Example: Configuring Scheduling Modes on Aggregated Interfaces
You can configure class-of-service parameters, such as queuing or shaping parameters on
aggregated interfaces, in either link-protect or non-link-protect mode. You can
configure these parameters for per-unit schedulers, hierarchical schedulers, or shaping
at the physical and logical interface level. You can control the way these parameters
are applied by configuring the aggregated interface to operate in scale
or replicate mode.
You can configure the applied parameters for aggregated interfaces operating in non-link-protected mode. In link-protected mode, only one link in the bundle is active at a time (the other link is a backup link) so schedulers cannot be scaled or replicated. In non-link-protected mode, all the links in the bundle are active and send traffic; however, there is no backup link. If a link fails or is added to the bundle in non-link-protected mode, the links’ traffic is redistributed among the active links.
To set the scheduling mode for aggregated interfaces, include the scale
or replicate option of the member-link-scheduler
statement at the [edit class-of-service interfaces
aen] hierarchy level, where n is the
configured number of the interface:
[edit class-of-service interfaces aen] member-link-scheduler (replicate | scale);
By default, if you do not include the member-link-scheduler statement,
scheduler parameters are applied to the member links in the scale mode
(also called “equal division mode”).
The aggregated Ethernet interfaces are otherwise configured as usual. For more information on configuring aggregated Ethernet interfaces, see the Junos OS Network Interfaces Library for Routing Devices.
The following examples set scale mode on the ae0
interface and replicate mode on the ae1 interface.
[edit class-of-service]
interfaces ae0 {
member-link-scheduler scale;
}
[edit class-of-service]
interfaces ae1 {
member-link-scheduler replicate;
}
The member-link-scheduler statement only appears for aggregated
interfaces. You configure this statement for aggregated interfaces in
non-link-protected mode. For more information about link protection modes, see the
Network Interfaces Configuration Guide.
Aggregated interfaces support both hierarchical and per-unit schedulers.
When interface parameters are using the scale option of the
member-link-scheduler statement, the following parameters under the
[edit class-of-service traffic-control-profiles
traffic-control-profile-name] configuration are
scaled on egress when hierarchical schedulers are configured:
-
shaping-rate(PIR) -
guaranteed-rate(CIR) -
delay–buffer-rate
When interface parameters are using the scale option of the
member-link-scheduler statement, the following parameters under the
[edit class-of-service schedulers
scheduler-name] configuration are scaled on egress when
per-unit schedulers are configured:
-
transmit-rate -
buffer-size
You cannot apply a hierarchical scheduler at the interface set level for an
ae interface. (Interface sets cannot be configured under an
ae interface.)
The following configuration parameters are not supported on ae
interfaces in non-link-protection mode:
-
Input scheduler maps
-
Input traffic control profiles
-
Input shaping rates
The following configuration conventions are also not supported:
-
Scaling of the
input-traffic-control-profile-remainingstatement. -
The
scheduler-map-chassisstatement and thederivedoption for theaeinterface. Chassis scheduler maps should be applied under the physical interfaces. -
Dynamic and demux interfaces are not supported as part of the
aebundle.
Depending on the whether the scale or replicate option
is configured, the member-link-scheduler statement operates in either
scaled mode (also called “equal division mode”) or replicated mode, respectively.
In scaled mode, a VLAN can have multiple flows that can be sent over multiple member
links of the ae interface. Likewise, a member link can receive traffic
from any VLAN in the ae bundle. In scaled mode, the physical interface
bandwidth is divided equally among all member links of the ae bundle.
In scaled mode, the following scheduler parameter values are divided equally among the member links:
-
When the parameters are configured using traffic control profiles, then the parameters scaled are the shaping rate, guaranteed rate, and delay buffer rate.
-
When the parameters are configured using scheduler maps, then the parameters scaled are the transmit rate and buffer size. Shaping rate is also scaled if you configure it in bits per second (bps). Shaping rate is not scaled if you configure it as a percentage of the available interface bandwidth.
For example, consider an ae bundle between routers R1 and R2 consisting
of three links. These are ge-0/0/1, ge-0/0/2 and
ge-0/0/3 (ae0) on R1; and
ge-1/0/0, ge-1/0/1, and ge-1/0/2
(ae2) on R2. Two logical interfaces (units) are also configured on
the ae0 bundle on R1: ae0.0 and
ae0.1.
On ae0, traffic control profiles on R1 are configured as follows:
-
ae0(the physical interface level) has a PIR of 450 Mbps. -
ae0.0(VLAN 100 at the logical interface level) has a PIR of 150 Mbps and a CIR of 90 Mbps. -
ae0.1(VLAN 200 at the logical interface level) has a PIR of 90 Mbps and a CIR of 60 Mbps.
