ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring a Conditional Default Route Policy
This example shows how to configure a conditional default route on one routing device and redistribute the default route into OSPF.
Requirements
No special configuration beyond device initialization is required before configuring this example.
Overview
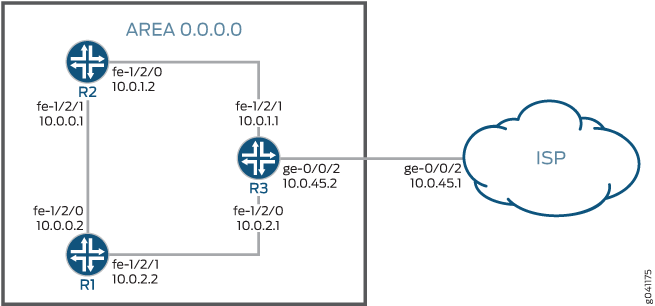
In this example, OSPF area 0 contains three routing devices. Device R3 has a BGP session with an external peer, for example, an Internet Service Provider (ISP).
To propagate a static route into BGP, this example includes the discard statement
when defining the route. The ISP injects a default static route into BGP, which provides the
customer network with a default static route to reach external networks. The static route
has a discard next hop. This means that if a packet does not match a more specific route,
the packet is rejected and a reject route for this destination is installed in the routing
table, but Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) unreachable messages are not sent. The
discard next hop allows you to originate a summary route, which can be advertised through
dynamic routing protocols.
Device R3 exports the default route into OSPF. The route policy on Device R3 is conditional such that if the connection to the ISP goes down, the default route is no longer exported into OSPF because it is no longer active in the routing table. This policy prevents packets from being silently dropped without notification (also known as null-route filtering).
This example shows the configuration for all of the devices and the step-by-step configuration on Device R3.
Topology
Figure 1 shows the sample network.
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the following commands, paste
them into a text file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your
network configuration, and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Device R1
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description R1->R3 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.1.2/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 2 description R1->R2 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 2 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/1.2
Device R2
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 1 description R2->R1 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 1 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 4 description R2->R3 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 4 family inet address 10.0.2.2/30 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/0.1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/1.4
Device R3
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 3 description R3->R2 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 3 family inet address 10.0.2.1/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 5 description R3->R1 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 5 family inet address 10.0.1.1/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 description R3->ISP set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.45.2/30 set protocols bgp group ext type external set protocols bgp group ext peer-as 64500 set protocols bgp group ext neighbor 10.0.45.1 set protocols ospf export gendefault set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/1.4 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/0.3 set policy-options policy-statement gendefault term upstreamroutes from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement gendefault term upstreamroutes from as-path upstream set policy-options policy-statement gendefault term upstreamroutes from route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 upto /16 set policy-options policy-statement gendefault term upstreamroutes then next-hop 10.0.45.1 set policy-options policy-statement gendefault term upstreamroutes then accept set policy-options policy-statement gendefault term end then reject set policy-options as-path upstream "^64500 " set routing-options autonomous-system 64501
Device ISP
set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.45.1/30 set protocols bgp group ext type external set protocols bgp group ext export advertise-default set protocols bgp group ext peer-as 64501 set protocols bgp group ext neighbor 10.0.45.2 set policy-options policy-statement advertise-default term 1 from route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact set policy-options policy-statement advertise-default term 1 then accept set routing-options static route 0.0.0.0/0 discard set routing-options autonomous-system 64500
Procedure
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the Junos OS CLI User Guide.
To configure Device R3:
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@R3# set fe-1/2/0 unit 3 description R3->R2 user@R3# set fe-1/2/0 unit 3 family inet address 10.0.2.1/30 user@R3# set fe-1/2/1 unit 5 description R3->R1 user@R3# set fe-1/2/1 unit 5 family inet address 10.0.1.1/30 user@R3# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 description R3->ISP user@R3# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.45.2/30
Configure the autonomous system (AS) number.
[edit routing-options] user@R3# set autonomous-system 64501
Configure the BGP session with the ISP device.
[edit protocols bgp group ext] user@R3# set type external user@R3# set peer-as 64500 user@R3# set neighbor 10.0.45.1
Configure OSPF.
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@R3# set interface fe-1/2/1.4 user@R3# set interface fe-1/2/0.3
Configure the routing policy.
[edit policy-options policy-statement gendefault] user@R3# set term upstreamroutes from protocol bgp user@R3# set term upstreamroutes from as-path upstream user@R3# set term upstreamroutes from route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 upto /16 user@R3# set term upstreamroutes then next-hop 10.0.45.1 user@R3# set term upstreamroutes then accept user@R3# set term end then reject [edit policy-options] user@R3# set as-path upstream "^64500 "
Apply the export policy to OSPF.
