About Policy Enforcer
Policy Enforcer
View the Policy Enforcer data sheet (This takes you out of the help center to the Juniper web site): https://www.juniper.net/content/dam/www/assets/datasheets/us/en/security/policy-enforcer-datasheet.pdf
Policy Enforcer provides centralized, integrated management of all your security devices (both physical and virtual), giving you the ability to combine threat intelligence from different solutions and act on that intelligence from one management point.
It also automates the enforcement of security policies across the network and quarantines infected endpoints to prevent threats across firewalls and switches. It works with cloud-based Juniper ATP Cloud to protect both perimeter-oriented threats as well as threats within the network. For example, if a user downloads a file from the Internet and that file passes through an SRX Series Firewall, the file can be sent to the Juniper ATP Cloud cloud for malware inspection (depending on your configuration settings.) If the file is determined to be malware, Policy Enforcer identifies the IP address and MAC address of the host that downloaded the file. Based on a user-defined policy, that host can be put into a quarantine VLAN or blocked from accessing the Internet.
Policy Enforcer provides the following:
Pervasive Security—Combine security features and intelligence from devices across your network, including switches, routers, firewalls, to create a “secure fabric” that leverages information you can use to create policies that address threats in real-time and into the future. With monitoring capabilities, it can also act as a sensor, providing visibility for intra- and inter-network communications.
User Intent-Based Policies—Create policies according to logical business structures such as users, user groups, geographical locations, sites, tenants, applications, or threat risks. This allows network devices (switches, routers, firewalls and other security devices) to share information, resources, and when threats are detected, remediation actions within the network.
Threat Intelligence Aggregation—Gather threat information from multiple locations and devices, both physical and virtual, as well as third party solutions.
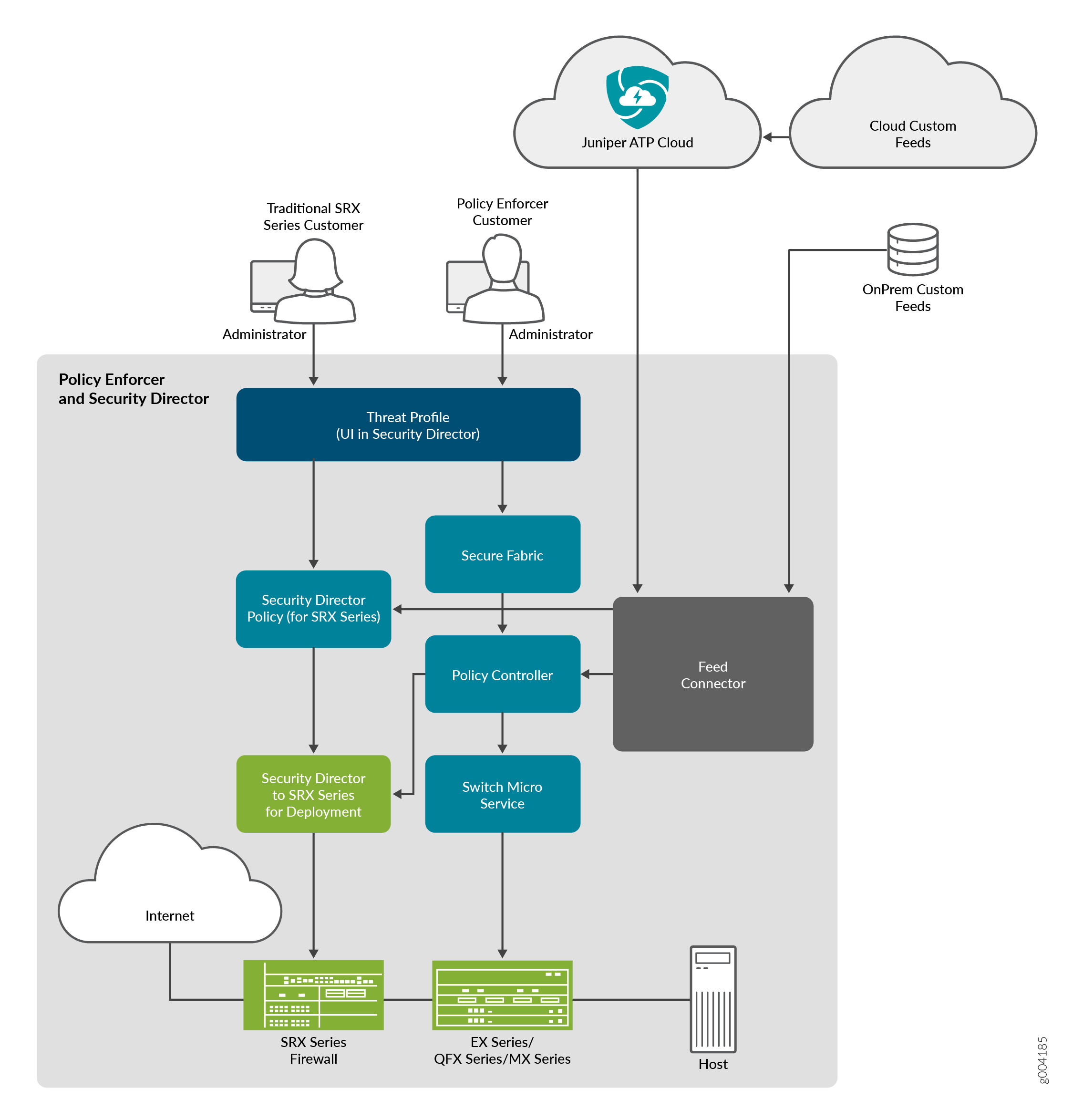
Figure 1 illustrates the flow diagram of Policy Enforcer over a traditional SRX configuration.