VLAN-Based Service for EVPN
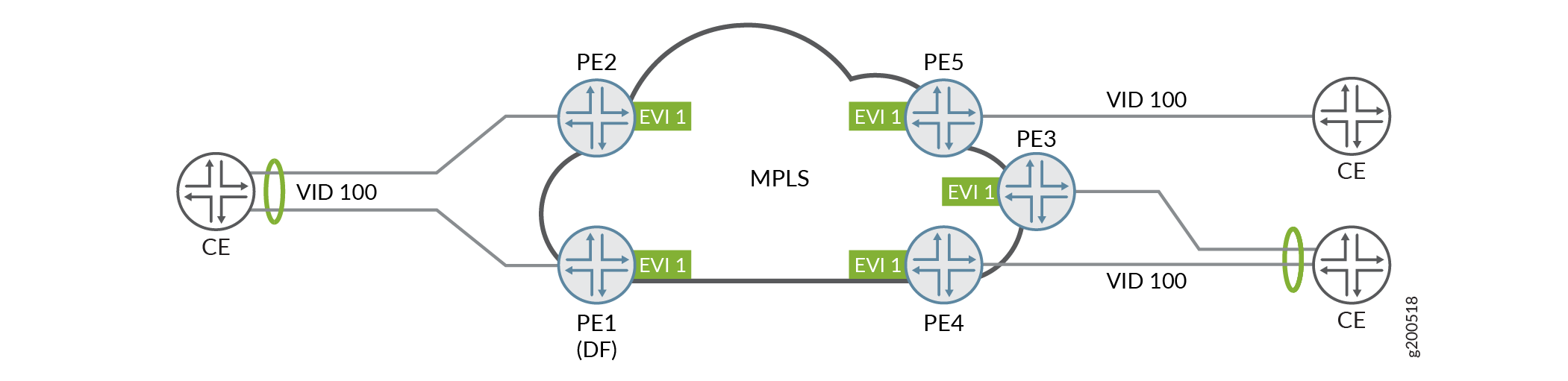
VLAN-based service allows a one-to-one mapping of a single broadcast domain to a single bridge domain. Each VLAN is mapped to a single EVPN instance (EVI), resulting in a separate bridge table for each VLAN. VLAN translation is not supported in older Junos releases. Without VLAN translation, the customer edge VLAN must use the same VLAN ID (VID). You can still send an MPLS encapsulated frames with the originating VID. Figure 1 illustrates a topology where all the CE devices use the same CE VID for a single VLAN-based EVI. VID translation is not needed.
VLAN-based service with VID translation as described in RFC 7432 is supported for devices running Junos OS software. This means that Junos supports VID translation and the customer can have a different VID for each VLAN. As described in the RFC, the VID translation must be performed at the egress PE device while the MPLS encapsulated frames should also retain the originating VID. Figure 2 illustrates a topology where CE devices use different CE-VIDs for single VLAN-based EVI.
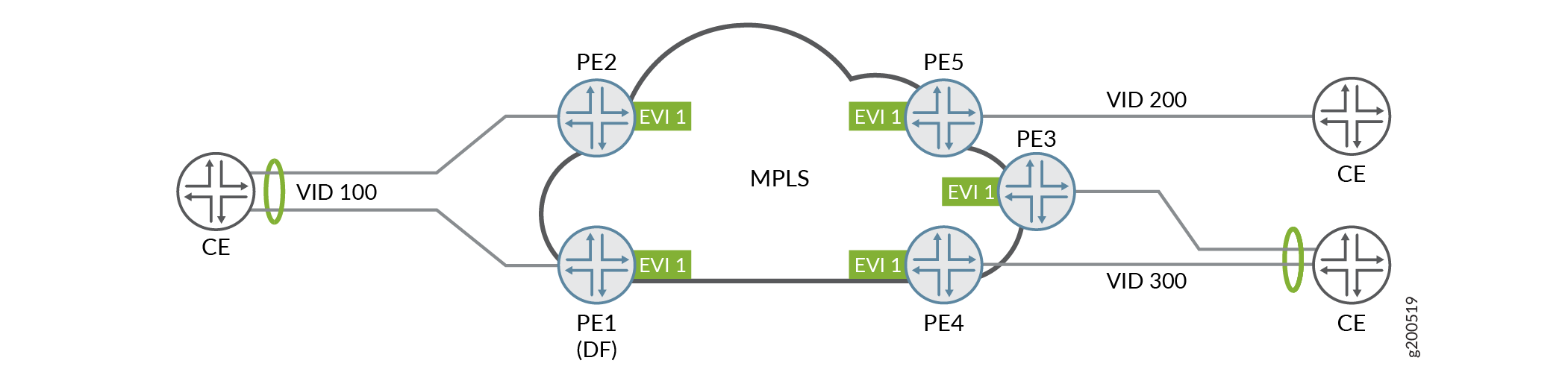
For more information on configuring VLAN-based service, see Configuring EVPN with VLAN-Based Service.
