ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring Redundant Virtual Tunnel Interfaces in MBGP MVPNs
This example shows how to configure redundant virtual tunnel (VT) interfaces in multiprotocol BGP (MBGP) multicast VPNs (MVPNs). To configure, include multiple VT interfaces in the routing instance and, optionally, apply the primary statement to one of the VT interfaces.
Overview
In this example, Device PE2 has redundant VT interfaces configured in a multicast LDP routing instance, and one of the VT interfaces is assigned to be the primary interface.
Figure 1 shows the topology used in this example.
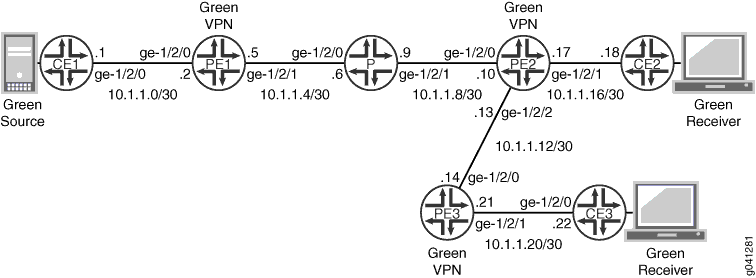
The following example shows the configuration for the customer edge (CE), provider (P), and provider edge (PE) devices in Figure 1. The section Step-by-Step Procedure describes the steps on Device PE2.
Configuration
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network configuration, and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Device CE1
set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.0.2.1/24 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols pim rp static address 198.51.100.0 set protocols pim interface all set routing-options router-id 192.0.2.1
Device CE2
set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.18/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.0.2.6/24 set protocols sap listen 192.168.0.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols pim rp static address 198.51.100.0 set protocols pim interface all set routing-options router-id 192.0.2.6
Device CE3
set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.22/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.0.2.7/24 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols pim rp static address 198.51.100.0 set protocols pim interface all set routing-options router-id 192.0.2.7
Device P
set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.6/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.9/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.0.2.3/24 set protocols mpls interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols mpls interface ge-1/2/1.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.0 set protocols ldp interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols ldp interface ge-1/2/1.0 set protocols ldp p2mp set routing-options router-id 192.0.2.3
Device PE1
set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.5/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces vt-1/2/0 unit 2 family inet set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.0.2.2/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 1 family inet address 198.51.100.0/24 set protocols mpls interface ge-1/2/1.0 set protocols bgp group ibgp type internal set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 192.0.2.2 set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet-vpn any set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet-mvpn signaling set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 192.0.2.4 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 192.0.2.5 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.0 set protocols ldp interface ge-1/2/1.0 set protocols ldp p2mp set policy-options policy-statement parent_vpn_routes from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement parent_vpn_routes then accept set routing-instances vpn-1 instance-type vrf set routing-instances vpn-1 interface ge-1/2/0.0 set routing-instances vpn-1 interface vt-1/2/0.2 multicast set routing-instances vpn-1 interface lo0.1 set routing-instances vpn-1 route-distinguisher 100:100 set routing-instances vpn-1 provider-tunnel ldp-p2mp set routing-instances vpn-1 vrf-target target:1:1 set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols ospf export parent_vpn_routes set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.1 passive set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.0 set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols pim rp static address 198.51.100.0 set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols pim interface ge-1/2/0.0 mode sparse set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols mvpn set routing-options router-id 192.0.2.2 set routing-options autonomous-system 1001
Device PE2
set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.10/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.13/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/2 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.17/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces vt-1/1/0 unit 0 family inet set interfaces vt-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.0.2.4/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 1 family inet address 203.0.113.4/24 set protocols mpls interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols mpls interface ge-1/2/2.0 set protocols bgp group ibgp type internal set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 192.0.2.4 set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet-vpn any set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet-mvpn signaling set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 192.0.2.2 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 192.0.2.5 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/2.0 set protocols ldp interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols ldp interface ge-1/2/2.0 set protocols ldp p2mp set policy-options policy-statement parent_vpn_routes from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement parent_vpn_routes then accept set routing-instances