Policer Implementation Overview
The Juniper Networks® Junos® operating system (Junos OS) supports three types of policers:
Single-rate two-color policer — The most common policer. Single-rate means that there is only a single bandwidth and burst rate referenced in the policer. The two colors associated with this policer are red (nonconforming) and green (conforming).
Single-rate three-color policer — Similar to the single-rate two-color policer with the addition of the color yellow. This type also introduces the committed information rate (CIR) and a committed burst rate (CBR).
Two-rate three-color policer — Builds off of the single-rate three-color policer by adding a second rate tier. Two-rate means there is an upper bandwidth limit and associated burst size as well as a peak information rate (PIR) and a peak burst rate (PBS).
There are two types of token bucket algorithms that can be used, depending on the type of policer that is applied to network traffic. Single-rate two-color policers use the single token bucket algorithm to measure traffic flow conformance to a two-color policer rate limit. Single-rate three-color policers and two-rate three-color policers both use the dual token bucket algorithm to measure traffic flow conformance to a three-color policer rate. The main difference between these two token bucket algorithms is that the single token bucket algorithm allows bursts of traffic for short periods, whereas the dual token bucket algorithm allows more sustained bursts of traffic. (The remainder of this topic discusses the single token bucket algorithm.)
To configure a policer, you need to set two parameters:
Bandwidth limit configured in bps (using the bandwidth-limit statement)
Burst size configured in bytes (using the burst-size-limit statement)
For single-rate two-color policers only, you can also specify the bandwidth limit as a percentage of either the physical interface port speed or the configured logical interface shaping rate by using the bandwidth-percent percentage statement. You cannot configure a policer to use bandwidth percentage for aggregate, tunnel, or software interfaces.
Use the following command to set the policer conditions:
user@router# set firewall policer <policer name> if-exceeding ? Possible completions: <[Enter]> Execute this command + apply-groups Groups from which to inherit configuration data + apply-groups-except Don't inherit configuration data from these groups bandwidth-limit Bandwidth limit (8000..100000000000 bits per second) bandwidth-percent Bandwidth limit in percentage (1..100 percent) burst-size-limit Burst size limit (1500..100000000000 bytes) | Pipe through a command
The bandwidth limit parameter is used to determine the average rate limit applied to the traffic, while the burst-size parameter is used to allow for short periods of traffic bursting (back-to-back traffic at average rates that exceed the configured bandwidth limit). Once you apply a set of policer configuration settings (bandwidth limit and burst size), the configured values are adjusted to hardware programmable values. The conversion adjustment introduced is normally less than 1 percent of the configured bandwidth limit. This adjustment is needed because the software allows you to configure the bandwidth limit and burst size to any value within the specified ranges, but those values must be adjusted to the nearest value that can be programmed in the hardware.
The policer bandwidth limit configuration in the hardware is represented by two values: the credit update frequency and the credit size. The credit update frequency is used by the hardware to determine how frequently tokens (bits of unused bandwidth) are added to the token bucket. The credit size is based on the number of tokens that can fit in the token bucket. Switches contain a set of credit update frequencies instead of having a single credit update frequency to minimize the adjustment difference from the configured bandwidth limit and to support a wide range of policer bandwidth rates (from 40 Kbps to 40 Gbps). One of the frequencies is used to program the policer (bandwidth limit and burst size) in the hardware.
The burst size is based on the overall traffic load and allows bursts of traffic to exceed the configured bandwidth limit. A policer with a large burst size effectively disables the configured bandwidth limit function, so the burst size must be relative to the configured bandwidth limit. You need to consider the traffic patterns in your network before determining the burst size. For more information about determining burst size, see Determining Proper Burst Size for Traffic Policers.
The configured burst size is adjusted in the hardware to a value that is based on the configured bandwidth limit. The burst size extends the configured bandwidth limit for bursty traffic that exceeds the configured bandwidth limit.
When a policer is applied to the traffic at an interface, the initial capacity for traffic bursting is equal to the number of bytes specified in the burst-size-limit statement.
Figure 1 represents how a policer is implemented using the token bucket algorithm. The token allocator allocates tokens to the policer based on the configured bandwidth limit, which is the token size multiplied by the token arrival rate.
token size x token arrival rate = policer rate (configured bandwidth limit)

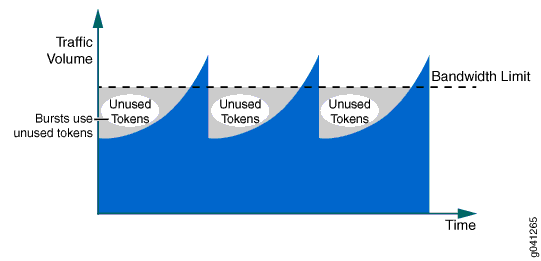
When a packet arrives at an interface configured with a policer, tokens that represent the number of bits that correspond to the length of the packet are used (or “cashed in”) from the token bucket. If the token arrival rate is higher than the rate of traffic so that there are tokens not being used, the token bucket is filled to capacity, and arriving tokens “overflow” the bucket and are lost. The token bucket depth represents the single user-configured burst size for the policer.
If there are tokens in the token bucket and the incoming traffic rate is higher than the token rate (the configured policer rate, bandwidth limit), the traffic can use the tokens until the bucket is empty. The token consumption rate can be as high as the incoming traffic rate, which creates the burst of traffic shown in Figure 2.
By using the token bucket algorithm, the average bandwidth rate being allowed is close to the configured bandwidth limit while simultaneously supporting bursty traffic, as shown in Figure 2.
The measured length of a packet changes according to the
family type that the policer applies to. If the policer is applied
under the family inet hierarchy, the policer considers
only the IPv4 packet length. If the policer is applied under the family vpls hierarchy, the entire Ethernet frame (including
the Ethernet MAC header) is included in the packet length.
The major factor that affects the policer shaping result is not the conversion adjustment, but the traffic pattern since most network traffic is not consistent and is not sent at a constant rate. Due to the fluctuation of the incoming traffic rate, some of the allocated tokens are not used. As a result, the shaped traffic rate is lower than you might expect, and the TCP connection behavior discussed in Understanding the Benefits of Policers and Token Bucket Algorithms is a typical example of this. To alleviate this effect of the lower shaped traffic rate, a proper burst size configuration is required.
