Example: Configuring a Specific Tunnel for IPv4 Multicast VPN Traffic (Using Draft-Rosen MVPNs)
This example shows how to configure different provider tunnels to carry IPv4 customer traffic in a multicast VPN network.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
Four Juniper Networks devices: Two PE routers and two CE switching or routing devices.
Overview
A multicast tunnel is a mechanism to deliver control and data traffic across the provider core in a multicast VPN. Control and data packets are transmitted over the multicast distribution tree in the provider core. When a service provider carries both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic from a single customer, it is sometimes useful to separate the IPv4 and IPv6 traffic onto different multicast tunnels within the customer VRF routing instance. Putting customer IPv4 and IPv6 traffic on two different tunnels provides flexibility and control. For example, it helps the service provider to charge appropriately, to manage and measure traffic patterns, and to have an improved capability to make decisions when deploying new services.
A draft-rosen 7 multicast VPN control plane is configured in this example. The control plane is configured to use source-specific multicast (SSM) mode. The provider tunnel is used for the draft-rosen 7 control traffic and IPv4 customer traffic.
This example uses the following statements to configure the draft-rosen 7 control plane and specify IPv4 traffic to be carried in the provider tunnel:
provider-tunnel pim-ssm family inet group-address 232.1.1.1pim mvpn family inet autodiscovery inet-mdtpim mvpn family inet6 disablemvpn family inet autodiscovery-only intra-as inclusivefamily inet-mdt signaling
Note the following limitations:
Junos OS does not currently support IPv6 with draft-rosen 6 or draft-rosen 7.
Junos OS does not support more than two provider tunnels in a routing instance. For example, you cannot configure an RSVP-TE provider tunnel plus two MVPN provider tunnels.
In a routing instance, you cannot configure both an any-source multicast (ASM) tunnel and an SSM tunnel.
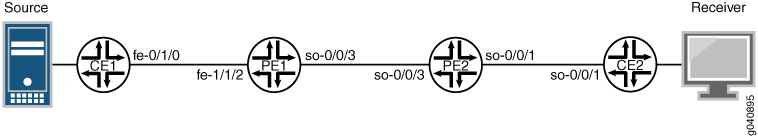
Topology Diagram
Figure 1 shows the topology used in this example.
PE Router Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Router PE1
set interfaces so-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.111.10.1/30 set interfaces so-0/0/3 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces fe-1/1/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.10.10.1/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.255.182.133/32 primary set interfaces lo0 unit 1 family inet address 10.10.47.100/32 set routing-options router-id 10.255.182.133 set routing-options route-distinguisher-id 10.255.182.133 set routing-options autonomous-system 100 set routing-instances VPN-A instance-type vrf set routing-instances VPN-A interface fe-1/1/2.0 set routing-instances VPN-A interface lo0.1 set routing-instances VPN-A provider-tunnel pim-ssm family inet group-address 232.1.1.1 set routing-instances VPN-A provider-tunnel mdt threshold group 224.1.1.0/24 source 10.240.0.242/32 rate 10 set routing-instances VPN-A provider-tunnel mdt tunnel-limit 20 set routing-instances VPN-A provider-tunnel mdt group-range 232.1.1.3/32 set routing-instances VPN-A vrf-target target:100:10 set routing-instances VPN-A vrf-table-label set routing-instances VPN-A protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set routing-instances VPN-A protocols ospf export bgp-to-ospf set routing-instances VPN-A protocols pim mvpn family inet autodiscovery inet-mdt set routing-instances VPN-A protocols pim mvpn family inet6 disable set routing-instances VPN-A protocols pim rp static address 10.255.182.144 set routing-instances VPN-A protocols pim interface lo0.1 mode sparse-dense set routing-instances VPN-A protocols pim interface fe-1/1/2.0 mode sparse-dense set routing-instances VPN-A protocols mvpn family inet autodiscovery-only intra-as inclusive set protocols mpls interface all set protocols mpls interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols bgp group ibgp type internal set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 10.255.182.133 set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet-vpn unicast set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet-mdt signaling set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.182.142 set protocols ospf traffic-engineering set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp interface all set protocols pim rp local address 10.255.182.133 set protocols pim interface all mode sparse set protocols pim interface all version 2 set protocols pim interface fxp0.0 disable set policy-options policy-statement bgp-to-ospf from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement bgp-to-ospf then accept
Router PE2
