Compromised Hosts: More Information
Infected hosts are systems where there is high confidence that attackers have gained unauthorized access. When a host is compromised, the attacker can do several things to the computer, such as:
Send junk or spam e-mails to attack other systems or distribute illegal software.
Collect personal information, such as passwords and account numbers.
Disable your computer’s security settings to allow easy access.
Infected hosts are listed as IP address or IP subnet of the host along with a threat level, for example, xxx.xxx.xxx.133 and threat level 5. Once identified, Juniper ATP Cloud recommends an action and you can create security policies to take enforcement actions on the inbound and outbound traffic on these infected hosts. Juniper ATP Cloud uses multiple indicators, such as a client attempting to contact a C&C server or a client attempting to download malware, and a proprietary algorithm to determine the infected host threat level.
The data feed URL is set up automatically for you when you run the op script to configure your SRX Series Firewall. See Download And Run the Juniper ATP Cloud Script.
Figure 1 shows one example of how devices are labelled as infected hosts by downloading malware.
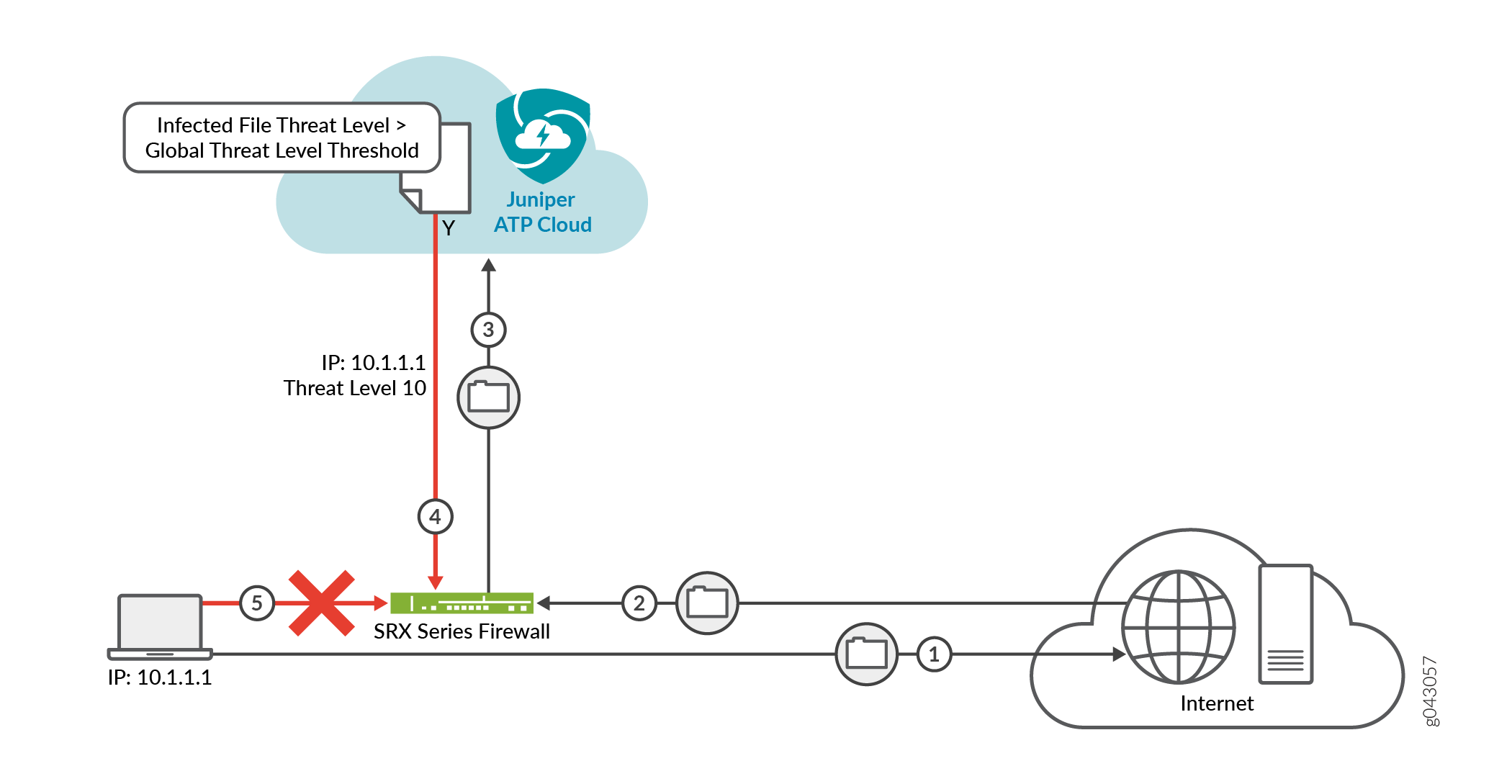
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
A client with IP address 10.1.1.1 is located behind an SRX Series Firewall and requests a file to be downloaded from the Internet. |
2 |
The SRX Series Firewall receives the file from the Internet and checks its security policies to see if any action needs to be taken before sending the file to the client. |
3 |
The SRX Series Firewall has a Juniper ATP Cloud policy that requires files of the same type that was just downloaded to be sent to the cloud for inspection. This file is not cached in the cloud, meaning this is the first time this specific file has been sent to the cloud for inspection. The SRX Series Firewall sends the file to the client while the cloud performs an exhaustive inspection. |
4 |
In this example, the cloud analysis determines the file has a threat level greater than the threshold indicating that the file is malware, and sends this information back to the SRX Series Firewall. The client is placed on the infected host list. |
5 |
Juniper ATP Cloud blocks the client from accessing the Internet. The client remains on the infected host list until an administrator performs further analysis and determines it is safe. |
