Example: Prioritizing Snooped and Inspected Packet
On EX Series switches you might need to use class of service (CoS) to protect packets from critical applications from being dropped during periods of network congestion and delay and you might also need the port security features of DHCP snooping and dynamic ARP inspection (DAI) on the same ports through which those critical packets are entering and leaving. You can combine the advantages of both these features by using CoS forwarding classes and queues to prioritize snooped and inspected packets. This type of configuration places the snooped and inspected packets in the desired egress queue, ensuring that the security procedure does not interfere with the transmittal of this high-priority traffic. This is especially important for traffic that is sensitive to jitter and delay, such as voice traffic.
This example shows how to configure the switch to prioritize snooped and inspected packets in heavy network traffic.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
One EX Series switch
Junos OS Release 11.2 or later for EX Series switches
A DHCP server to provide IP addresses to network devices on the switch
Before you specify CoS forwarding classes for snooped and inspected packets, be sure you have:
Connected the DHCP server to the switch.
Configured the VLAN VLAN200 on the switch. See Configuring VLANs for EX Series Switches.
Configured two interfaces, ge-0/0/1 and ge-0/0/8, to belong to VLAN200.
Overview and Topology
Ethernet LANs are vulnerable to address spoofing and DoS attacks on network devices. To protect the devices from such attacks, you can configure DHCP snooping to validate DHCP server messages and DAI to protect against MAC spoofing. If you have to deal with periods of heavy network congestion and you want to ensure that sensitive traffic is not disrupted, you can combine the port security features with CoS forwarding classes to prioritize the handling of the snooped and inspected security packets.
In the default switch configuration:
Secure port access is activated on the switch.
DHCP snooping and DAI are disabled on all VLANs.
All access ports are untrusted and all trunk ports are trusted for DHCP snooping.
This example shows how to combine the DHCP snooping and DAI security features with prioritized forwarding of snooped and inspected packets.
The setup for this example includes the VLAN VLAN200 on the switch. Figure 1 illustrates the topology for this example.
Topology
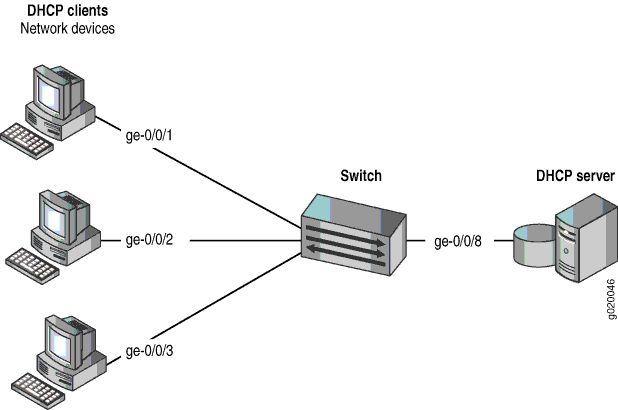
The components of the topology for this example are shown in Table 1.
| Properties | Settings |
|---|---|
Switch hardware |
EX Series switch |
VLAN name |
VLAN200 |
Interfaces in VLAN200 |
ge-0/0/1,ge-0/0/2,ge-0/0/3,ge-0/0/8 |
Interface for DHCP server |
ge-0/0/8 |
In the configuration tasks for this example, you create a user-defined forwarding class c1, you enable DHCP snooping and DAI on VLAN200, and you assign the snooped and inspected packets to forwarding class c1 and queue 6. Queues 6 and 7 are reserved for high priority, control packets. The packets that are subjected to DHCP snooping and DAI are control (not data) packets; therefore, it is appropriate to place these snooped and inspected high-priority control packets in queue 6. (Queue 7 is higher priority than queue 6 and can also be used for this purpose.)
Configuration
To configure DHCP snooping and DAI on VLAN200, and to prioritize the snooped and inspected packets:
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure DHCP snooping and DAI with prioritized forwarding of snooped and inspected packets, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit]
set class-of-service forwarding-classes class c1 queue 6
set ethernet-switching-options security-access-port vlan VLAN200 examine-dhcp forwarding-class c1
set ethernet-switching-options security-access-port vlan VLAN200 arp-inspection forwarding-class c1Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure DHCP and DAI with prioritized forwarding of snooped and inspected packets:
Create a user-defined forwarding class to be used for prioritizing the snooped and inspected packets.
[edit class-of-service] user@switch# set forwarding-classes class c1 queue 6
Enable DHCP snooping on the VLAN and apply forwarding class c1 to the snooped packets:
[edit ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port] user@switch# set vlan VLAN200 examine-dhcp forwarding-class c1
Enable DAI on the VLAN and apply forwarding class c1 to the inspected packets:
[edit ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port] user@switch# set vlan VLAN200 arp-inspection forwarding-class c1
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
[edit ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port]
user@switch# show
vlan VLAN200 {
arp-inspection forwarding-class c1;
examine-dhcp forwarding-class c1;
}
[edit class-of-service]
user@switch# show
}
forwarding-classes {
class c1 queue-num 6;
}
Verification
To confirm that the configuration is working properly, perform these tasks:
- Verifying That Prioritized Forwarding Is Working Correctly on the Snooped Packets
- Verifying That Prioritized Forwarding Is Working Correctly on the DAI Inspected Packets
Verifying That Prioritized Forwarding Is Working Correctly on the Snooped Packets
Purpose
Verify that prioritized forwarding is working on the DHCP snooped packets.
Action
Send some DHCP requests from network devices to the switch. Display the output queue for one of the interfaces in VLAN200 to make sure that the packets are being transmitted in the designated queue:
user@switch> show interfaces ge 0/0/1 extensive
Egress queues: 8 supported, 5 in use
Queue counters: Queued packets Transmitted packets Dropped packets
0 best-effort 0 0 0
1 assured-forw 0 0 0
5 expedited-fo 0 0 0
6 c1 0 3209 0
7 network-cont 0 126371 0
Meaning
The command output shows that packets have been transmitted on forwarding class c1 queue 6.
Continue testing by changing the setting of examine-dhcp forwarding-class to
use one of the default queues, such as best-effort, and repeat the show interfaces command to compare the difference in the output. You can tell that the setting is working
correctly by seeing the difference in the number of transmitted packets reported for forwarding
class c1 queue 6.
Verifying That Prioritized Forwarding Is Working Correctly on the DAI Inspected Packets
Purpose
Verify that prioritized forwarding is working on the DAI inspected packets.
Action
Send some ARP requests from network devices to the switch. Display the output queue for one of the interfaces in VLAN200 to make sure that the packets are being transmitted in the designated queue:
user@switch> show interfaces ge-0/0/1 extensive
Egress queues: 8 supported, 5 in use
Queue counters: Queued packets Transmitted packets Dropped packets
0 best-effort 0 0 0
1 assured-forw 0 0 0
5 expedited-fo 0 0 0
6 c1 0 3209 0
7 network-cont 0 126371 0
Meaning
The command output shows that packets have been transmitted on forwarding class c1 queue 6.
Continue testing by changing the setting of arp-inspection forwarding-class to use one of the default queues, such as best-effort, and repeat the show interfaces command to compare the difference in the output. You can tell that the setting is working
correctly by seeing the difference in the number of transmitted packets reported for forwarding
class c1 queue 6.
