Example: Configuring MLD Snooping on Switches with ELS Support
This example uses Junos OS with support for the Enhanced Layer 2 Software (ELS) configuration style. For ELS details, see Using the Enhanced Layer 2 Software CLI.
You can enable MLD snooping on a VLAN to constrain the flooding of IPv6 multicast traffic on a VLAN. When MLD snooping is enabled, a switch examines MLD messages between hosts and multicast routers and learns which hosts are interested in receiving multicast traffic for a multicast group. On the basis of what it learns, the switch then forwards IPv6 multicast traffic only to those interfaces connected to interested receivers instead of flooding the traffic to all interfaces.
This example describes how to configure MLD snooping:
Requirements
This example uses the following software and hardware components:
One switch running Junos OS with ELS
Before you configure MLD snooping, be sure you have:
Configured the vlan 100 VLAN on the switch.
Assigned interfaces ge-0/0/0, ge-0/0/1, ge-0/0/2, and ge-0/0/12 to vlan100.
Configured ge-0/0/12 as a trunk interface.
See Configuring VLANs for EX Series Switches or Configuring VLANs on Switches with Enhanced Layer 2 Support.
Overview and Topology
In this example, interfaces ge-0/0/0, ge-0/0/1, and ge-0/0/2 on the switch are in vlan100 and are connected to hosts that are potential multicast receivers. Interface ge-0/0/12, a trunk interface also in vlan100, is connected to a multicast router. The router acts as the MLD querier and forwards multicast traffic for group ff1e::2010 to the switch from a multicast source.
Topology
The topology for this example is illustrated in Figure 1.
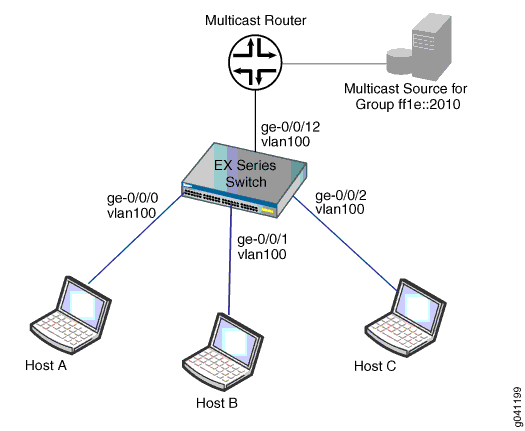
In this sample topology, the multicast router forwards multicast traffic to the switch from the source when it receives a membership report for group ff1e::2010 from one of the hosts—for example, Host B. If MLD snooping is not enabled on vlan100, the switch floods the multicast traffic on all interfaces in vlan100 (except for interface ge-0/0/12). If MLD snooping is enabled on vlan100, the switch monitors the MLD messages between the hosts and router, allowing it to determine that only Host B is interested in receiving the multicast traffic. The switch then forwards the multicast traffic only to interface ge-0/0/1.
This example shows how to enable MLD snooping on vlan100. It also shows how to perform the following optional configurations, which can reduce group join and leave latency:
Configure immediate leave on the VLAN. When immediate leave is configured, the switch stops forwarding multicast traffic on an interface when it detects that the last member of the multicast group has left the group. If immediate leave is not configured, the switch waits until the group-specific membership queries time out before it stops forwarding traffic.
Configure ge-0/0/12 as a static multicast-router interface. In this topology, ge-0/0/12 always leads to the multicast router. By statically configuring ge-0/0/12 as a multicast-router interface, you avoid any delay imposed by the switch having to learn that ge-0/0/12 is a multicast-router interface.
Configuration
To configure MLD snooping on a switch:
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure MLD snooping, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit] set protocols mld-snooping vlan vlan100 set protocols mld-snooping vlan vlan100 immediate-leave set protocols mld-snooping vlan vlan100 interface ge-0/0/12 multicast-router-interface
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure MLD snooping:
Enable MLD snooping on the VLAN vlan100:
[edit protocols] user@switch# set mld-snooping vlan vlan100
Configure the switch to immediately remove a group membership from an interface when it receives a leave report from the last member of the group on the interface:
[edit protocols] user@switch# set mld-snooping vlan vlan100 immediate-leave
Statically configure interface ge-0/0/12 as a multicast-router interface:
[edit protocols] user@switch# set mld-snooping vlan vlan100 interface ge-0/0/12 multicast-router-interface
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
[edit protocols]
user@switch# show mld-snooping
vlan vlan100 {
immediate-leave;
interface ge-0/0/12.0 {
multicast-router-interface;
}
}Verifying MLD Snooping Configuration
To verify that MLD snooping is enabled on the VLAN and the MLD snooping forwarding interfaces are correct, perform the following task:
Verifying MLD Snooping Interface Membership on VLAN vlan100
Purpose
Verify that MLD snooping is enabled on the VLAN vlan 100 and that the multicast-router interface is statically configured:
Action
Show the MLD snooping information for ge-0/0/12.0:
user@switch> show mld snooping interface
Instance: default-switch
Vlan: vlan100
Learning-Domain: default
Interface: ge-0/0/12.0
State: Up Groups: 3
Immediate leave: On
Router interface: yes
Configured Parameters:
MLD Query Interval: 125.0
MLD Query Response Interval: 10.0
MLD Last Member Query Interval: 1.0
MLD Robustness Count: 2Meaning
MLD snooping is running on vlan100, and interface ge-0/0/12.0 is a statically configured multicast-router interface. Immediate
leave is enabled on the interface.
