EVPN-VXLAN with an IPv6 Underlay
This topic describes how to set up an IPv6 underlay for the VXLAN overlay tunneling in an EVPN-VXLAN fabric.
IPv6 Underlay Support in EVPN-VXLAN Fabrics
Ethernet VPNs (EVPNs) connect devices with Layer 2 (L2) virtual bridges. Virtual Extensible LANs (VXLANs) establish overlay tunnels that stretch the L2 connections over a Layer 3 (L3) network. In EVPN-VXLAN network configurations, a leaf or spine device can function as a VXLAN gateway at L2, L3, or both layers. The underlay network for the VXLAN overlay can be an IPv4 or an IPv6 network. This topic describes using an IPv6 underlay instead of an IPv4 underlay.
- Benefits of Using an IPv6 Underlay with a VXLAN Overlay
- Platform Support
- Overview
- Underlay Routing Protocols with an IPv6 Underlay
- EVPN-VXLAN Features Supported with an IPv6 Underlay
- Limitations in IPv6 Underlay Support
Benefits of Using an IPv6 Underlay with a VXLAN Overlay
With an IPv6 underlay VXLAN tunnel configuration, you can take advantage of the expanded addressing capabilities and efficient packet processing that the IPv6 protocol offers.
Platform Support
For information on supported platforms and Junos releases, see Feature Explorer.
Overview