set interfaces so-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.10.20.1/30 set interfaces so-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.111.10.2/30 set interfaces so-0/0/3 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-0/0/3 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.255.182.142/32 primary set interfaces lo0 unit 1 family inet address 10.10.47.101/32 set routing-options router-id 10.255.182.142 set routing-options route-distinguisher-id 10.255.182.142 set routing-options autonomous-system 100 set routing-instances VPN-A instance-type vrf set routing-instances VPN-A interface so-0/0/1.0 set routing-instances VPN-A interface lo0.1 set routing-instances VPN-A provider-tunnel pim-ssm family inet group-address 232.1.1.1 set routing-instances VPN-A provider-tunnel mdt threshold group 224.1.1.0/24 source 10.240.0.242/32 rate 10 set routing-instances VPN-A provider-tunnel mdt tunnel-limit 20 set routing-instances VPN-A provider-tunnel mdt group-range 232.1.1.3/32 set routing-instances VPN-A vrf-target target:100:10 set routing-instances VPN-A vrf-table-label set routing-instances VPN-A routing-options graceful-restart set routing-instances VPN-A protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set routing-instances VPN-A protocols ospf export bgp-to-ospf set routing-instances VPN-A protocols pim mvpn family inet autodiscovery inet-mdt set routing-instances VPN-A protocols pim mvpn family inet6 disable set routing-instances VPN-A protocols pim rp static address 10.255.182.144 set routing-instances VPN-A protocols pim interface lo0.1 mode sparse-dense set routing-instances VPN-A protocols pim interface so-0/0/1.0 mode sparse-dense set routing-instances VPN-A protocols mvpn family inet autodiscovery-only intra-as inclusive set protocols mpls interface all set protocols mpls interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols bgp group ibgp type internal set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 10.255.182.142 set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet-vpn unicast set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet-mdt signaling set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.182.133 set protocols ospf traffic-engineering set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp interface all set protocols pim rp static address 10.255.182.133 set protocols pim interface all mode sparse set protocols pim interface all version 2 set protocols pim interface fxp0.0 disable set policy-options policy-statement bgp-to-ospf from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement bgp-to-ospf then accept
Router PE1
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see the Junos OS CLI User Guide.
To configure Router PE1:
Configure the router interfaces, enabling IPv4 traffic.
Also enable MPLS on the interface facing Router PE2.
The
lo0.1interface is for theVPN-Arouting instance.[edit interfaces] user@PE1# set so-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.111.10.1/30 user@PE1# set so-0/0/3 unit 0 family mpls user@PE1# set fe-1/1/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.10.10.1/30 user@PE1# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.255.182.133/32 primary user@PE1# set lo0 unit 1 family inet address 10.10.47.100/32
Configure a routing policy to export BGP routes from the routing table into OSPF.
[edit policy-options policy-statement bgp-to-ospf] user@PE1# set from protocol bgp user@PE1# set then accept
Configure the router ID, route distinguisher, and autonomous system number.
[edit routing-options] user@PE1# set router-id 10.255.182.133 user@PE1# set route-distinguisher-id 10.255.182.133 user@PE1# set autonomous-system 100
Configure the protocols that need to run in the main routing instance to enable MPLS, BGP, the IGP, VPNs, and PIM sparse mode.
[edit protocols ] user@PE1# set mpls interface all user@PE1# set mpls interface fxp0.0 disable user@PE1# set bgp group ibgp type internal user@PE1# set bgp group ibgp local-address 10.255.182.133 user@PE1# set bgp group ibgp family inet-vpn unicast user@PE1# set bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.182.142 user@PE1# set ospf traffic-engineering user@PE1# set ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all user@PE1# set ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fxp0.0 disable user@PE1# set ldp interface all user@PE1# set pim rp local address 10.255.182.133 user@PE1# set pim interface all mode sparse user@PE1# set pim interface all version 2 user@PE1# set pim interface fxp0.0 disable
Create the customer VRF routing instance.
[edit routing-instances VPN-A] user@PE1# set instance-type vrf user@PE1# set interface fe-1/1/2.0 user@PE1# set interface lo0.1 user@PE1# set vrf-target target:100:10 user@PE1# set vrf-table-label user@PE1# set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all user@PE1# set protocols ospf export bgp-to-ospf user@PE1# set protocols pim rp static address 10.255.182.144 user@PE1# set protocols pim interface lo0.1 mode sparse-dense user@PE1# set protocols pim interface fe-1/1/2.0 mode sparse-dense
Configure the draft-rosen 7 control plane, and specify IPv4 traffic to be carried in the provider tunnel.
