ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring SRGB in Segment Routing for IS-IS
This example shows how to define the segment routing label block (SRGB) label range for segment packet routing in networking (SPRING) or segment routing (SR) for the IS-IS protocol. This configuration ensures that the labels are more predictable across the segment routing domain with a beneficial impact on network speed.
Our content testing team has validated and updated this example.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
-
Two MX Series routers
-
Junos OS Release 17.2 or later running on all devices
-
Updated and revalidated using vMX on Junos OS Release 21.1R1.
-
Are you interested in getting hands-on experience on this feature?
Visit Juniper vLabs to reserve your pre-configured vLab Sandbox: Segment Routing - Basic and try it out for free!
Before you configure the SRGB label range for segment routing in the IS-IS domain, be sure you configured the routing and signaling protocols.
Overview
Currently, Junos OS allows you to configure only node segment indices. The value of the start label depends on the dynamic label available in the system. Because there is no predictability of the dynamic label range being allocated to the SRGB, Junos OS allows you to configure the SRGB label range used by segment routing. The labels in the SRGB range are used for segment routing in the IS-IS domain. This means the labels advertised are more predictable and deterministic across the segment routing domain.
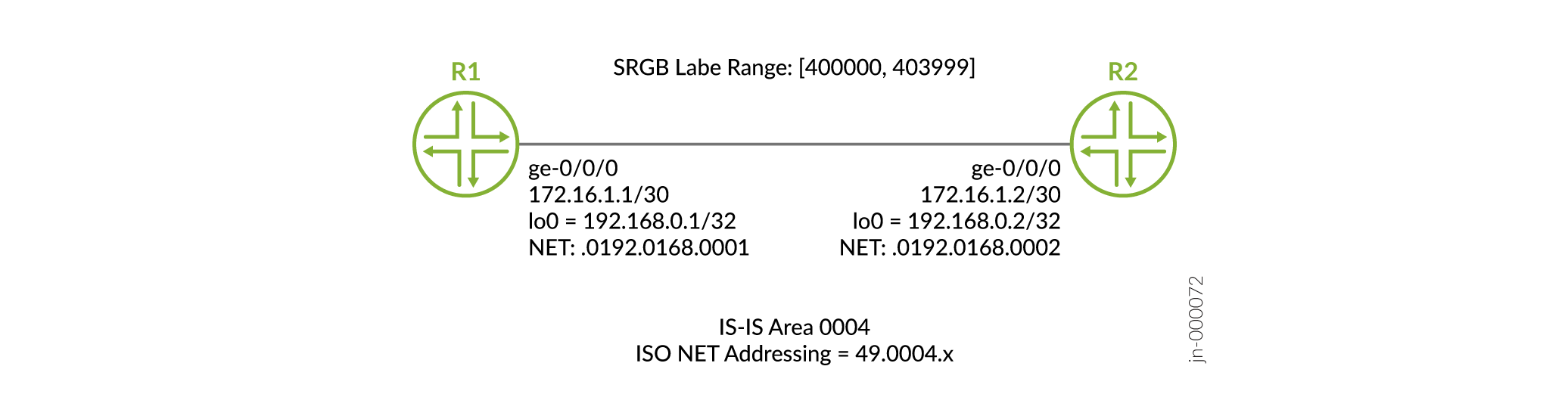
Topology
Figure 1 shows SRGB configured on router R1 and router R2.
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the following commands, paste them into a
text file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your
network configuration, copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the
[edit] hierarchy level, and then enter
commit from configuration mode.
R1
set chassis network-services enhanced-ip set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.1.1/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:1:1::1/128 set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0004.0192.0168.0001.00 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:10:10::1/128 set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 set protocols isis interface lo0.0 passive set protocols isis source-packet-routing srgb start-label 400000 set protocols isis source-packet-routing srgb index-range 4000 set protocols isis source-packet-routing node-segment ipv4-index 2001 set protocols isis source-packet-routing node-segment ipv6-index 3001 set protocols isis level 1 disable set protocols mpls interface ge-0/0/0.0
R2
set chassis network-services enhanced-ip set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.1.2/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:1:1::2/64 set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.2/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0004.0192.0168.0002.00 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:20:20::1/128 set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 set protocols isis interface lo0.0 passive set protocols isis source-packet-routing srgb start-label 400000 set protocols isis source-packet-routing srgb index-range 4000 set protocols isis source-packet-routing node-segment ipv4-index 2002 set protocols isis source-packet-routing node-segment ipv6-index 3002 set protocols isis level 1 disable set protocols mpls interface ge-0/0/0.0
Configuring Device R1
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires that you navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the Junos OS CLI User Guide.