You can view the status of hosts from the Juniper ATP Cloud Web Portal by navigating to
Monitor>Hosts. You can also use the
show services security-intelligence statistics CLI command on the SRX
Series Firewall to view a quick report.
host> show services security-intelligence statistics
Category Infected-Hosts:
Profile pr2:
Total processed sessions: 37
Permit sessions: 0
Block drop sessions: 35
Block close sessions: 2
An email can be configured in the Configure > Infected Hosts window to alert users when a host’s threat level is at or above a specified threshold.
A malware and host status event syslog message is created in /var/log/messages.
Junos OS supports forwarding logs using stream mode and event mode.
To use syslog, you must configure system logging for all SRX Series Firewall within the same organization. For example, if Organization1 contains SRX1 and SRX2, both SRX1 and SRX2 must have system logging enabled. For more information about configuring system logging, see SRX Getting Started - System Logging.
Malware event syslog using stream mode.
Sep 20 00:01:14 6.0.0.254 host-example RT_AAMW: AAMW_MALWARE_EVENT_LOG: timestamp=Thu Jun 23 09:55:38 2016 tenant-id=ABC123456 sample-sha256=ABC123 client-ip=192.0.2.0 mw-score=9 mw-info=Eicar:TestVirus client-username=admin client-hostname=host.example.com
Host status event syslog using stream mode.
Sep 20 00:01:54 6.0.0.254 host-example RT_AAMW: AAMW_HOST_INFECTED_EVENT_LOG: timestamp=Thu Jun 23 09:55:38 2016 tenant-id=ABC123 client-ip=192.0.2.0 client-hostname=host.example.com host-status=in_progress host-policy=default threat-level=7 infected-host-status=added reason=malware details=malware analysis detected host downloaded a malicious_file with score 9, sha256 ABC123
Malware event syslog using event mode
<14>1 2016-09-20T10:43:30.330-07:00 host-example RT_AAMW - AAMW_MALWARE_EVENT_LOG [junos@xxxx.1.1.x.x.xxx timestamp="Thu Jun 23 09:55:38 2016" tenant-id="ABC123456" sample-sha256="ABC123" client-ip-str="192.0.2.0" verdict-number="9" malware-info="Eicar:TestVirus" username="admin" hostname="host.example.com"] timestamp=Thu Jun 23 09:55:38 2016 tenant-id=ABC123456 sample-sha256=ABC123 client-ip=172.24.0.12 mw-score=9 mw-info=Eicar:TestVirus client-username=admin client-hostname=host.example.com
Host status event syslog using event mode.