[edit routing-instances VPN-A] user@PE1# set provider-tunnel pim-ssm family inet group-address 232.1.1.1 user@PE1# set protocols pim mvpn family inet autodiscovery inet-mdt user@PE1# set protocols pim mvpn family inet6 disable user@PE1# set protocols mvpn family inet autodiscovery-only intra-as inclusive [edit protocols bgp group ibgp] user@PE1# set family inet-mdt signaling
(Optional) Configure a data MDT tunnel.
[edit routing-instances VPN-A] user@PE1# set provider-tunnel mdt threshold group 224.1.1.0/24 source 10.240.0.242/32 rate 10 user@PE1# set provider-tunnel mdt tunnel-limit 20 user@PE1# set provider-tunnel mdt group-range 232.1.1.3/32
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show interfaces, show policy-options, show protocols, show routing-instances, and show routing-options commands. If the output does not display
the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example
to correct the configuration.
user@PE1# show interfaces
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.255.182.133/32 {
primary;
}
}
}
unit 1 {
family inet {
address 10.10.47.100/32;
}
}
}
so-0/0/3 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.111.10.1/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
fe-1/1/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.10.10.1/30;
}
}
}
user@PE1# show policy-options
policy-statement bgp-to-ospf {
from protocol bgp;
then accept;
}
user@PE1# show protocols
mpls {
ipv6-tunneling;
interface all;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
bgp {
group ibgp {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.182.133;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
family inet-mdt {
signaling;
}
neighbor 10.255.182.142;
}
}
ospf {
traffic-engineering;
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface all;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
}
ldp {
interface all;
}
pim {
rp {
local {
address 10.255.182.133;
}
}
interface all {
mode sparse;
version 2;
}
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
user@PE1# show routing-instances
VPN-A {
instance-type vrf;
interface fe-1/1/2.0;
interface lo0.1;
provider-tunnel {
pim-ssm {
family {
inet {
group-address 232.1.1.1;
}
}
}
mdt {
threshold {
group 224.1.1.0/24 {
source 10.240.0.242/32 {
rate 10;
}
}
}
tunnel-limit 20;
group-range 232.1.1.3/32;
}
}
vrf-target target:100:10;
vrf-table-label;
protocols {
ospf {
export bgp-to-ospf;
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface all;
}
}
pim {
mvpn {
family {
inet {
autodiscovery {
inet-mdt;
}
}
inet6 {
disable;
}
}
}
rp {
static {
address 10.255.182.144;
}
}
interface lo0.1 {
mode sparse-dense;
}
interface fe-1/1/2.0 {
mode sparse-dense;
}
}
mvpn {
family {
inet {
autodiscovery-only {
intra-as {
inclusive;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
user@PE1# show routing-options route-distinguisher-id 10.255.182.133; autonomous-system 100; router-id 10.255.182.133;
If you are done configuring the router, enter commit from configuration mode.
Repeat the procedure for Router PE2, using the appropriate interface names and IP addresses.
CE Device Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Device CE1
set interfaces fe-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.10.10.2/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.255.182.144/32 primary set routing-options router-id 10.255.182.144 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols pim rp local address 10.255.182.144 set protocols pim interface all mode sparse-dense set protocols pim interface fxp0.0 disable
Device CE2
set interfaces so-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.10.20.2/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 127.0.0.1/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.255.182.140/32 primary set routing-options router-id 10.255.182.140 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols pim rp static address 10.255.182.144 set protocols pim interface all mode sparse-dense set protocols pim interface fxp0.0 disable
Device CE1
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure Device CE1:
Configure the router interfaces, enabling IPv4 and IPv6 traffic.
[edit interfaces] user@CE1# set fe-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.10.10.2/30 user@CE1# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.255.182.144/32 primary
Configure the router ID.
[edit routing-options] user@CE1# set router-id 10.255.182.144
Configure the protocols that need to run on the CE device to enable OSPF (for IPv4) and PIM sparse-dense mode.
[edit protocols] user@CE1# set ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all user@CE1# set ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fxp0.0 disable user@CE1# set pim rp local address 10.255.182.144 user@CE1# set pim interface all mode sparse-dense user@CE1# set pim interface fxp0.0 disable
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show interfaces, show protocols, and show routing-options commands. If the output does
not display the intended configuration, repeat the configuration instructions
in this example to correct it.
user@CE1# show interfaces
fe-0/1/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.10.10.2/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.255.182.144/32 {
primary;
}
}
}
}
user@CE1# show protocols
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface all;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
}
pim {
rp {
local {
address 10.255.182.144;
}
}
interface all {
mode sparse-dense;
}
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
user@CE1# show routing-options router-id 10.255.182.144;
If you are done configuring the router, enter commit from configuration mode.
