ON THIS PAGE
Configure Threshold Values for Local Fault Events on an Interface
Example: Configure IEEE 802.3ah OAM Support for an Interface on ACX Series
Example: Configure Ethernet LFM Between Provider Edge and Customer Edge
Specify the Actions to Be Taken for Link-Fault Management Events
Configure Threshold Values for Fault Events in an Action Profile
Configure Link Fault Management
Use this topic to understand how to configure link fault management features on your device. You can also use this topic to configure an action profile to specify the LFM action that must be performed when a specific LFM event occurs and apply the action profile.
Starting in Junos OS Evolved 22.4R1 Release, the Ethernet link fault management process
(lfmd) runs only when the link-fault-management protocol is
configured.
Configure Link Discovery
When the IEEE 802.3ah OAM protocol is enabled on a physical interface, the discovery process is automatically triggered. The discovery process permits Ethernet interfaces to discover and monitor the peer on the link if it also supports the IEEE 802.3ah standard.
You can specify the discovery mode used for IEEE 802.3ah OAM support. The discovery process is triggered automatically when OAM IEEE 802.3ah functionality is enabled on a port. Link monitoring is done when the interface sends periodic OAM PDUs.
To configure the discovery mode, include the link-discovery statement at the [edit protocol oam ethernet link-fault-management
interface interface-name] hierarchy level:
[edit protocol oam ethernet link-fault-management interface interface-name] link-discovery (active | passive);
In active mode, the interface discovers and monitors the peer on the link if the peer also supports IEEE 802.3ah OAM functionality. In passive mode, the peer initiates the discovery process. After the discovery process has been initiated, both sides participate in discovery.
See Also
Configure the OAM PDU Interval
Periodic OAM PDUs are sent to perform link monitoring.
You can specify the periodic OAM PDU sending interval for fault detection.
To configure the sending interval, include the pdu-interval statement at the [edit protocol oam ethernet link-fault-management
interface interface-name] hierarchy level:
[edit protocol oam ethernet link-fault-management interface interface-name] pdu-interval interval;
The periodic OAM PDU interval range is from 100 through 1000 milliseconds. The default sending interval is 1000 milliseconds.
See Also
Configure the OAM PDU Threshold
You can specify the number of OAM PDUs that an interface can miss before the link between peers is considered down.
To configure the number of PDUs that can be missed from the
peer, include the pdu-threshold statement at the [edit
protocol oam ethernet link-fault-management interface interface-name] hierarchy level:
[edit protocol oam ethernet link-fault-management interface interface-name] pdu-threshold threshold-value;
The threshold value range is from 3 through 10. The default is three PDUs.
See Also
Configure Threshold Values for Local Fault Events on an Interface
You can configure threshold values on an interface for the local errors that trigger the sending of link event TLVs.
To set the error threshold values for sending event TLVs, include
the frame-error, frame-period, frame-period-summary, and symbol-period statements at the [edit protocols
oam ethernet link-fault-management interface interface-name event-thresholds] hierarchy level:
[edit protocol oam ethernet link-fault-management interface interface-name] event-thresholds { frame-error count; frame-period count; frame-period-summary count; symbol-period count; }
See Also
Disable the Sending of Link Event TLVs
You can disable the sending of link event TLVs.
To disable the monitoring and sending of PDUs containing link
event TLVs in periodic PDUs, include the no-allow-link-events statement at the [edit protocols oam ethernet link-fault-management
interface interface-name negotiation-options] hierarchy level:
[edit protocol oam ethernet link-fault-management interface interface-name negotiation-options] no-allow-link-events;
See Also
Example: Configure IEEE 802.3ah OAM Support on an Interface
Configure 802.3ah OAM support on a 10-Gigabit Ethernet interface:
[edit]
protocols {
oam {
ethernet {
link-fault-management {
interface xe-0/0/0 {
link-discovery active;
pdu-interval 800;
pdu-threshold 4;
remote-loopback;
negotiation-options {
allow-remote-loopback;
}
event-thresholds {
frame-error 30;
frame-period 50;
frame-period summary 40;
symbol-period 20;
}
}
}
}
}
}
See Also
Example: Configure IEEE 802.3ah OAM Support for an Interface on ACX Series
Junos OS for ACX Series routers allows the Ethernet interfaces on these routers to support the IEEE 802.3ah standard for the Operation, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) of Ethernet in access networks. The standard defines OAM link fault management (LFM). You can configure IEEE 802.3ah OAM LFM on point-to-point Ethernet links that are connected either directly or through Ethernet repeaters.