To configure device R1:
Repeat this procedure for device R2 after modifying the appropriate interface names, addresses, and other parameters.
Configure enhanced-ip mode on the MX Series because the SRGB functionality is supported on routers with MPCs and MIC interfaces only. A system reboot is required after you commit this configuration.
[edit chassis] user@R1# set network-services enhanced-ip
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@R1# set ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.1.1/30 user@R1# set ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family iso user@R1# set ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:1:1::1/128 user@R1# set ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family mpls user@R1# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 user@R1# set lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0004.0192.0168.0001.00 user@R1# set lo0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:10:10::1/128
-
Configure the MPLS protocol on the interface. For segment routing to work, you can configure any of the statements under the [
edit protocols mpls] hierarchy. For example,abstract-hop,class-of-service,label-range,optimize-switchover-delay, et cetra.[edit protocols] user@R1# set mpls interface ge-0/0/0.0
Configure the start label and index range of SRGB.
Note:Ensure that the MPLS label for a binding segment ID (SID) is the sum of the SRGB start label and SID index value. In addition, SID index value must be less than or equal to the index-range value specified in the configuration.
-
Junos does not check whether the SID index is within the SRGB's range when the SID index is assigned through an IS-IS export policy. If you configure an index that is out of range of the configured SRGB, you won’t see any error message in the logs or while committing the configuration. Junos OS shows a commit error only when you configure the SID under the [edit protocols isis source-packet-routing] hierarchy level.
[edit protocols] user@R1# set isis source-packet-routing srgb start-label 400000 user@R1# set isis source-packet-routing srgb index-range 4000
Configure the IPv4 index value of the node segment.
[edit protocols] user@R1# set isis source-packet-routing node-segment ipv4-index 2001
Configure the IPv6 index value of the node segment.
[edit protocols] user@R1# set isis source-packet-routing node-segment ipv6-index 3001
Disable level 1, configure the IS-IS protocol on the interface, and configure loopback interface lo0.0 as passive..
[edit protocols] user@R1# set isis level 1 disable user@R1# set isis interface ge-0/0/0.0 user@R1# set isis interface lo0.0 passive
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show chassis, show interfaces, and show protocols commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
user@R1# show chassis network-services enhanced-ip;
user@R1# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.16.1.1/30;
}
family iso;
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:1:1::1/128;
}
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.0.1/32;
}
family iso {
address 49.0004.0192.0168.0001.00;
}
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:10:10::1/128;
}
}
}user@R1# show protocols
isis {
interface ge-0/0/0.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
source-packet-routing {
srgb start-label 400000 index-range 4000;
node-segment {
ipv4-index 2001;
ipv6-index 3001;
}
}
level 1 disable;
}
mpls {
interface ge-0/0/0.0;
}Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
Verifying the Configurable SRGB
Purpose
Verify the configurable SRGB label range in the IS-IS overview information.
Action
From operational mode, run the show isis overview command to
display the IS-IS overview information.
user@R1> show isis overview
Instance: master
Router ID: 128.53.50.230
IPv6 Router ID: abcd::128:53:50:230
Hostname: R1
Sysid: 1280.5305.0230
Areaid: 47.0005.80ff.f800.0000.0108.0001
Adjacency holddown: enabled
Maximum Areas: 3
LSP life time: 1200
Attached bit evaluation: enabled
SPF delay: 200 msec, SPF holddown: 5000 msec, SPF rapid runs: 3
IPv4 is enabled, IPv6 is enabled, SPRING based MPLS is enabled
Traffic engineering: enabled
Traffic engineering v6: disabled
Restart: Disabled
Helper mode: Enabled
Layer2-map: Disabled
Source Packet Routing (SPRING): Enabled
SRGB Config Range :
SRGB Start-Label : 400000, SRGB Index-Range : 4000
SRGB Block Allocation: Success
SRGB Start Index : 400000, SRGB Size : 4000, Label-Range: [ 400000, 403999 ]
Node Segments: Enabled
Ipv4 Index : 2001, Ipv6 Index : 3001
SRv6: Disabled
Post Convergence Backup: Disabled
Level 1
Internal route preference: 15
External route preference: 160
Prefix export count: 0
Wide metrics are enabled, Narrow metrics are enabled
Source Packet Routing is enabled
Level 2
Internal route preference: 18
External route preference: 165
Prefix export count: 0
Wide metrics are enabled, Narrow metrics are enabled
Source Packet Routing is enabled
Meaning
The output displays the configured SRGB start label and the SRGB index range. The end of the SRGB label range is the summation of the start label value and the index range. All devices in the segment routing domain must have the same SRGB range values.
