Understanding How to Configure VXLANs and Layer 3 Logical Interfaces to Interoperate
The use case and additional configuration described in this topic apply only to QFX5110 switches.
In the sample EVPN-VXLAN network segments shown in Figure 1 (Before), hosts A and B need to exchange traffic. When host A sends a packet to host B or vice versa, the packet must traverse the following networking entities:
-
On QFX5110 switch: a pure Layer 3 logical interface configured using the
set interfaces interface-name unit logical-unit-number family inet address ip-address/prefix-lengthor theset interfaces interface-name unit logical-unit-number family inet6 address ipv6-address/prefix-lengthcommand. -
A VXLAN tunnel between the QFX5110 switch and the QFX10002 switch.
-
On QFX10002 switch: a pure Layer 3 logical interface configured as described in the first bullet.
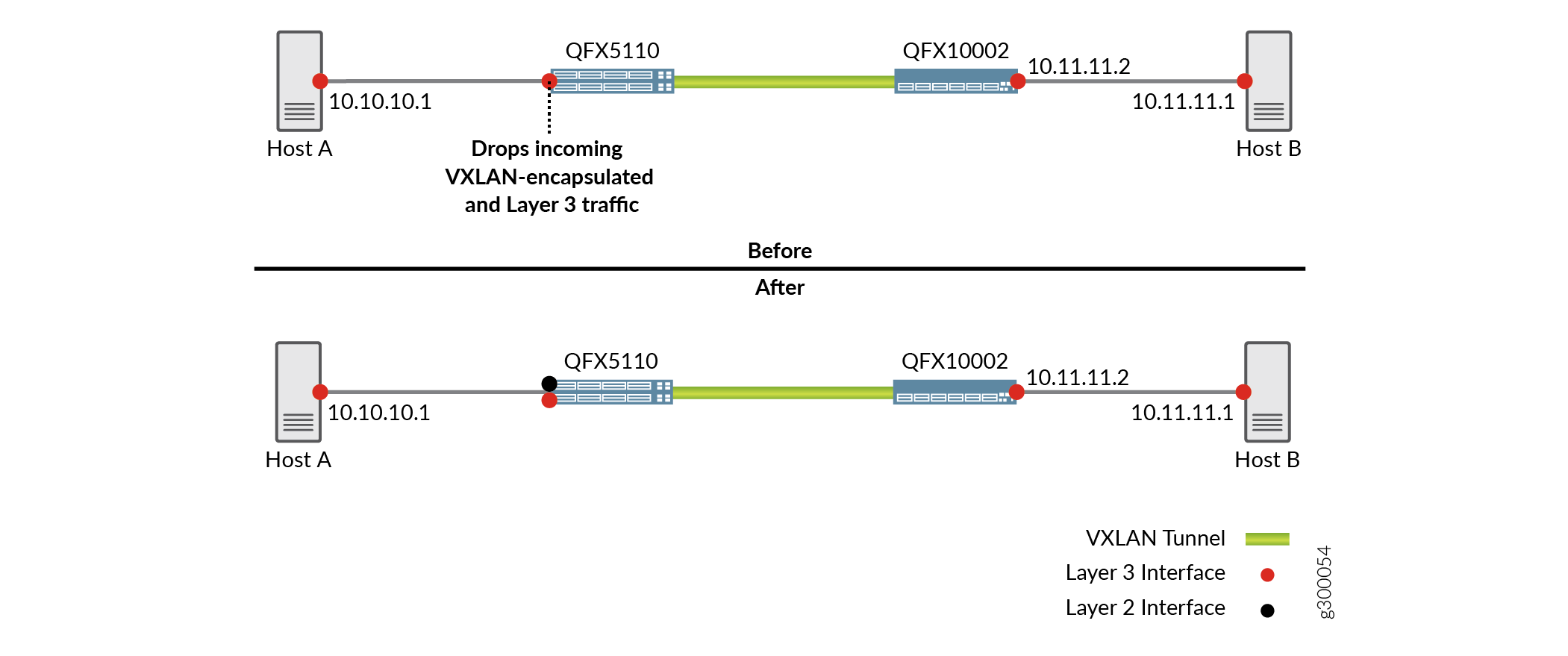
By default, routing traffic between a VXLAN and a Layer 3 logical interface is disabled. When this functionality is disabled, the pure Layer 3 logical interface on the QFX5110 switch drops Layer 3 traffic from host A and VXLAN-encapsulated traffic from the QFX10002 switch. To prevent the pure Layer 3 logical interface on the QFX5110 switch from dropping this traffic, you can perform some additional configuration on the switch.
The additional configuration on the QFX5110 switch entails the following on a physical interface (Figure 1 (After)):
-
Reconfiguring the pure Layer 3 logical interface as a Layer 2 logical interface and associating this interface with a dummy VLAN and a dummy VXLAN network identifier (VNI).
-
Creating an IRB interface, which provides Layer 3 functionality within the dummy VLAN.
For example:
set interfaces irb unit 3500 family inet address 10.10.10.2/30
set interfaces xe-0/0/13 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
set interfaces xe-0/0/13 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members VLAN-3500
set vlans VLAN-3500 vlan-id 3500
set vlans VLAN-3500 l3-interface irb.3500
set vlans VLAN-3500 vxlan vni 16770000
In lieu of the original pure Layer 3 logical interface, the newly created Layer 2-Layer 3 logical interfaces can now handle Layer 3 traffic from host A and VXLAN-encapsulated traffic from the QFX10002 switch.