The following is a sample configuration for a single VLAN-based EVI. In this example, the
VLAN-id=none statement is included to remove the originating VID
and to set the Ethernet tag ID to zero in the MPLS frame. This ensures that the same
VID is used on all the PE devices and VLAN translation is not required.
interfaces {
xe-0/0/1 {
unit 100 {
encapsulation vlan-bridge;
vlan-id 100;
}
}
}
routing-instances evpn-vlan-based-no-vid {
instance-type evpn;
vlan-id none;
interface xe-0/0/1.100;
route-distinguisher 10.0.0.1:100;
vrf-target target:65303:101100;
protocols evpn;
}
The following is a sample configuration for a single VLAN-based EVI. The same VID is used on all the PE devices, so VLAN translation is not required. In this example, the CE-VID is used and sent as part of the MPLS frame.
interfaces {
xe-0/0/1 {
unit 100 {
encapsulation vlan-bridge;
vlan-id 100;
}
}
}
routing-instances evpn-vlan-based-with-vid {
instance-type evpn;
interface xe-0/0/1.100;
route-distinguisher 10.0.0.1:100;
vrf-target target:65303:101100;
protocols evpn;
}
Junos supports VLAN-based service with translation as described in RFC 7432. The following
is a sample VLAN-based service configuration that adheres to a strict compliance of RFC
7432. Strict compliance to RFC 7432 requires that translation occurs at the egress PE
device, the originating VID be carried in the MPLS frame, and the Ethernet tag ID be set
to zero for all EVPN routes. Therefore, the VLAN-id=none and the
no-normalization statements are included. This will set the
Ethernet tag ID to zero, while ensuring that different VIDs can still be used.
interfaces {
xe-0/0/1 {
unit 100 {
encapsulation vlan-bridge;
vlan-id 100;
output-vlan-map {
swap;
}
}
}
}
routing-instances evpn-vlan-based-normalization-strict-RFC-compliance {
instance-type evpn;
vlan-id none;
no-normalization;
interface xe-0/0/1.100;
route-distinguisher 10.0.0.1:100;
vrf-target target:65303:101100;
protocols evpn;
}
The following is a sample VLAN-based service configuration that adheres to RFC 7432 except for the condition that the originating VID be carried in the Ethernet frame. The originating VID is removed and the Ethernet tag ID is set to zero.
interfaces {
xe-0/0/1 {
unit 100 {
encapsulation vlan-bridge;
vlan-id 100;
}
}
}
routing-instances evpn-vlan-based-normalization-loose-RFC-compliance {
instance-type evpn;
vlan-id none;
interface xe-0/0/1.100;
route-distinguisher 10.0.0.1:100;
vrf-target target:65303:101100;
protocols evpn;
}
Starting
with Junos OS Release 24.2R1, you can use the advertise-zero-ethernet-tag configuration statement when you need a
vlan-based service with a valid vlan-id that provides Layer 3 gateway
functionality. This also provides RFC 7432 compliance for Layer 2 gateway functionality
with control plane EVPN routes advertised with an Ethernet Tag ID value of 0. You use
this statement with instance-type evpn routing instances and must have
a valid vlan-id and no-normalization configured.
Please refer to Feature Explorer VLAN-based EVPN with IRB interfaces for a complete list of the products that support this feature.
The following is a sample configuration using the
advertise-zero-ethernet-tag statement and a valid
vlan-id:
[edit routing-instances evpna] instance-type evpn; protocols { evpn { advertise-zero-ethernet-tag; } } vlan-id 600; routing-interface irb.600; no-normalization; interface ge-0/0/1.600; route-distinguisher 1:1; vrf-target target:1:1;
