Configure BGP on Switches via Mist
Understand the benefits of Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and follow these steps to configure a BGP group on your switch.
BGP is an exterior gateway protocol (EGP) that is used to exchange routing information among routers or layer 3 switches in different autonomous systems (AS). The routing information includes the complete route to each destination. BGP uses this information to maintain a database of network reachability information, which it exchanges with other BGP systems. BGP uses the network reachability information to construct a graph of AS connectivity, which enables BGP to prevent routing loops and enforce policy decisions at the AS level.
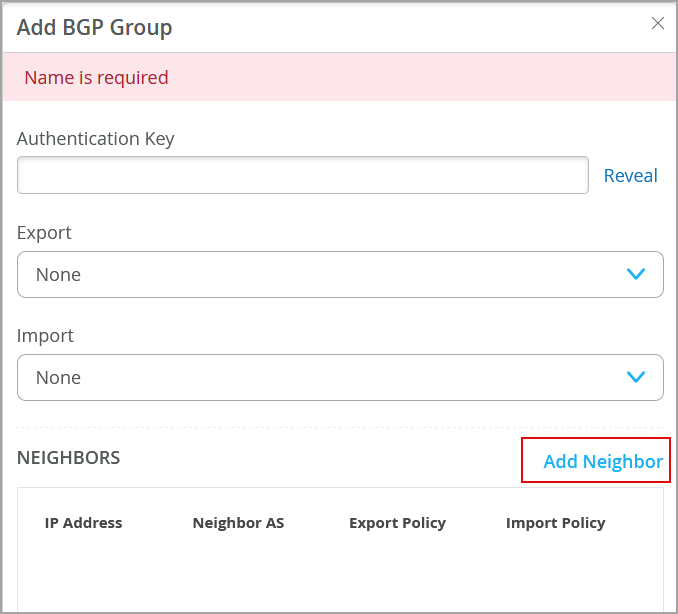
At a high level BGP configuration includes a BGP group, BGP neighbors, and a routing policy to advertise the BGP routes.
For BGP configuration examples and CLI steps, see BGP Configuration Overview.
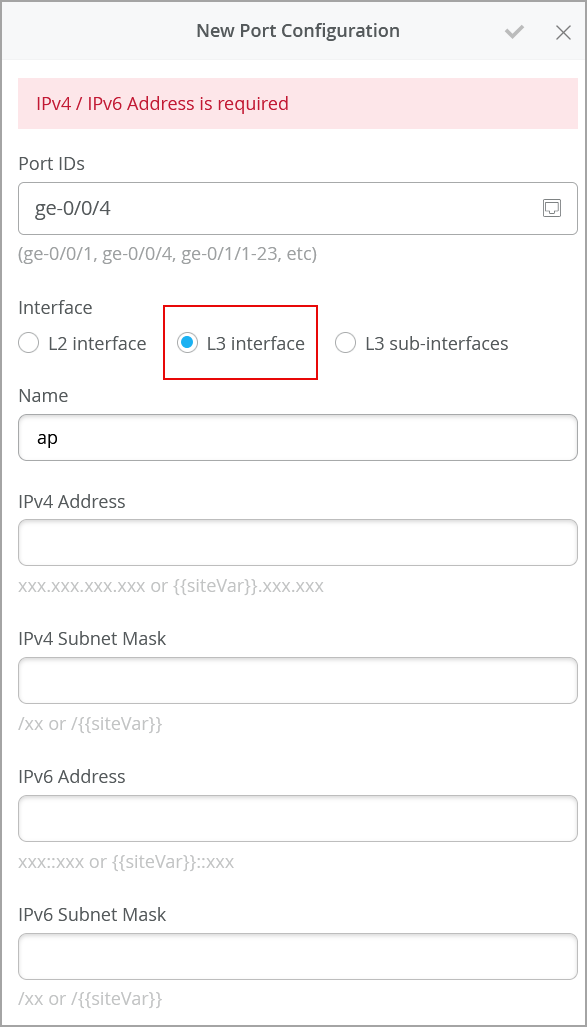
Before you configure BGP, ensure that you have configured the network interfaces (L3 interfaces). You can configure L3 interface from the Port Configuration tile on the switch details page (Switches > Switch Name). In this configuration, you need to specify the ports, interface type (L3), IP address, and subnet mask (see the image below).
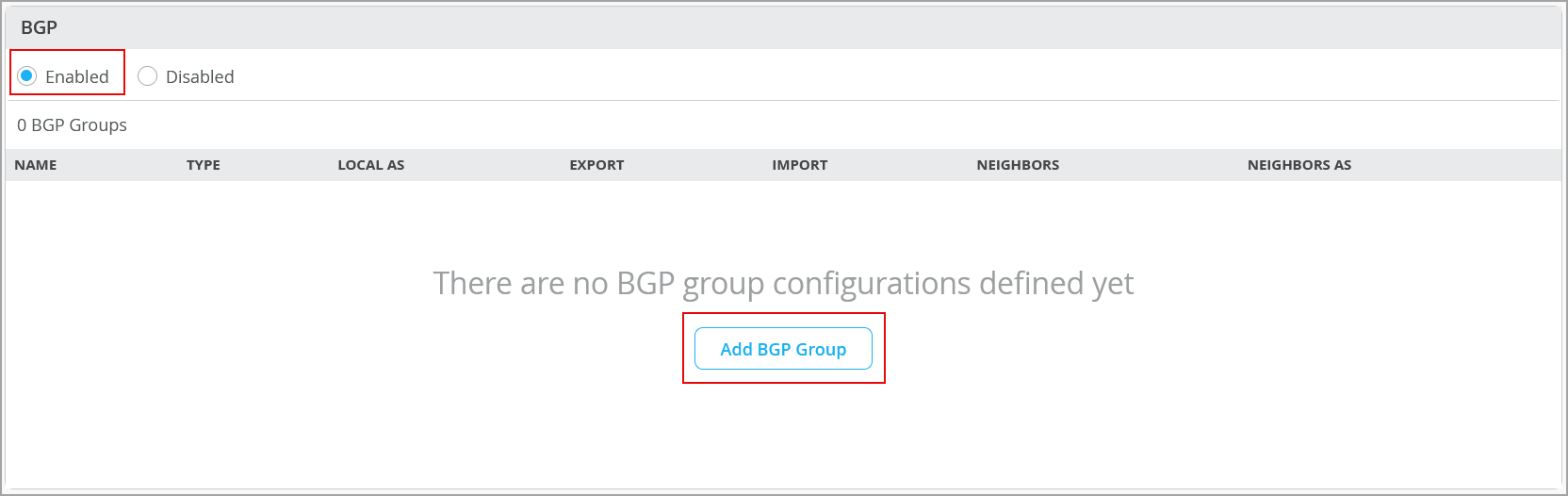
To configure BGP on a switch via Mist: