ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring IGMP Snooping on Switches
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping constrains the flooding of IPv4 multicast traffic on VLANs on a device. With IGMP snooping enabled, the device monitors IGMP traffic on the network and uses what it learns to forward multicast traffic to only the downstream interfaces that are connected to interested receivers. The device conserves bandwidth by sending multicast traffic only to interfaces connected to devices that want to receive the traffic, instead of flooding the traffic to all the downstream interfaces in a VLAN.
This example describes how to configure IGMP snooping:
Requirements
This example requires a Junos switching device.
Before you configure IGMP snooping, be sure you have:
Configured the
employee-vlanVLANAssigned interfaces
ge-0/0/1,ge-0/0/2,ge-0/0/3, andge-0/0/4toemployee-vlan
Overview and Topology
In this example you configure an interface to receive multicast traffic from a source and configure some multicast-related behavior for downstream interfaces. The example assumes that IGMP snooping was previously disabled for the VLAN.
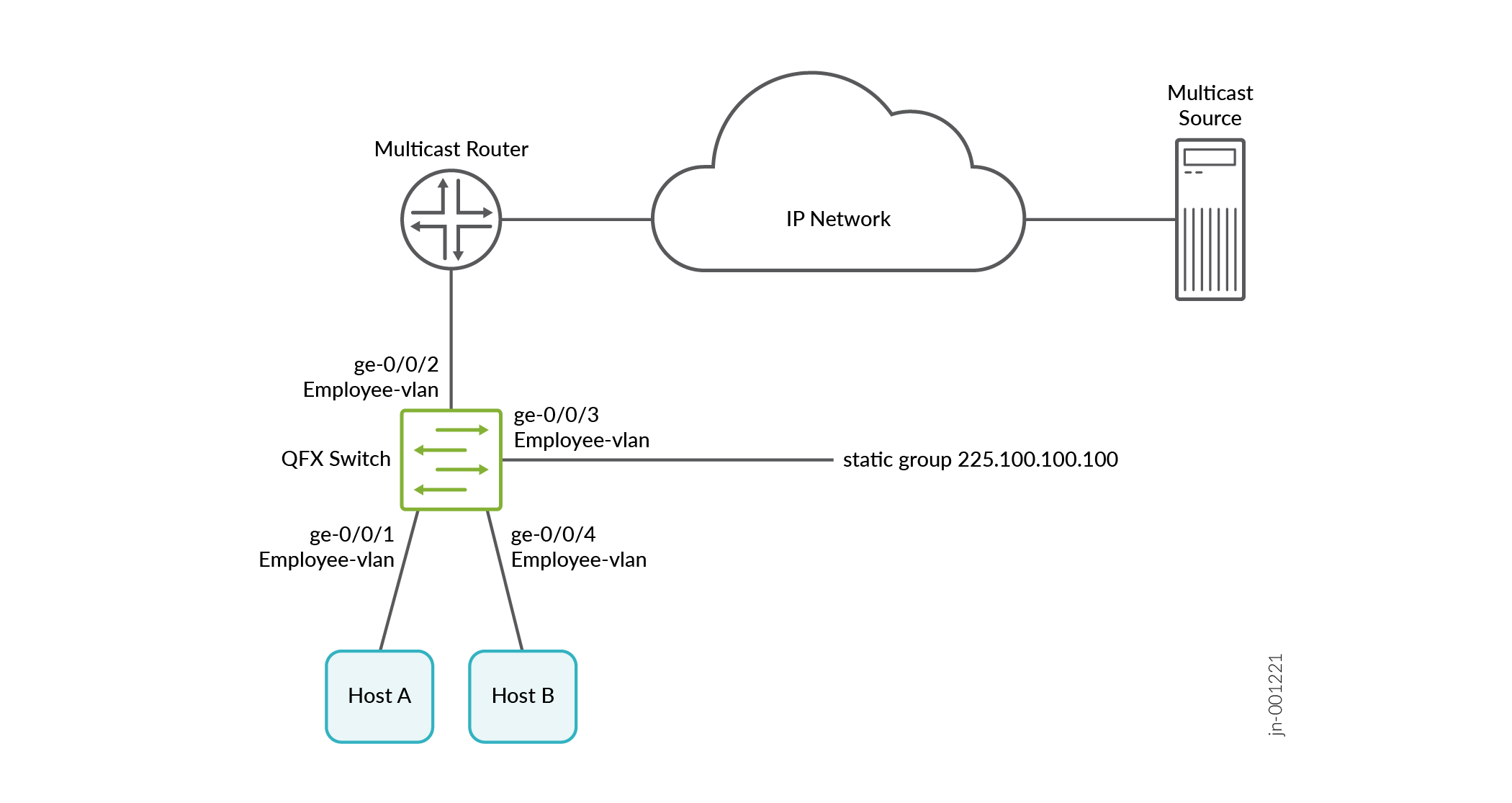
By enabling IGMP snooping on a switch, interfaces can be either host-only interfaces or multicast-router interfaces. If the interfaces are not configured explicitly, through IGMP snooping the switch learns which interfaces are host-only and which ones are multicast-router interfaces.
Topology
Table 1 shows the components of the topology for this example.
|
Components |
Settings |
|---|---|
|
VLAN name |
|
|
Interfaces in |
|
|
Multicast IP address for |
|
Configuration
To configure basic IGMP snooping on a switch:
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure IGMP snooping, copy the following commands and paste them into a terminal window:
[edit protocols] set igmp-snooping vlan employee-vlan set igmp-snooping vlan employee-vlan interface ge-0/0/3 static group 225.100.100.100 set igmp-snooping vlan employee-vlan interface ge-0/0/2 multicast-router-interface set igmp-snooping vlan employee-vlan robust-count 4
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure IGMP snooping:
-
Enable and configure IGMP snooping on the VLAN
employee-vlan:[edit protocols] user@switch# set igmp-snooping vlan employee-vlan
Optionally, you can configure an interface to belong to a multicast group. For example, for testing IGMP snooping with Layer 2 multicast forwarding, you might assign an interface to a static multicast group:
[edit protocols] user@switch# set igmp-snooping vlan employee-vlan interface ge-0/0/3 static group 225.100.100.100
(See static (IGMP Snooping) for more on how static groups work at Layer 2.)
-
Configure an interface to forward IGMP queries received from multicast routers.
[edit protocols] user@switch# set igmp-snooping vlan employee-vlan interface ge-0/0/2 multicast-router-interface
-
Configure the switch to wait for four timeout intervals before timing out a multicast group on a VLAN:
[edit protocols] user@switch# set igmp-snooping vlan employee-vlan robust-count 4
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
user@switch# show protocols igmp-snooping
vlan employee-vlan {
robust-count 4;
}
interface ge-0/0/2 {
multicast-router-interface;
}
interface ge-0/0/3 {
static {
group 255.100.100.100;
}
}
}