In EVPN-VXLAN installations, you configure a VXLAN overlay on L2 or L3 VXLAN gateway devices called virtual tunnel endpoints (VTEPs). The VXLAN overlay extends virtual tunnels between VTEPs over the underlying IP fabric. On supporting platforms, you can configure the IP underlay with IPv6 addressing to support the VXLAN overlay tunnels. For example:
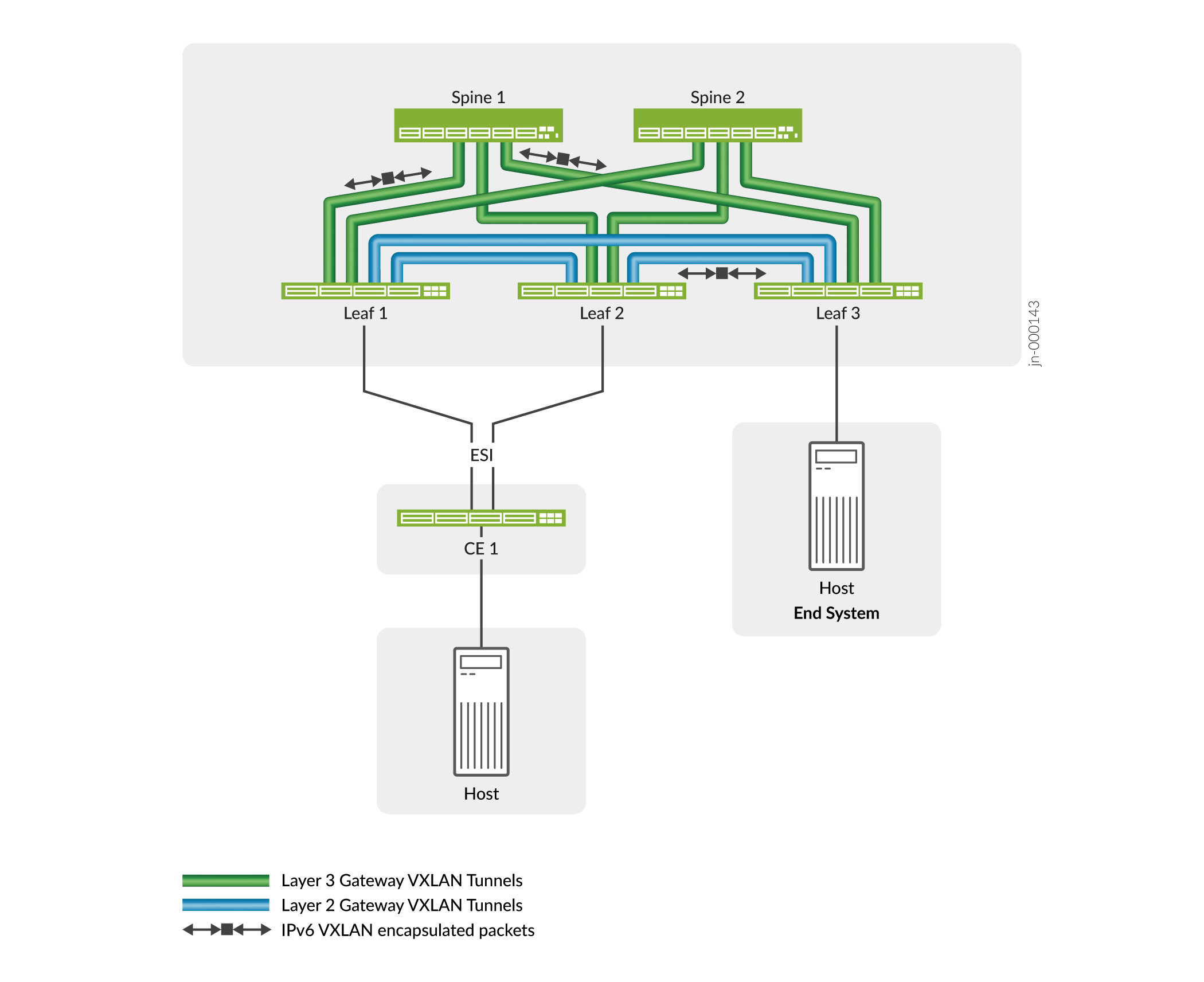
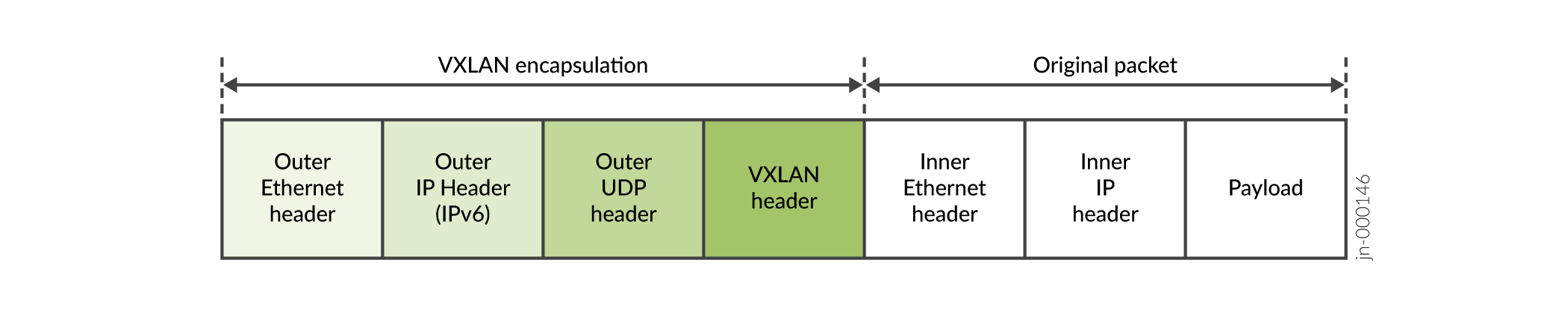
When you use an IPv6 underlay, the VTEPs encapsulate VXLAN packets with an IPv6 outer header and tunnel the packets through an IPv6 underlay network.
IPv6 underlay configurations are similar to IPv4 underlay configurations, except you set the VTEP source addresses as IPv6 addresses. You also assign IPv6 addresses in the underlay and establish reachability using the IPv6 protocol.
Underlay Routing Protocols with an IPv6 Underlay
We've qualified an IPv6 underlay with the following routing protocols in the underlay configuration:
BGP—Internal BGP (IBGP) and external BGP (eBGP)
OSPFv3—Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol for IPv6
EVPN-VXLAN Features Supported with an IPv6 Underlay
We support the following EVPN-VXLAN features with an IPv6 underlay:
We support the items below on all platforms that support EVPN-VXLAN with an IPv6 underlay unless the item lists particular platforms. Use Feature Explorer to confirm platform and release support for specific features.
