Example: Protecting Against ARP Spoofing Attacks
In an ARP spoofing attack, the attacker associates its own MAC address with the IP address of a network device connected to the switch. Traffic intended for that IP address is now sent to the attacker instead of being sent to the intended destination. The attacker can send faked, or “spoofed,” ARP messages on the LAN.
When dynamic ARP inspection (DAI) is enabled, the switch logs the number of invalid ARP packets that it receives on each interface, along with the sender’s IP and MAC addresses. You can use these log messages to discover ARP spoofing on the network. ARP probe packets are not subjected to dynamic ARP inspection. The switch always forwards such packets.
This example describes how to configure DHCP snooping and dynamic ARP inspection (DAI), two port security features, to protect the switch against ARP spoofing attacks:
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
One EX Series switch or one QFX3500 switch
Junos OS Release 11.4 or later for EX Series switches or Junos OS Release 12.1 or later for the QFX Series
A DHCP server to provide IP addresses to network devices on the switch
Before you configure DHCP snooping and DAI (two port security features) to mitigate ARP spoofing attacks, be sure you have:
Connected the DHCP server to the switch.
Configured a VLAN on the switch. See the task for your platform:
Overview and Topology
Ethernet LANs are vulnerable to address spoofing and DoS attacks on network devices. This example describes how to protect the switch against one common type of attack, an ARP spoofing attack.
In an ARP spoofing attack, the attacker sends faked ARP messages, thus creating various types of problems on the LAN—for example, the attacker might launch a man-in-the middle attack.
This example shows how to configure port security features on a switch that is connected to a DHCP server. The setup for this example includes the VLAN employee-vlan on the switch. The procedure for creating that VLAN is described in the topic Example: Setting Up Bridging with Multiple VLANs for EX Series Switches and Example: Setting Up Bridging with Multiple VLANs on Switches for the QFX Series. That procedure is not repeated here. Figure 1 illustrates the topology for this example.
Topology
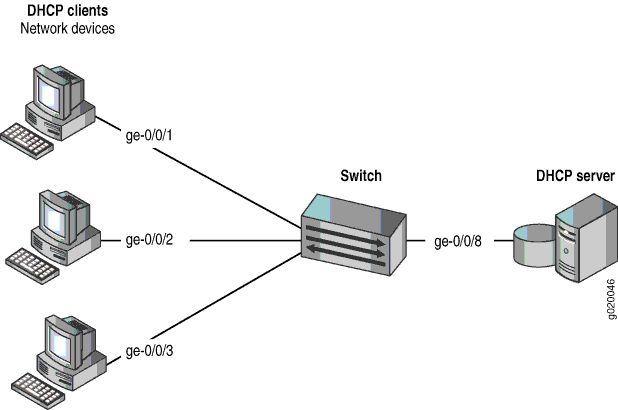
The components of the topology for this example are shown in Table 1.
| Properties | Settings |
|---|---|
Switch hardware |
One EX3200-24P, 24 ports (8 PoE ports) or one QFX3500 switch |
VLAN name and ID |
employee-vlan, tag 20 |
VLAN subnets |
192.0.2.16/28 192.0.2.17 through 192.0.2.30192.0.2.31 is the subnet's broadcast address |
Interfaces in employee-vlan |
ge-0/0/1,ge-0/0/2, ge-0/0/3, ge-0/0/8 |
Interface for DHCP server |
ge-0/0/8 |
In this example, the switch has already been configured as follows:
Secure port access is activated on the switch.
DHCP snooping is disabled on the VLAN employee-vlan.
All access ports are untrusted, which is the default setting.
Configuration
To configure DHCP snooping and dynamic ARP inspection (DAI) to protect the switch against ARP attacks:
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure DHCP snooping and dynamic ARP inspection (DAI), copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port] user@switch# set interface ge-0/0/8 dhcp-trusted user@switch# set vlan employee-vlan examine-dhcp user@switch# set vlan employee-vlan arp-inspection
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure DHCP snooping and dynamic ARP inspection (DAI) on the VLAN:
Set the ge-0/0/8 interface as trusted:
[edit ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port] user@switch# set interface ge-0/0/8 dhcp-trusted
Enable DHCP snooping on the VLAN:
[edit ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port] user@switch# set vlan employee-vlan examine-dhcp
Enable DAI on the VLAN:
[edit ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port] user@switch# set vlan employee-vlan arp-inspection
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
[edit ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port]
user@switch# show
interface ge-0/0/8.0 {
dhcp-trusted;
}
vlan employee-vlan {
arp-inspection;
examine-dhcp;
}
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Verifying That DHCP Snooping Is Working Correctly on the Switch
- Verifying That DAI Is Working Correctly on the Switch
Verifying That DHCP Snooping Is Working Correctly on the Switch
Purpose
Verify that DHCP snooping is working on the switch.
Action
Send some DHCP requests from network devices (here they are DHCP clients) connected to the switch.
Display the DHCP snooping information when the port on which the DHCP server connects to the switch is trusted. The following output results when requests are sent from the MAC addresses and the server has provided the IP addresses and leases:
user@switch> show dhcp-snooping binding DHCP Snooping Information: MAC Address IP Address Lease Type VLAN Interface ----------------- ---------- ----- ---- ---- --------- 00:05:85:3A:82:77 192.0.2.17 600 dynamic employee-vlan ge-0/0/1.0 00:05:85:3A:82:79 192.0.2.18 653 dynamic employee-vlan ge-0/0/1.0 00:05:85:3A:82:80 192.0.2.19 720 dynamic employee-vlan ge-0/0/2.0 00:05:85:3A:82:81 192.0.2.20 932 dynamic employee-vlan ge-0/0/2.0 00:05:85:3A:82:83 192.0.2.21 1230 dynamic employee-vlan ge-0/0/2.0 00:05:85:27:32:88 192.0.2.22 3200 dynamic employee-vlan ge-0/0/3.0
Meaning
When the interface on which the DHCP server connects to the switch has been set to trusted, the output (see preceding sample) shows, for each MAC address, the assigned IP address and lease time—that is, the time, in seconds, remaining before the lease expires.
Verifying That DAI Is Working Correctly on the Switch
Purpose
Verify that DAI is working on the switch.
Action
Send some ARP requests from network devices connected to the switch.
Display the DAI information:
user@switch> show arp inspection statistics ARP inspection statistics: Interface Packets received ARP inspection pass ARP inspection failed --------------- --------------- -------------------- --------------------- ge-0/0/1.0 7 5 2 ge-0/0/2.0 10 10 0 ge-0/0/3.0 12 12 0
Meaning
The sample output shows the number of ARP packets received and inspected per interface, with a listing of how many packets passed and how many failed the inspection on each interface. The switch compares the ARP requests and replies against the entries in the DHCP snooping database. If a MAC address or IP address in the ARP packet does not match a valid entry in the database, the packet is dropped.