<11>1 2016-09-20T10:40:30.050-07:00 host-example RT_AAMW - AAMW_HOST_INFECTED_EVENT_LOG [junos@xxxx.1.1.x.x.xxx timestamp="Thu Jun 23 09:55:38 2016" tenant-id="ABC123456" client-ip-str="192.0.2.0" hostname="host.example.com" status="in_progress" policy-name="default" th="7" state="added" reason="malware" message="malware analysis detected host downloaded a malicious_file with score 9, sha256 ABC123"] timestamp=Thu Jun 23 09:55:38 2016 tenant-id=ABC123456 client-ip=192.0.2.0 client-hostname=host.example.com host-status=in_progress host-policy=default threat-level=7 infected-host-status=added reason=malware details=malware analysis detected host downloaded a malicious_file with score 9, sha256 ABC123
The syslog record contains the following fields:
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
timestamp |
Date and time of syslog entry |
tenant_id |
Internal unique ID |
sample_sha256 |
SHA-256 hash value of the downloaded file. |
client_ip |
Client IP address, supporting both IP4 and IP6. |
mw_score |
Malware score. This is an integer between 0-10. |
mw_info |
Malware name or brief description. |
client_username |
Username of person that downloaded the possible malware. |
client_hostname |
Hostname of device that downloaded the possible malware. |
host_status |
Host status. Currently it is only |
host_policy |
Name of Juniper ATP Cloud policy that enforced this action. |
threat_level |
Host threat level. This is an integer between 0-10. |
infected_host_status |
Infected host status. It can be one of the following: |
reason |
Reason for the log entry. It can be one of the following: |
details |
Brief description of the entry reason, for example: |
About Block Drop and Block Close
If you use the show services security-intelligence statistics CLI command, you’ll see block drop and block close sessions.
host> show services security-intelligence statistics
Category Infected-Hosts:
Profile pr2:
Total processed sessions: 37
Permit sessions: 0
Block drop sessions: 35
Block close sessions: 2
You can configure either block drop or block close. If you choose block drop, then the SRX Series Firewall silently drops the session’s packet and the session eventually times out. If block close is configured, the SRX Series Firewalls sends a TCP RST packet to the client and server and the session is dropped immediately.
You can use block close, for example, to protect the resource of your client or server. It releases the client and server sockets immediately. If client or server resources is not a concern or you don’t want anyone to know there is a firewall located in the network, you can use block drop.
Block close is valid only for TCP traffic. Non-TCP traffic uses block drop even if you configure it block close. For example, if you configure infected hosts to block close:
... set services security-intelligence profile pr2 rule r2 then action block close ...
When you send icmp traffic through the device, it is block dropped.
For more information about setting block drop and block close, see Configure the SRX Series Firewall to Block Infected Hosts.
Host Details
Click the host IP address on the hosts main page to view detailed information about current threats to the selected host by time frame. From the details page, you can also change the investigation status and the blocked status of the host. For more information about the host details, see the web UI tooltips and online help.
You can also use the show security dynamic-address category-name
Infected-Hosts CLI command to view the infected host list.
host> show security dynamic-address category-name Infected-Hosts No. IP-start IP-end Feed Address 1 x.0.0.7 x.0.0.7 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500011 2 x.0.0.10 x.0.0.10 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500011 3 x.0.0.21 x.0.0.21 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500011 4 x.0.0.11 x.0.0.11 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500012 5 x.0.0.12 x.0.0.12 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500012 6 x.0.0.22 x.0.0.22 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500012 7 x.0.0.6 x.0.0.6 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500013 8 x.0.0.9 x.0.0.9 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500013 9 x.0.0.13 x.0.0.13 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500013 10 x.0.0.23 x.0.0.23 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500013 11 x.0.0.14 x.0.0.14 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500014 12 x.0.0.24 x.0.0.24 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500014 13 x.0.0.1 x.0.0.1 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500015 14 x.0.0.2 x.0.0.2 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500015 15 x.0.0.3 x.0.0.3 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500015 16 x.0.0.4 x.0.0.4 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500015 17 x.0.0.5 x.0.0.5 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500015 18 x.0.0.15 x.0.0.15 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500015 19 x.0.0.25 x.0.0.25 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500015 20 x.0.0.16 x.0.0.16 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500016 21 x.0.0.26 x.0.0.26 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500016 22 x.0.0.17 x.0.0.17 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500017 23 x.0.0.27 x.0.0.27 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500017 24 x.0.0.18 x.0.0.18 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500018 25 x.0.0.28 x.0.0.28 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500018 26 x.0.0.19 x.0.0.19 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500019 27 x.0.0.29 x.0.0.29 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-21500019 28 x.0.0.8 x.0.0.8 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-2150001a 29 x.0.0.20 x.0.0.20 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-2150001a 30 x.0.0.30 x.0.0.30 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-2150001a Total number of matching entries: 30
Automatic Lowering of Host Threat Level or Removal from Infected Hosts Feed
The threat level of a host might decrease automatically if there have been no security events for that host for the period of one month. The month in question is a rolling window of time relative to the current time. The number and type of events seen over that month determine the threat level score of the host. A host might automatically be removed from the infected hosts list by the same process, if all malware events fall outside of that month long window.
If the manual resolution of a host sets the threat level to zero and another malware event occurs, the resolution event is ignored. The resulting threat score for the host once again takes into consideration all the suspicious events within the period of one month to determine the new threat score.