Repeat the procedure for Device CE2, using the appropriate interface names and IP addresses.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Verifying Tunnel Encapsulation
- Verifying PIM Neighbors
- Verifying the Provider Tunnel and Control Plane
- Checking Routes
- Verifying MDT Tunnels
Verifying Tunnel Encapsulation
Purpose
Verify that PIM multicast tunnel (mt) encapsulation
and deencapsulation interfaces come up.
Action
user@PE1> show pim interfaces instance VPN-A Instance: PIM.VPN-A Name Stat Mode IP V State NbrCnt JoinCnt(sg) JoinCnt(*g) DR address fe-1/1/2.0 Up SparseDense 4 2 NotDR 1 1 1 10.10.10.2 lo0.1 Up SparseDense 4 2 DR 0 0 0 10.10.47.100 lsi.2304 Up SparseDense 4 2 P2P 0 0 0 mt-0/3/0.32769 Up SparseDense 4 2 P2P 0 0 0 mt-1/2/0.1081344 Up SparseDense 4 2 P2P 0 0 0 mt-1/2/0.32768 Up SparseDense 4 2 P2P 1 0 0 pe-0/3/0.32770 Up Sparse 4 2 P2P 0 0 0
Meaning
The multicast
tunnel interface that is used for encapsulation, mt-[xxxxx], is in the range from 32,768 through 49,151.
The interface mt-[yyyyy], used for
de-encapsulation, is in the range from 1,081,344 through 1,107,827.
PIM runs only on the encapsulation interface. The de-encapsulation
interface populates downstream interface information.
Verifying PIM Neighbors
Purpose
Verify that PIM neighborship is established over the multicast tunnel interface.
Action
user@PE1> show pim neighbors instance VPN-A Instance: PIM.VPN-A B = Bidirectional Capable, G = Generation Identifier, H = Hello Option Holdtime, L = Hello Option LAN Prune Delay, P = Hello Option DR Priority, T = Tracking Bit Interface IP V Mode Option Uptime Neighbor addr fe-1/1/2.0 4 2 HPLGT 00:29:35 10.10.10.2 mt-1/2/0.32768 4 2 HPLGT 00:28:32 10.10.47.101
Meaning
When the neighbor address is listed and the uptime is incrementing, it means that PIM neighborship is established over the multicast tunnel interface.
Verifying the Provider Tunnel and Control Plane
Purpose
Confirm that the provider tunnel and control-plane protocols are correct.
Action
user@PE1> show pim mvpn Instance Family VPN-Group Mode Tunnel PIM.VPN-A INET 225.1.1.1 PIM-MVPN PIM-SSM
Meaning
For draft-rosen, the MVPN mode appears in the output
as PIM-MVPN.
Checking Routes
Purpose
Verify that traffic flows as expected.
Action
user@R1> show multicast route extensive instance VPN-A
Family: INET
Group: 224.1.1.1
Source: 10.240.0.242/32
Upstream interface: fe-1/1/2.0
Downstream interface list:
mt-1/2/0.32768
Session description: NOB Cross media facilities
Statistics: 92 kBps, 1001 pps, 1869820 packets
Next-hop ID: 1048581
Upstream protocol: PIM
Route state: Active
Forwarding state: Forwarding
Cache lifetime/timeout: 360 seconds
Wrong incoming interface notifications: 0
Meaning
For draft-rosen, the upstream protocol appears in the
output as PIM.
Verifying MDT Tunnels
Purpose
Verify that both default and data MDT tunnels are correct.
Action
user@PE1> show pim mdt instance VPN-A Instance: PIM.VPN-A Tunnel direction: Outgoing Tunnel mode: PIM-SSM Default group address: 232.1.1.1 Default source address: 10.255.182.133 Default tunnel interface: mt-1/2/0.32769 Default tunnel source: 0.0.0.0 C-group address C-source address P-group address Data tunnel interface 224.1.1.1 10.240.0.242 232.1.1.3 mt-0/3/0.32771 Instance: PIM.VPN-A Tunnel direction: Incoming Tunnel mode: PIM-SSM Default group address: 232.1.1.1 Default source address: 10.255.182.142 Default tunnel interface: mt-1/2/0.1081345 Default tunnel source: 0.0.0.0