vpn-1 instance-type vrf set routing-instances vpn-1 interface vt-1/1/0.0 multicast set routing-instances vpn-1 interface vt-1/1/0.0 primary set routing-instances vpn-1 interface vt-1/2/1.0 multicast set routing-instances vpn-1 interface ge-1/2/1.0 set routing-instances vpn-1 interface lo0.1 set routing-instances vpn-1 route-distinguisher 100:100 set routing-instances vpn-1 vrf-target target:1:1 set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols ospf export parent_vpn_routes set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.1 passive set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.0 set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols pim rp static address 198.51.100.0 set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols pim interface ge-1/2/1.0 mode sparse set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols mvpn set routing-options router-id 192.0.2.4 set routing-options autonomous-system 1001
Device PE3
set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.14/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.21/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces vt-1/2/0 unit 5 family inet set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.0.2.5/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 1 family inet address 203.0.113.5/24 set protocols mpls interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols bgp group ibgp type internal set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 192.0.2.5 set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet-vpn any set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet-mvpn signaling set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 192.0.2.2 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 192.0.2.4 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols ldp interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols ldp p2mp set policy-options policy-statement parent_vpn_routes from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement parent_vpn_routes then accept set routing-instances vpn-1 instance-type vrf set routing-instances vpn-1 interface vt-1/2/0.5 multicast set routing-instances vpn-1 interface ge-1/2/1.0 set routing-instances vpn-1 interface lo0.1 set routing-instances vpn-1 route-distinguisher 100:100 set routing-instances vpn-1 vrf-target target:1:1 set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols ospf export parent_vpn_routes set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.1 passive set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.0 set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols pim rp static address 198.51.100.0 set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols pim interface ge-1/2/1.0 mode sparse set routing-instances vpn-1 protocols mvpn set routing-options router-id 192.0.2.5 set routing-options autonomous-system 1001
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the CLI User Guide.
To configure redundant VT interfaces in an MBGP MVPN:
Configure the physical interfaces and loopback interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@PE2# set ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.10/30 user@PE2# set ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls user@PE2# set ge-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.13/30 user@PE2# set ge-1/2/2 unit 0 family mpls user@PE2# set ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.17/30 user@PE2# set ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls user@PE2# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.0.2.4/24 user@PE2# set lo0 unit 1 family inet address 203.0.113.4/24
Configure the VT interfaces.
Each VT interface is configurable under one routing instance.
[edit interfaces] user@PE2# set vt-1/1/0 unit 0 family inet user@PE2# set vt-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet
Configure MPLS on the physical interfaces.
[edit protocols mpls] user@PE2# set interface ge-1/2/0.0 user@PE2# set interface ge-1/2/2.0
Configure BGP.
[edit protocols bgp group ibgp] user@PE2# set type internal user@PE2# set local-address 192.0.2.4 user@PE2# set family inet-vpn any user@PE2# set family inet-mvpn signaling user@PE2# set neighbor 192.0.2.2 user@PE2# set neighbor 192.0.2.5
Configure an interior gateway protocol.
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@PE2# set interface lo0.0 passive user@PE2# set interface ge-1/2/0.0 user@PE2# set interface ge-1/2/2.0
Configure LDP.
[edit protocols ldp] user@PE2# set interface ge-1/2/0.0 user@PE2# set interface ge-1/2/2.0 user@PE2# set p2mp
Configure the routing policy.
[edit policy-options policy-statement parent_vpn_routes] user@PE2# set from protocol bgp user@PE2# set then accept
Configure the routing instance.
[edit routing-instances vpn-1] user@PE2# set instance-type vrf user@PE2# set interface ge-1/2/1.0 user@PE2# set interface lo0.1 user@PE2# set route-distinguisher 100:100 user@PE2# set vrf-target target:1:1 user@PE2# set protocols ospf export parent_vpn_routes user@PE2# set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.1 passive user@PE2# set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.0 user@PE2# set protocols pim rp static address 198.51.100.0 user@PE2# set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/1.0 mode sparse user@PE2# set protocols mvpn
Configure redundant VT interfaces in the routing instance.
Make vt-1/1/0.0 the primary interface.
[edit routing-instances vpn-1] user@PE2# set interface vt-1/1/0.0 multicast primary user@PE2# set interface vt-1/2/1.0 multicast
Configure the router ID and autonomous system (AS) number.
