Example: Configure Ethernet CFM on Bridge Connections
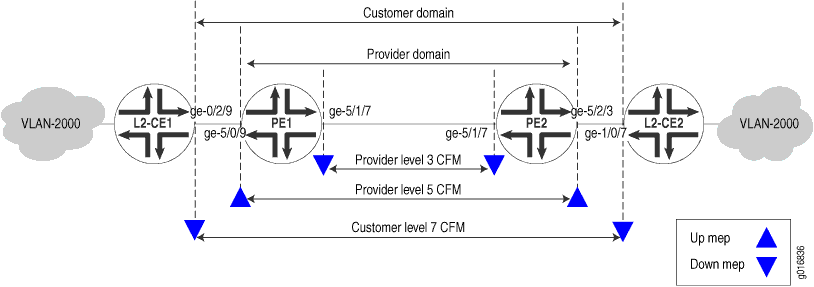
In this example, both the customer and service provider are running Ethernet CFM over a simple bridge network, as shown in Figure 1. The customer configures Ethernet CFM on routers that function as Layer 2 customer edge (CE) devices. The service provider configures Ethernet CFM on routers operate as provider edge (PE) and provider (P) devices.
The configurations in this example are only partial examples of complete and functional router configurations. Do not copy these configurations and use them directly on an actual system.
The service provider is using CFM level 3 for the link between PE1 and PE2 and level 5 from one CE facing port to the other. The customer is using CFM level 7. The boundaries are marked with “up mep” and “down mep” CFM terminology in the figure.
Here are the configurations of CFM on the customer routers.
CFM on L2-CE1
[edit interfaces]
ge-0/2/9 {
vlan-tagging;
unit 0 {
vlan-id 2000;
}
}
[edit protocols oam ethernet]
connectivity-fault-management {
maintenance-domain customer {
level 7;
maintenance-association customer-site1 {
continuity-check {
interval 1s;
}
mep 700 {
interface ge-0/2/9.0;
direction down;
auto-discovery;
}
}
}
}
CFM on L2-CE2
[edit interfaces]
ge-1/0/7 {
vlan-tagging;
unit 0 {
vlan-id 2000;
}
}
[edit protocols oam ethernet]
connectivity-fault-management {
maintenance-domain customer {
level 7;
maintenance-association customer-site2 {
continuity-check {
interval 1s;
}
mep 800 {
interface ge-1/0/7.0;
direction down;
auto-discovery;
}
}
}
}
Here are the configurations of CFM on the provider routers.
CFM on PE1
[edit interfaces]
ge-5/0/9 {
vlan-tagging;
encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services;
unit 0 {
encapsulation vlan-bridge;
vlan-id 2000;
}
}
ge-5/1/7 {
vlan-tagging;
encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services;
unit 0 {
encapsulation vlan-bridge;
vlan-id 2000;
}
}
[edit bridge-domains]
bridge-vlan2000 {
domain-type bridge;
vlan-id 2000;
interface ge-5/0/9.0;
interface ge-5/1/7.0;
}
[edit protocols oam ethernet connectivity-fault-management]
maintenance-domain provider-outer {
level 5;
maintenance-association provider-outer-site1 {
continuity-check {
interval 1s;
}
mep 200 {
interface ge-5/0/9.0;
direction up;
auto-discovery;
}
}
}
maintenance-domain provider-inner {
level 3;
maintenance-association provider-inner-site1 {
continuity-check {
interval 1s;
}
mep 200 {
interface ge-5/1/7.0;
direction down;
auto-discovery;
}
}
}
CFM on PE2
[edit interfaces]
ge-5/1/7 {
vlan-tagging;
encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services;
unit 0 {
encapsulation vlan-bridge;
vlan-id 2000;
}
}
ge-5/2/3 {
vlan-tagging;
encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services;
unit 0 {
encapsulation vlan-bridge;
vlan-id 2000;
}
}
[edit bridge-domains]
bridge-vlan2000 {
domain-type bridge;
interface ge-5/2/3.0;
interface ge-5/1/7.0;
}
[edit protocols oam ethernet connectivity-fault-management]
maintenance-domain provider-outer {
level 5;
maintenance-association provider-outer-site1 {
continuity-check {
interval 1s;
}
mep 100 {
interface ge-5/2/3.0;
direction up;
auto-discovery;
}
}
}
maintenance-domain provider-inner {
level 3;
maintenance-association provider-inner-site1 {
continuity-check {
interval 1s;
}
mep 100 {
interface ge-5/1/7.0;
direction down;
auto-discovery;
}
}
}