[edit protocols ospf] user@R3# set export gendefault
If you are done configuring the device, commit the configuration.
[edit] user@R3# commit
Results
Confirm your configuration by issuing the show command. If the output
does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to correct
the configuration.
user@R3# show
interfaces {
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 3 {
description R3->R2;
family inet {
address 10.0.2.1/30;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/1 {
unit 5 {
description R3->R1;
family inet {
address 10.0.1.1/30;
}
}
}
ge-1/2/0 {
unit 0 {
description R3->ISP;
family inet {
address 10.0.45.2/30;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group ext {
type external;
peer-as 64500;
neighbor 10.0.45.1;
}
}
ospf {
export gendefault;
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface fe-1/2/1.4;
interface fe-1/2/0.3;
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement gendefault {
term upstreamroutes {
from {
protocol bgp;
as-path upstream;
route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 upto /16;
}
then {
next-hop 10.0.45.1;
accept;
}
}
term end {
then reject;
}
}
as-path upstream "^64500 ";
}
routing-options {
autonomous-system 64501;
}
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Verifying That the Route to the ISP Is Working
- Verifying That the Static Route Is Redistributed
- Testing the Policy Condition
Verifying That the Route to the ISP Is Working
Purpose
Make sure connectivity is established between Device R3 and the ISP’s router.
Action
user@R3> ping 10.0.45.1 PING 10.0.45.1 (10.0.45.1): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.45.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=1.185 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.45.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.199 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.45.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.186 ms
Meaning
The ping command confirms reachability.
Verifying That the Static Route Is Redistributed
Purpose
Make sure that the BGP policy is redistributing the static route into Device R3’s routing table. Also make sure that the OSPF policy is redistributing the static route into the routing tables of Device R1 and Device R2.
Action
user@R3> show route protocol bgp
inet.0: 9 destinations, 10 routes (9 active, 0 holddown, 1 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
0.0.0.0/0 *[BGP/170] 00:00:25, localpref 100
AS path: 64500 I
> to 10.0.45.1 via ge-0/0/2.6user@R1> show route protocol ospf
inet.0: 7 destinations, 7 routes (7 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
0.0.0.0/0 *[OSPF/150] 00:03:58, metric 0, tag 0
> to 10.0.1.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.2.0/30 *[OSPF/10] 03:37:45, metric 2
to 10.0.1.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/1.2
172.16.233.5/32 *[OSPF/10] 03:38:41, metric 1
MultiRecv
user@R2> show route protocol ospf
inet.0: 7 destinations, 7 routes (7 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
0.0.0.0/0 *[OSPF/150] 00:04:04, metric 0, tag 0
> to 10.0.2.1 via fe-1/2/1.4
10.0.1.0/30 *[OSPF/10] 03:37:46, metric 2
to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.1
> to 10.0.2.1 via fe-1/2/1.4
172.16.233.5/32 *[OSPF/10] 03:38:47, metric 1
MultiRecvMeaning
The routing tables contain the default 0.0.0.0/0 route. If Device R1 and Device R2 receive packets destined for networks not specified in their routing tables, those packets will be sent to Device R3 for further processing. If Device R3 receives packets destined for networks not specified in its routing table, those packets will be sent to the ISP for further processing.
Testing the Policy Condition
Purpose
Deactivate the interface to make sure that the route is removed from the routing tables if the external network becomes unreachable.
Action
user@R3> deactivate interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.45.2/30 user@R3> commit
user@R1> show route protocol ospf
inet.0: 6 destinations, 6 routes (6 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.2.0/30 *[OSPF/10] 03:41:48, metric 2
to 10.0.1.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/1.2
172.16.233.5/32 *[OSPF/10] 03:42:44, metric 1
MultiRecv
user@R2> show route protocol ospf
inet.0: 6 destinations, 6 routes (6 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.1.0/30 *[OSPF/10] 03:42:10, metric 2
to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.1
> to 10.0.2.1 via fe-1/2/1.4
172.16.233.5/32 *[OSPF/10] 03:43:11, metric 1
MultiRecvMeaning
The routing tables on Device R1 and Device R2 do not contain the default 0.0.0.0/0
route. This verifies that the default route is no longer present in the OSPF domain. To reactivate
the ge-0/0/2.6 interface, issue the activate interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address
10.0.45.2/30 configuration mode command.