[edit routing-options] user@PE2# set router-id 192.0.2.4 user@PE2# set autonomous-system 1001
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options, show routing-instances, and show routing-options commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the configuration instructions in this example to correct it.
user@PE2# show interfaces
ge-1/2/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.1.1.10/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/2/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.1.1.13/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/2/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.1.1.17/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
vt-1/1/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet;
}
}
vt-1/2/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.0.2.4/24;
}
}
unit 1 {
family inet {
address 203.0.113.4/24;
}
}
}
user@PE2# show protocols
mpls {
interface ge-1/2/0.0;
interface ge-1/2/2.0;
}
bgp {
group ibgp {
type internal;
local-address 192.0.2.4;
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
family inet-mvpn {
signaling;
}
neighbor 192.0.2.2;
neighbor 192.0.2.5;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface ge-1/2/0.0;
interface ge-1/2/2.0;
}
}
ldp {
interface ge-1/2/0.0;
interface ge-1/2/2.0;
p2mp;
}
user@PE2# show policy-options
policy-statement parent_vpn_routes {
from protocol bgp;
then accept;
}
user@PE2# show routing-instances
vpn-1 {
instance-type vrf;
interface vt-1/1/0.0 {
multicast;
primary;
}
interface vt-1/2/1.0 {
multicast;
}
interface ge-1/2/1.0;
interface lo0.1;
route-distinguisher 100:100;
vrf-target target:1:1;
protocols {
ospf {
export parent_vpn_routes;
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.1 {
passive;
}
interface ge-1/2/1.0;
}
}
pim {
rp {
static {
address 198.51.100.0;
}
}
interface ge-1/2/1.0 {
mode sparse;
}
}
mvpn;
}
}
user@PE2# show routing-options router-id 192.0.2.4; autonomous-system 1001;
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
The show multicast route extensive instance instance-name command also displays the VT interface in the multicast forwarding table when multicast traffic is transmitted across the VPN.
Checking the LSP Route
Purpose
Verify that the expected LT interface is assigned to the LDP-learned route.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show route table mpls command.
user@PE2> show route table mpls mpls.0: 13 destinations, 13 routes (13 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 0 *[MPLS/0] 02:09:36, metric 1 Receive 1 *[MPLS/0] 02:09:36, metric 1 Receive 2 *[MPLS/0] 02:09:36, metric 1 Receive 13 *[MPLS/0] 02:09:36, metric 1 Receive 299776 *[LDP/9] 02:09:14, metric 1 > via ge-1/2/0.0, Pop 299776(S=0) *[LDP/9] 02:09:14, metric 1 > via ge-1/2/0.0, Pop 299792 *[LDP/9] 02:09:09, metric 1 > via ge-1/2/2.0, Pop 299792(S=0) *[LDP/9] 02:09:09, metric 1 > via ge-1/2/2.0, Pop 299808 *[LDP/9] 02:09:04, metric 1 > via ge-1/2/0.0, Swap 299808 299824 *[VPN/170] 02:08:56 > via ge-1/2/1.0, Pop 299840 *[VPN/170] 02:08:56 > via ge-1/2/1.0, Pop 299856 *[VPN/170] 02:08:56 receive table vpn-1.inet.0, Pop 299872 *[LDP/9] 02:08:54, metric 1 > via vt-1/1/0.0, Pop via ge-1/2/2.0, Swap 299872From configuration mode, change the primary VT interface by removing the
primarystatement from the vt-1/1/0.0 interface and adding it to the vt-1/2/1.0 interface.[edit routing-instances vpn-1] user@PE2# delete interface vt-1/1/0.0 primary user@PE2# set interface vt-1/2/1.0 primary user@PE2# commit
From operational mode, enter the show route table mpls command.
user@PE2> show route table mpls mpls.0: 13 destinations, 13 routes (13 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 0 *[MPLS/0] 02:09:36, metric 1 Receive 1 *[MPLS/0] 02:09:36, metric 1 Receive 2 *[MPLS/0] 02:09:36, metric 1 Receive 13 *[MPLS/0] 02:09:36, metric 1 Receive 299776 *[LDP/9] 02:09:14, metric 1 > via ge-1/2/0.0, Pop 299776(S=0) *[LDP/9] 02:09:14, metric 1 > via ge-1/2/0.0, Pop 299792 *[LDP/9] 02:09:09, metric 1 > via ge-1/2/2.0, Pop 299792(S=0) *[LDP/9] 02:09:09, metric 1 > via ge-1/2/2.0, Pop 299808 *[LDP/9] 02:09:04, metric 1 > via ge-1/2/0.0, Swap 299808 299824 *[VPN/170] 02:08:56 > via ge-1/2/1.0, Pop 299840 *[VPN/170] 02:08:56 > via ge-1/2/1.0, Pop 299856 *[VPN/170] 02:08:56 receive table vpn-1.inet.0, Pop 299872 *[LDP/9] 02:08:54, metric 1 > via vt-1/2/1.0, Pop via ge-1/2/2.0, Swap 299872
Meaning
With the original configuration, the output shows the vt-1/1/0.0 interface. If you change the primary interface to vt-1/2/1.0, the output shows the vt-1/2/1.0 interface.