This example describes how to enable and configure OAM on a Gigabit Ethernet interface.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
Junos OS Release 12.2 or later for ACX Series routers.
An ACX1000 or ACX2000 router.
Overview and Topology
In this example, you configure a 10-Gigabit Ethernet interface on an ACX Series router with 802.3ah OAM support, which includes: link discovery, protocol data units (PDUs), remote loopback, negotiation, and event thresholds.
Configuring IEEE 802.3ah OAM on an ACX Series Router
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure IEEE 802.3ah Ethernet OAM, copy the following commands and paste them into the CLI:
edit edit protocols oam ethernet link-fault-management set interface xe-0/0/0 link-discovery active pdu-interval 800 pdu-threshold 4 remote-loopback negotiation-options allow-remote-loopback set interface xe-0/0/0 event-thresholds frame-error 30 frame-period 50 frame-period-summary 40 symbol-period 20
Procedure
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure IEEE 802.3ah OAM support on an interface:
Enable IEEE 802.3ah OAM support on an interface:
[edit protocols oam ethernet link-fault-management]
user@router1# set interface (OAM Link-Fault Management) xe-0/0/0
Specify that the interface initiates the discovery process by setting the link discovery mode to active:
user@router# set interface xe-0/0/0 link-discovery active
Set the periodic OAM PDU-sending interval (in milliseconds) to 800:
user@router# set interface xe-0/0/0 pdu-interval 800
Define the number of OAM PDUs to miss before an error is logged as 4:
user@router# set interface xe-0/0/0 pdu-threshold 4
Configure the remote interface into loopback mode so that all frames except OAM PDUs are looped back without any changes:
user@router# set interface xe-0/0/0 remote-loopback
Configure remote loopback support for the local interface:
user@router# set interface xe-0/0/0 negotiation-options allow-remote-loopback
Set the threshold count for sending frame error events to 30:
user@router# set interface xe-0/0/0 event-thresholds frame-error 30
Set the threshold count for sending frame period error events to 50:
user@router# set interface xe-0/0/0 event-thresholds frame-period 50
Configure the threshold count for sending frame period summary error events to 40:
user@router# set interface xe-0/0/0 event-thresholds frame-period-summary 40
Set the threshold count for sending symbol period events to 20:
user@router# set interface xe-0/0/0 event-thresholds symbol-period 20
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
[edit] user@router# show
[edit]
protocols {
oam {
ethernet {
link-fault-management {
interface xe-0/0/0 {
link-discovery active;
pdu-interval 800;
pdu-threshold 4;
remote-loopback;
negotiation-options {
allow-remote-loopback;
}
event-thresholds {
frame-error 30;
frame-period 50;
frame-period-summary 40;
symbol-period 20;
}
}
}
}
}
}
Example: Configure Ethernet LFM Between Provider Edge and Customer Edge
In this example, LFM is enabled on an IP link between the provider edge (PE) and customer edge (CE) interfaces. If the link goes down, the fault will be detected by LFM and the interfaces on both sides will be marked Link-Layer-Down. This results in notifications to various subsystems (for example, routing) which will take appropriate action.
The link running LFM is shown in Figure 1.