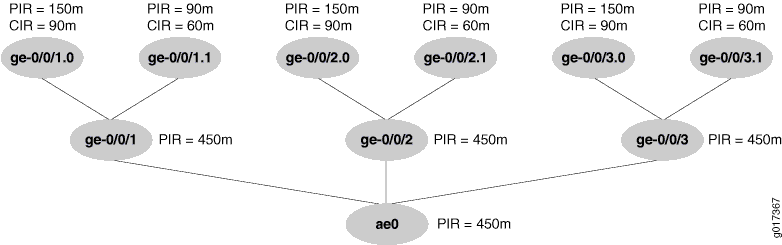
In scaled mode, the ae0 PIR is first divided among the member physical
interfaces. Because there are three members, each receives 450 / 3 = 150 Mbps as a
derived value. So the scaled PIR for the members interfaces is 150 Mbps each.
However, there are also two logical interfaces (ae0.0 and
ae0.1) and VLANs (100 and 200) on ae0. Traffic can
leave on any of the three physical interfaces (ge-0/0/1,
ge-0/0/2, or ge-0/0/3) in the bundle. Therefore,
two derived logical interfaces are added to the member links to represent the two
VLANs.
There are now six logical interfaces on the physical interfaces of the links making up
the ae bundle, one set for VLAN 100 and the other for VLAN 200:
-
ge-0/0/1.0andge-0/0/1.1 -
ge-0/0/2.0andge-0/0/2.1 -
ge-0/0/3.0andge-0/0/3.1
The traffic control profile parameters configured on ae0.0 are divided
across all the underlying logical interfaces (the unit 0s). In the same way, the traffic
control profile parameters configured on ae0.1 are divided across all
the underlying logical interfaces (the unit 1s).
Therefore, the derived values of the scaled parameters on the interfaces are:
-
For
ge-0/0/1.0andge-0/0/2.0andge-0/0/3.0, each CIR = 90 / 3 = 30 Mbps, and each PIR = 150 / 3 = 50 Mbps. -
For
ge-0/0/1.1andge-0/0/2.1andge-0/0/3.1, each CIR = 60 / 3 = 20 Mbps, and each PIR = 90 / 3 = 30 Mbps.
The scaled values are shown in Figure 1.

In scaled mode, when a new member link is added to the bundle, or an existing member link is either removed or fails, then the scaling factor (based on the number of active links) is recomputed and the new scheduler or traffic control profile parameters are reassigned. Only the PIR, CIR, and buffer parameters are recomputed: all other parameters are simply copied at each level.
In show class-of-service scheduler-map commands, values derived in
scaled mode instead of explicitly configured are flagged with
&**sf**n suffix, where
n indicates the value of the scaling factor.
The following sample shows the output for the scheduler map named
smap-all-abs with and without a scaling factor:
user@host> show class-of-service scheduler-map
Scheduler map: smap-all-abs, Index: 65452
Scheduler: q0_sch_abs, Forwarding class: be, Index: 6775
Transmit rate: 40000000 bps, Rate Limit: none, Buffer size: remainder,
Priority: low
Excess Priority: unspecified
Drop profiles:
Loss priority Protocol Index Name
Low any 1 <default-drop-profile>
Medium low any 1 <default-drop-profile>
Medium high any 1 <default-drop-profile>
High any 1 <default-drop-profile>
user@host> show class-of-service scheduler-map
Scheduler map: smap-all-abs, Index: 65452
Scheduler: q0_sch_abs&**sf**3, Forwarding class: be, Index: 2128
Transmit rate: 13333333 bps, Rate Limit: none, Buffer size: remainder,
Priority: low
Excess Priority: unspecified
Drop profiles:
Loss priority Protocol Index Name
Low any 1 <default-drop-profile>
Medium low any 1 <default-drop-profile>
Medium high any 1 <default-drop-profile>
High any 1 <default—drop—profile> There can be multiple scheduler maps created with different scaling factors,
depending on when the child interfaces come up. For example, if there are only two
active children on a parent interface, a new scheduler map with a scaling factor of
2 is created. The scheduler map name is
smap-all-abs&**sf**2.
In replicated mode, in contrast to scaled mode, the configured scheduler parameters are
simply replicated, not divided, among all member links of the ae
bundle.
In replicated mode, the following scheduler parameter values are replicated among the member links and logical interfaces:
-
When the parameters are configured using traffic control profiles, then the parameters replicated are the shaping rate, guaranteed rate, and delay buffer rate.
-
When the parameters are configured using scheduler maps, then the parameters replicated are the transmit rate and buffer size.
If the scheduler parameters in the example configuration between routers R1 and R2 are
applied with the member-link-scheduler replicate statement and option,
the following parameters are applied:
-
The
ae0PIR is copied among the member physical interfaces. Each receives 450 Mbps as a PIR. -
For each logical interface unit
.0, the configured PIR and CIR forae0.0is replicated (copied). Each logical interface unit.0receives a PIR of 150 Mbps and a CIR of 90 Mbps. -
For each logical interface unit
.1, the configured PIR and CIR forae0.1is replicated (copied). Each logical interface unit.1receives a PIR of 90 Mbps and a CIR of 60 Mbps.
The replicated values are shown in Figure 2.
In replicated mode, when a new member link is added to the bundle, or an existing member link is either removed or fails, the values are either copied or deleted from the required levels.
