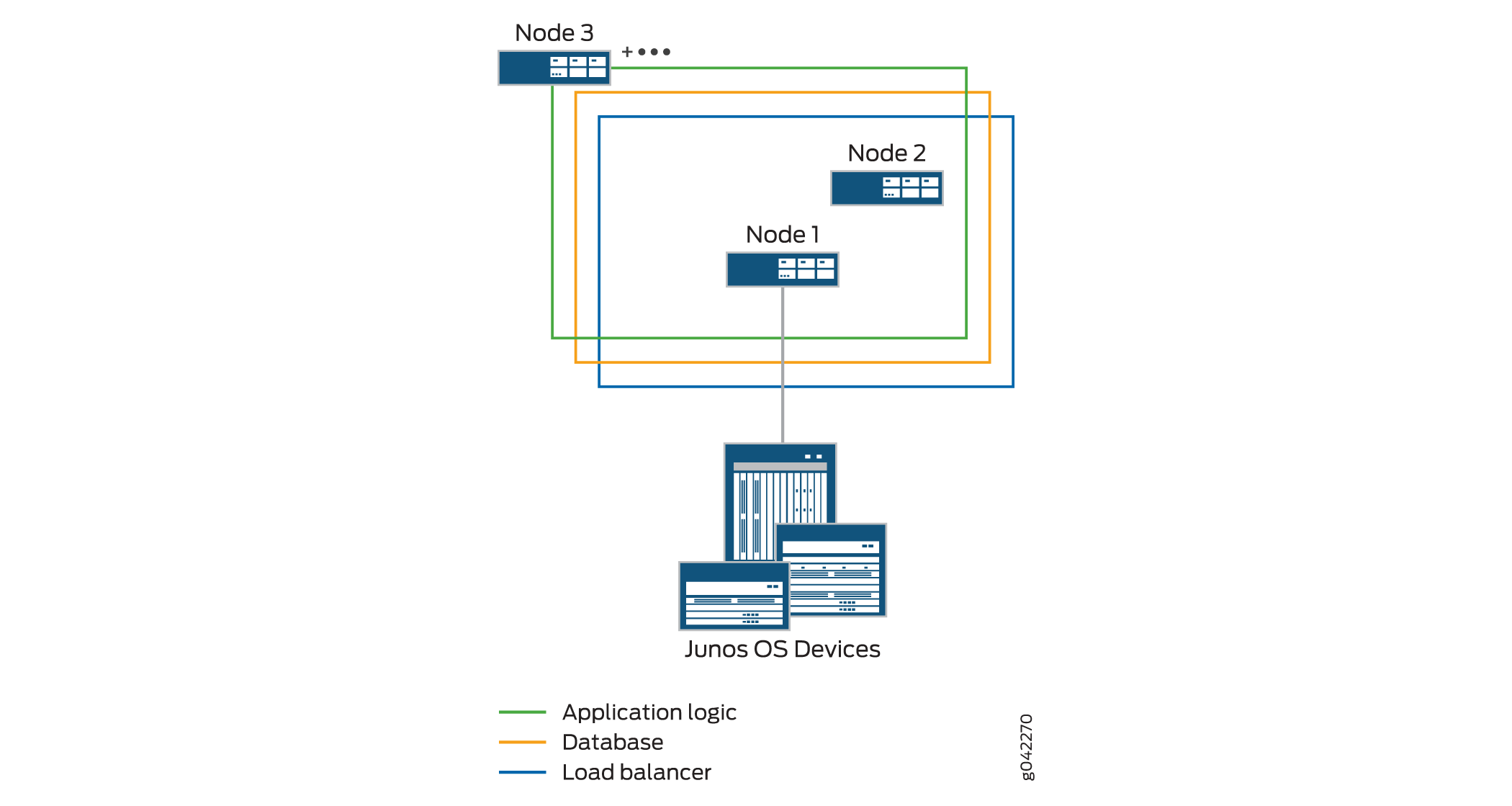
In addition to the load balancer and JBoss nodes, you can also include dedicated database nodes in the Junos Space fabric. For more information about dedicated database nodes, see Dedicated Database Nodes in the Junos Space Fabric Overview.
You can add a Junos Space node to an existing fabric as one of the following types of nodes on the basis of the functions you want the node to perform.
-
JBoss, database and load-balancer node:
When you add a node to an existing fabric that has one JBoss, database and load-balancer node, you can choose to add the new node as another JBoss, database and load-balancer node. This node functions as the standby load-balancer server and ensures high availability for the Junos Space fabric. The node also provides database and application logic functionality to the fabric.
-
JBoss and load-balancer node:
When you add a node to an existing fabric that has two dedicated database nodes in addition to a JBoss and load-balancer node, the fourth node can be added only as another JBoss and load-balancer node. This node functions as the standby load-balancer server and ensures high availability for the Junos Space fabric. In this case, both the active and standby load-balancer nodes provide load balancing and application logic functionality only and the dedicated database nodes provide the database functionality.
-
JBoss node:
When you add a node to an existing fabric that already has two load-balancer nodes, you can choose to add the new node as a JBoss-only node. This node provides only the application logic functionality.
-
Dedicated database node:
When you add a node to an existing fabric, you can choose to add the node as a dedicated database node. If no dedicated database nodes exist in the fabric, you must add two nodes together, one as the primary database node and the other as the secondary database node. If a dedicated database node is already part of the fabric, you can add one node as the secondary database node. You cannot have more than two dedicated database nodes in a fabric. The dedicated database nodes function as the primary and secondary MySQL servers.