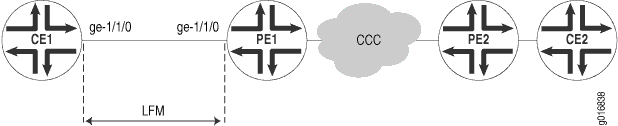
To configure Ethernet LFM on an IP link between PE and CE interfaces:
-
Configure LFM on the PE router:
[edit] interfaces ge-1/1/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address 11.11.11.1/24; } } } protocols { oam { ethernet { link-fault-management { interface ge-1/1/0 { pdu-interval 1000; pdu-threshold 5; } } } } } -
Configure LFM on the CE router:
[edit] interfaces ge-1/1/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address 11.11.11.2/24; } } } protocols { oam { ethernet { link-fault-management { interface ge-1/1/0 { pdu-interval 1000; pdu-threshold 5; } } } } }
See Also
Example: Configuring Ethernet LFM for CCC
In this example, LFM is configured between two PEs (PE1 and PE2) connected using CCC. With LFM in place, a link fault will be detected immediately, instead of depending on routing protocols to find the fault on end-to-end CCC connection. This also helps in detecting the exact failed link instead of only finding that the end-to-end CCC connectivity has failed. Also, because LFM runs at the link-layer level, it does not need a IP address to operate and so can be used where bidirectional fault detection (BFD) cannot.
The links running LFM are shown in Figure 2
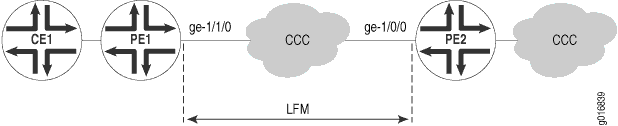
To configure Ethernet LFM between two PEs connected using CCC:
-
Configure LFM on the PE1 router with CCC:
[edit] interfaces ge-1/1/0 { encapsulation ethernet-ccc; unit 0; } protocols { oam { ethernet { link-fault-management { interface ge-1/1/0 { pdu-interval 1000; pdu-threshold 5; } } } } } -
Configure LFM on the PE2 router with CCC:
[edit] interfaces ge-1/0/0 { encapsulation ethernet-ccc; unit 0; } protocols { oam { ethernet { link-fault-management { interface ge-1/0/0 { pdu-interval 1000; pdu-threshold 5; } } } } }
See Also
Example: Configure Ethernet LFM for Aggregated Ethernet
In this example, LFM is configured on an aggregated Ethernet interface (AE0) between Router 1 and Router 2. When configured on aggregated Ethernet, LFM runs on all the individual member links. LFM is enabled or disabled on the member links as they are added or deleted from the aggregation group. The status of individual links is used to determine the status of the aggregated interface.
The use of LFM with aggregated Ethernet is shown in Figure 3.
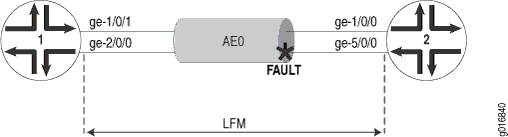
To configure LFM on an aggregated Ethernet interface between two routers:
-
Configure LFM on Router 1 for AE0:
[edit] chassis { aggregated-devices { ethernet { device-count 1; } } } interfaces ge-1/0/1 { gigether-options { 802.3ad ae0; } } interfaces ge-2/0/0 { gigether-options { 802.3ad ae0; } } interfaces ae0 { unit 0 { family inet { address 11.11.11.2/24; } } } protocols { oam { ethernet { link-fault-management { interface ae0; } } } } -
Configure LFM on Router 2 for AE0:
[edit] chassis { aggregated-devices { ethernet { device-count 1; } } } interfaces ge-1/0/0 { gigether-options { 802.3ad ae0; } } interfaces ge-5/0/0 { gigether-options { 802.3ad ae0; } } interfaces ae0 { unit 0 { family inet { address 11.11.11.1/24; } } } protocols { oam { ethernet { link-fault-management { interface ae0; } } } }
See Also
Configure an OAM Action Profile
You can create an action profile to define event fault flags and thresholds and the action to be taken. You can then apply the action profile to one or more interfaces.