EVPN Type 1, Type 2, Type 3, and Type 4 routes.
(QFX Series, ACX Series, PTX Series, and MX Series devices) EVPN Type 5 routes.
See EVPN Type 5 Route with VXLAN Encapsulation for EVPN-VXLAN for more about these EVPN route types.
(QFX5130-32CD, QFX5700, ACX Series, and PTX Series devices) EVPN Type 2 and Type 5 route coexistence.
See EVPN Type 2 and Type 5 Route Coexistence with EVPN-VXLAN.
(QFX Series and MX Series devices) Shared VTEP tunnels.
On QFX series switches, we support an EVPN-VXLAN IPv6 underlay only with MAC-VRF EVPN routing instances. The MAC-VRF implementation relies on the shared VTEP tunnels feature to avoid VTEP scaling issues on some devices. On the devices that require shared tunnels but don't have the feature enabled by default, when you configure an IPv6 underlay, you must enable the
shared-tunnelsoption at the[edit forwarding-options evpn-vxlan]hierarchy level. See MAC-VRF Routing Instance Type Overview for more about MAC-VRF instances.Note:After you configure the
shared-tunnelsoption, you must reboot the device for the setting to take effect.(All devices) VLAN-aware bundle, VLAN-based, and VLAN bundle Ethernet service types.
(MX Series routers, additionally) Port-based service, a VLAN bundle service where all VLANs for a port are part of the same VLAN bundle.
See Understanding VLAN-Aware Bundle and VLAN-Based Service for EVPN and MAC-VRF Routing Instance Type Overview for more about MAC-VRF instances and these service types.
All-active multihoming.
Underlay and overlay load balancing over multiple IPv6 VXLAN tunnels with multihoming.
See Load Balancing VXLAN Traffic and Dynamic Load Balancing in an EVPN-VXLAN Network.
Loop prevention on link recovery.
When multihoming interfaces on an Ethernet segment ID (ESI) flap, the device drops broadcast, unknown unicast, and multicast (BUM) traffic that comes into the ESI interface for a configured hold timer interval.
EVPN core isolation.
See Understanding When to Disable EVPN-VXLAN Core Isolation.
EVPN-VXLAN L2 and L3 gateway functions in ERB and CRB overlays with IPv4 or IPv6 traffic.
Bridged overlays.
(EX Series and QFX Series switches) IPv4 and IPv6 multicast data traffic with the following multicast modes in an EVPN-VXLAN network:
Centrally-routed multicast with local-remote forwarding mode—see Multicast Support in EVPN-VXLAN Overlay Networks.
Enhanced optimized intersubnet multicast (OISM) mode—see Overview of Enhanced OISM.
Flood policers in EVPN-VXLAN bridge domains (VLANs) with IPv6 VXLAN tunnels using filters.
(PTX Series routers) Overlay ping and overlay traceroute, and CE-IP ping and CE-IP traceroute.
See ping overlay, traceroute overlay, and Pinging Customer Edge Device IP Address.
(EX Series, QFX Series, and PTX Series devices) Quality of service (QoS) and Class of Service (CoS) classification, including:
Classification using Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) or IEEE 802.1p code points.
Note:(PTX Series routers) No support for DSCP copy or IEEE 802.1p rewrite operations.
(PTX Series routers) Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) field copy:
During VXLAN encapsulation, the device copies the ECN field from the inner header to the outer header.
During VXLAN decapsulation, the device interprets the ECN field from the outer header and propagates it to the inner header if the inner header ECN field value is non-zero (the inner header is ECN-capable).
See CoS Support on EVPN VXLANs for details.
L3 protocols over IRB interfaces with BFD—Static routing, BGP, IS-IS, OSPF and OSPFv3.
Data center interconnect (DCI) over-the-top (OTT) full mesh.
See Over-the-Top Data Center Interconnect in an EVPN Network for details on the OTT DCI method.
DCI seamless stitching, and optimized multicast traffic over DCI seamless stitching using enhanced OISM.
See EVPN-VXLAN DCI Multicast with Enhanced OISM for details on how these features work together in EVPN fabrics with IPv4 or IPv6 underlay peering.
