ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring BFD for IS-IS
This example describes how to configure the Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) protocol to detect failures in an IS-IS network.
BFD is not supported with ISIS for IPV6 on QFX10000 series switches.
Requirements
Before you begin, configure IS-IS on both routers. See Example: Configuring IS-IS for information about the required IS-IS configuration.
We provide the IS-IS configuration in the CLI quick configuration section but do not cover the IS-IS configuration in the step-by-step.
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
-
Junos OS Release 7.3 or later
-
Updated and revalidated using Junos OS Release 22.4
-
-
M Series, MX Series, and T Series routers
Overview
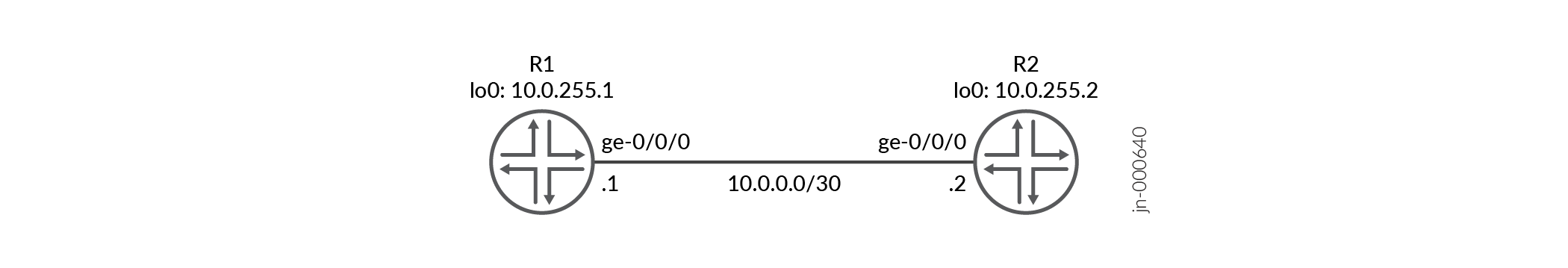
This example shows two routers connected to each other. A loopback interface is configured on each router. IS-IS and BFD protocols are configured on both routers.
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the following commands, paste them into a
text file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your
network configuration, and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the
[edit] hierarchy level.
Router R1
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.255.1/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0001.0010.0255.0001.00 set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection version automatic set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection minimum-interval 200 set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection minimum-receive-interval 100 set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection multiplier 2 set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection no-adaptation set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection transmit-interval minimum-interval 100 set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection transmit-interval threshold 300 set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection detection-time threshold 500 set protocols isis interface lo0.0
Router R2
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.255.2/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0001.0010.0255.0002.00 set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection version automatic set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection minimum-interval 200 set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection minimum-receive-interval 100 set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection multiplier 2 set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection no-adaptation set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection transmit-interval minimum-interval 100 set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection transmit-interval threshold 300 set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection detection-time threshold 500 set protocols isis interface lo0.0
Procedure
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode.
To simply configure BFD for IS-IS, only the
minimum-interval statement is required. The BFD
protocol selects default parameters for all the other configuration
statements when you use the bfd-liveness-detection
statement without specifying any parameters.
You can change parameters at any time without stopping or restarting the existing session. BFD automatically adjusts to the new parameter value. However, no changes to BFD parameters take place until the values resynchronize with each BFD peer.
To configure BFD for IS-IS on Routers R1 and R2:
We are only showing the steps for R1.
-
Configure the threshold for the adaptation of the detection time, which must be greater than the multiplier number multiplied by the minimum interval.
[edit protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection] user@R1# set detection-time threshold 500
-
Configure the minimum transmit and receive intervals for failure detection.
[edit protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection] user@R1# set minimum-interval 200
-
Configure only the minimum receive interval for failure detection.
[edit protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection] user@R1# set minimum-receive-interval 100
-
Disable BFD adaptation.
[edit protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection] user@R1# set no-adaptation
-
Configure the threshold for the transmit interval, which must be greater than the minimum transmit interval.
[edit protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection] user@R1# set transmit-interval threshold 300
-
Configure the minimum transmit interval for failure detection.
[edit protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection] user@R1# set transmit-interval minimum-interval 100
-
Configure the multiplier number, which is the number of hello packets not received by the neighbor that causes the originating interface to be declared down.
[edit protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection] user@R1# set multiplier 2
-
Configure the BFD version used for detection.
The default is to have the version detected automatically.
[edit protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet bfd-liveness-detection] user@R1# set version automatic
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by issuing the show
protocols isis interface command. If the output does not display
the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to correct
the configuration.
user@R1# show protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 family inet
bfd-liveness-detection {
version automatic;
minimum-interval 200;
minimum-receive-interval 100;
multiplier 2;
no-adaptation;
transmit-interval {
minimum-interval 100;
threshold 300;
}
detection-time {
threshold 500;
}
}Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Verifying the Connection Between Routers R1 and R2
- Verifying That IS-IS Is Configured
- Verifying That BFD Is configured
Verifying the Connection Between Routers R1 and R2
Purpose
Make sure that Routers R1 and R2 can reach each other.
Action
Ping the other router to check the connectivity between the two routers as per the network topology.
user@R1> ping 10.0.0.2 count 2 PING 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=2.148 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.923 ms --- 10.0.0.2 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.923/2.035/2.148/0.113 ms
Meaning
Routers R1 and R2 are able to ping each other.
Verifying That IS-IS Is Configured
Purpose
Make sure that the IS-IS instance is running on both routers.
Action
Use the show isis database statement to check if the IS-IS
instance is running on both routers, R1 and R2.
user@R1> show isis database IS-IS level 1 link-state database: LSP ID Sequence Checksum Lifetime Attributes R1.00-00 0x1b 0xa2d5 552 L1 L2 R1.02-00 0x2b 0x8da3 545 L1 L2 R2.00-00 0x1a 0x628d 543 L1 L2 3 LSPs IS-IS level 2 link-state database: LSP ID Sequence Checksum Lifetime Attributes R1.00-00 0x1e 0xb9ba 552 L1 L2 R1.02-00 0x2b 0x8da3 545 L1 L2 R2.00-00 0x1d 0x877e 543 L1 L2 3 LSPs
Meaning
IS-IS is configured on both routers, R1 and R2.
Verifying That BFD Is configured
Purpose
Make sure that the BFD instance is running on both routers, R1 and R2.
Action
Use the show bfd session detail statement to check if BFD
instance is running on the routers.
user@R1> show bfd session detail
Detect Transmit
Address State Interface Time Interval Multiplier
10.0.0.2 Up ge-0/0/0.0 0.200 0.100 2
Client ISIS L1, TX interval 0.100, RX interval 0.100
Client ISIS L2, TX interval 0.100, RX interval 0.100
Session up time 00:02:41, previous down time 00:00:09
Local diagnostic None, remote diagnostic None
Remote state Up, version 1
Session type: Single hop BFD
1 sessions, 2 clients
Cumulative transmit rate 10.0 pps, cumulative receive rate 10.0 ppsMeaning
BFD is configured on Routers R1 and R2 for detecting failures in the IS-IS network.