To configure an action profile, include the action-profile statement at the [edit protocols oam ethernet link-fault-management] hierarchy level:
action-profile profile-name { action { syslog; link-down; send-critical-event; } event { link-adjacency-loss; link-event-rate { frame-error count; frame-period count; frame-period-summary count; symbol-period count; } protocol-down; } }
Starting from Junos OS Release 14.2, whenever link-fault management (LFM) with an action profile is configured to mark the interface as down (by including the link-down statement at the [edit protocols oam ethernet link-fault-management] hierarchy level), the port is placed in the blocked state (STP state). In such a state of the interface, data traffic is not transmitted out on that interface. Because the connectivity-fault management (CFM) downstream maintenance MEPs come up on blocked ports, the CFM sessions come up properly. However, the interface is down and the interface status TLV does not contain the correct status. Only if you configure the port status TLV, the actual status of the port is reflected. The interface status TLV does not carry the actual state of the port.
See Also
Specify the Actions to Be Taken for Link-Fault Management Events
You can specify the action to be taken by the system when the configured link-fault event occurs. Multiple action profiles can be applied to a single interface. For each action-profile, at least one event and one action must be specified. The actions are taken only when all of the events in the action profile are true. If more than one action is specified, all the actions are executed.
You might want to set a lower threshold for a specific action such as logging the error and set a higher threshold for another action such as sending a critical event TLV.
To specify the action, include the action statement
at the [edit protocols oam ethernet link-fault-management action-profile profile-name] hierarchy level:
[edit protocol oam ethernet link-fault-management action-profile profile-name]
event {
link-adjacency-loss;
protocol-down;
}
action {
syslog;
link-down;
send-critical-event;
}
To create a system log entry when the link-fault event occurs,
include the syslog statement.
To administratively disable the link when the link-fault event
occurs, include the link-down statement.
To send IEEE 802.3ah link event TLVs in the OAM PDU when a link-fault
event occurs, include the send-critical-event statement.
If multiple actions are specified in the action profile, all of the actions are executed in no particular order.
See Also
Monitor the Loss of Link Adjacency
You can specify actions be taken when link adjacency is lost.
When link adjacency is lost, the system takes the action defined in
the action statement of the action profile.
To configure the system to take action when link adjacency is
lost, include the link-adjacency-loss statement at the [edit protocols oam ethernet link-fault-management action-profile profile-name event] hierarchy level:
[edit protocol oam ethernet link-fault-management action-profile profile-name] link-adjacency-loss;
See Also
Monitor Protocol Status
The CCC-DOWN flag is associated with a circuit cross-connect (CCC) connection, Layer 2 circuit, and Layer 2 VPN, which send the CCC-DOWN status to the kernel. The CCC-DOWN flag indicates that the CCC is down. The CCC-DOWN status is sent to the kernel when the CCC connection, Layer 2 circuit, or Layer 2 VPN is down. This in turn, brings down the CE-facing PE interface associated with the CCC connection, Layer 2 circuit, or Layer 2 VPN.
When the CCC-DOWN flag is signaled to the IEEE 802.3ah protocol,
the system takes the action defined in the action statement
of the action profile. For
additional information about Layer 2 circuits, see the Junos OS Layer
2 Circuits User Guide, Junos OS VPNs Configuration Guide.
To monitor the IEEE 802.3ah protocol, on
the CE-facing PE interface, include the protocol-down statement
at the [edit protocols oam ethernet link-fault-management action-profile profile-name event] hierarchy level:
If multiple events are specified in the action profile, all the events must occur before the specified action is taken.
See Also
Configure Threshold Values for Fault Events in an Action Profile
You can configure link event thresholds for received error events
that trigger the action specified in the action statement.
You can then apply the action profile to one or more interfaces.
To configure link event thresholds, include the link-event-rate statement at the [edit protocols oam ethernet link-fault-management
action-profile profile-name event] hierarchy
level:
link-event-rate { frame-error count; frame-period count; frame-period-summary count; symbol-period count; }
See Also
Apply an Action Profile
You can apply an action profile to one or more interfaces.
To apply an action profile to an interface, include the apply-action-profile statement at the [edit protocols
oam ethernet link-fault-management action-profile interface interface-name] hierarchy level:
[edit protocol oam ethernet link-fault-management interface interface-name] apply-action-profile profile-name;
See Also
Change History Table
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.