EVPN proxy ARP and ARP suppression, as well as EVPN proxy NDP and NDP suppression.
See EVPN Proxy ARP and ARP Suppression, and Proxy NDP and NDP Suppression for more information on these features.
(EX Series and QFX Series switches) Remote port mirroring and analyzers.
See MAC Filtering, Storm Control, and Port Mirroring Support in an EVPN-VXLAN Environment.
(EX Series, QFX Series, and PTX Series devices) DHCP relay with DHCPv4 and DHCPv6.
Limitations in IPv6 Underlay Support
Note the following limitations in IPv6 underlay support:
You can't mix IPv4 and IPv6 underlay configurations for the VXLAN overlays across the EVPN instances in the same fabric.
We don't support the Open vSwitch database (OVSDB) management protocol for IPv6 underlays.
(EX9200 switches) We don't support EVPN Type 5 routes with an IPv6 underlay.
(QFX10002-60C switches) You can only use enterprise style interface configuration; we don't support service provider style interface configuration and Q-in-Q tunneling with IPv4 or IPv6 underlays on these switches.
You must use MAC-VRF routing instances with EVPN protocol and VXLAN encapsulation. We don't support IPv6 underlays with other instance types such as
evpn,evpn-vpws,virtual-switchor the default switching instance.
Configure an IPv6 Underlay with EVPN-VXLAN
This section describes the key steps to configure the IP underlay for the VXLAN tunnels in an EVPN-VXLAN fabric to use the IPv6 protocol (instead of an IPv4 underlay). You can use an IPv6 underlay in many different EVPN-VXLAN configurations and use cases. See these detailed configuration examples we provide for a few common use cases:
Example: Configure an IPv6 Underlay for Layer 2 VXLAN Gateway Leaf Devices—OSPFv3 in the underlay and IBGP for the overlay connectivity
IPv6 Fabric Underlay and Overlay Network Design and Implementation with EBGP—EBGP with LACP for load-balancing in the underlay and EBGP for the overlay connectivity
BGP Unnumbered IPv6 Underlay in an EVPN-VXLAN Data Center—BGP autodiscovery with ECMP for load-balancing in the underlay that works with a variety of protocols for the overlay connectivity
Keep the following configuration options and requirements in mind when you plan to configure EVPN-VXLAN with an IPv6 underlay:
You can configure your EVPN-VXLAN fabric with any of the underlay routing protocols that support IPv6 underlays. See Underlay Routing Protocols with an IPv6 Underlay.
We support IPv6 underlays only with MAC-VRF routing instances in EVPN-VXLAN fabrics. You must configure your EVPN instances with VXLAN encapsulation in all MAC-VRF routing instances. The routing instances mentioned in the steps here are always EVPN-VXLAN MAC-VRF instances. See MAC-VRF Routing Instance Type Overview for more about MAC-VRF instances.
If the network uses an IPv4 underlay and you're switching the configuration to an IPv6 underlay, you must:
Remove any existing VXLAN IPv4 underlay configuration items.
(ACX7100-32C, AX7100-48L, and ACX7024 devices only) To enable an IPv6 underlay, you must configure the
vxlan-extendedsystem profile option on the device, as follows:set system packet-forwarding-options system-profile vxlan-extended
When you change the system profile, the Packet Forwarding Engine reboots. After the Packet Forwarding Engine comes back up, you can continue with the IPv6 VXLAN underlay configuration.
Note:If you switch a configuration from an IPv6 underlay to an IPv4 underlay, be sure to delete the
vxlan-extendedoption configuration item to restore the device to the default system profile as part of setting up the IPv4 underlay.Configure the IPv6 underlay statements, and commit that configuration.
Reboot the device.
(PTX Series routers only) In any EVPN-VXLAN network, whether the configuration uses an IPv4 underlay or an IPv6 underlay, you must enable the tunnel-termination option at the
[edit forwarding-options]global hierarchy level, or at the[edit interfaces name unit unit-number family inet6]physical interface hierarchy level. A more specific interface level setting supersedes a global setting.
To enable an IPv6 underlay for VXLAN tunneling, include these items in your EVPN-VXLAN fabric configuration:
