Upgrade Multicore vSRX Virtual Firewall with Contrail
Starting in Junos OS Release 15.1X49-D70 and Junos OS Release 17.3R1, you can scale up the number of vCPUs or vRAM for a vSRX Virtual Firewall VM. You must gracefully power off the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM before you can scale up vSRX Virtual Firewall. See Manage the vSRX VM for details.
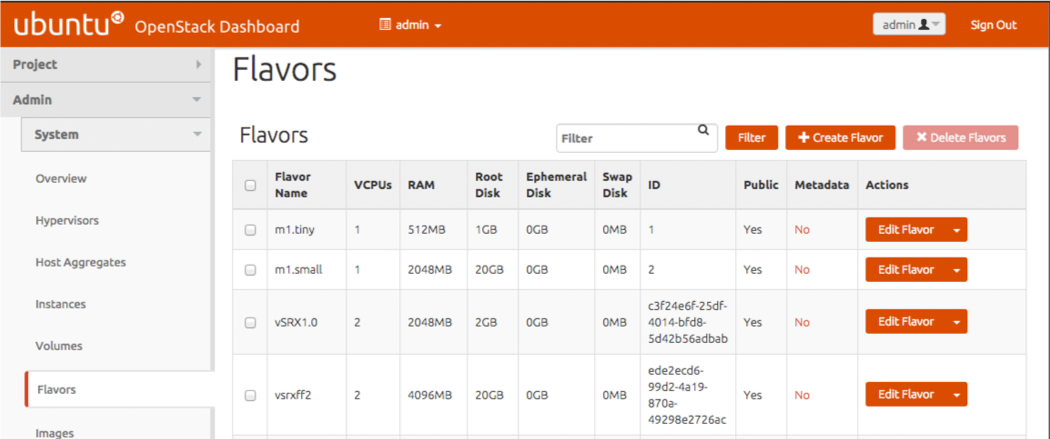
You can modify an existing flavor with the OpenStack Dashboard
(Horizon). You cannot use the OpenStack CLI (nova flavor) commands to modify the CPU or RAM settings on an existing flavor.
Instead, create a new flavor and modify the vSRX Virtual Firewall service template
in Contrail to use this new flavor. See the Create an Image Flavor with OpenStack for details.
You cannot scale down the number of vCPUs or vRAM for an existing vSRX Virtual Firewall VM.
Configure Multi-queue Virtio Interface for vSRX Virtual Firewall VM with OpenStack
Before you plan to scale up vSRX Virtual Firewall performance, enable network multi-queuing as a means to support an increased number of dataplane vCPUs for the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM. The default for vSRX Virtual Firewall in Contrail is 2 dataplane vCPUs, but you can scale that number to 4 vCPUs.
To use multiqueue virtio interfaces, ensure your system meets the following requirements:
OpenStack Liberty supports the ability to create VMs with multiple queues on their virtio interfaces. Virtio is a Linux platform for I/O virtualization, providing a common set of I/O virtualization drivers. Multiqueue virtio is an approach that enables the processing of packet sending and receiving to be scaled to the number of available virtual CPUs (vCPUs) of a guest, through the use of multiple queues
VIRTIO has a limitation of maximum of 64 MAC addresses per interface. If deploying a protocol which creates its own MAC (like VRRP), then you must ensure that sub-interfaces per interface does not exceed the limit of 64 MAC addresses. If the MAC address limit is exceeded then, there will be traffic loss.
The OpenStack version must be Liberty or greater.
The maximum number of queues in the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM interface is set to the same value as the number of vCPUs in the guest.
The vSRX Virtual Firewall VM image metadata property is set to enable multiple queues inside the VM.
Use the following command on the OpenStack node to enable multiple queues on a vSRX Virtual Firewall VM in Contrail:
source /etc/contrail/openstackrc
nova image-meta <image_name> set hw_vif_multiqueue_enabled="true"
After the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM is spawned, use the following command on the virtio interface in the guest to enable multiple queues inside the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM:
ethtool –L <interface_name> combined <#queues>
Modify an Image Flavor for vSRX Virtual Firewall with the Dashboard
OpenStack uses VM templates, or flavors, to set the memory, vCPU, and storage requirements for an image.
To Modify an image flavor for vSRX Virtual Firewall with the OpenStack dashboard:
Update a Service Template
If you created a new image flavor for an existing vSRx instance, you need to update the service template to use this new image flavor before you relaunch the vSRX Virtual Firewall instance.
To update a service template:
- From Contrail, select Configure>Services>Service Templates. The list of existing service templates appears.
- Click on the vSRX Virtual Firewall service template and select edit.
- Expand Advanced Options and select the new instance flavor from the Instance Flavor list.
- Click Save to update this service template.
- Power on the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM. See Manage the vSRX VM for details.
Change History Table
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.