Configuring Micro-SIDs in EVPN-VPWS
The segment routing headers (SRHs) for SRv6 can have a long list of SIDs when data packets are routed through many SRv6 nodes before it reaches its destination address (DA). A long list of segment identifiers (SIDs) adds overhead to the data payload and reduces the efficiency of the payload. Micro-SIDs (uSIDs) extend SRv6 network programming by compressing up to 6 SRv6 SIDs into one SRv6 address within an SRH.
Use Feature Explorer to confirm platform and release support for specific features, including Micro-SIDs in EVPN-VPWS.
For uSID, the router divides the 128-bit SID into the following:
-
Prefix/Block—The prefix contains the locator address of the network.
-
List of uSID instructions—The list of uSID contains either micro-node IDs or a uSID function/behavior.
-
Argument—The argument is an optional field in the SRH.
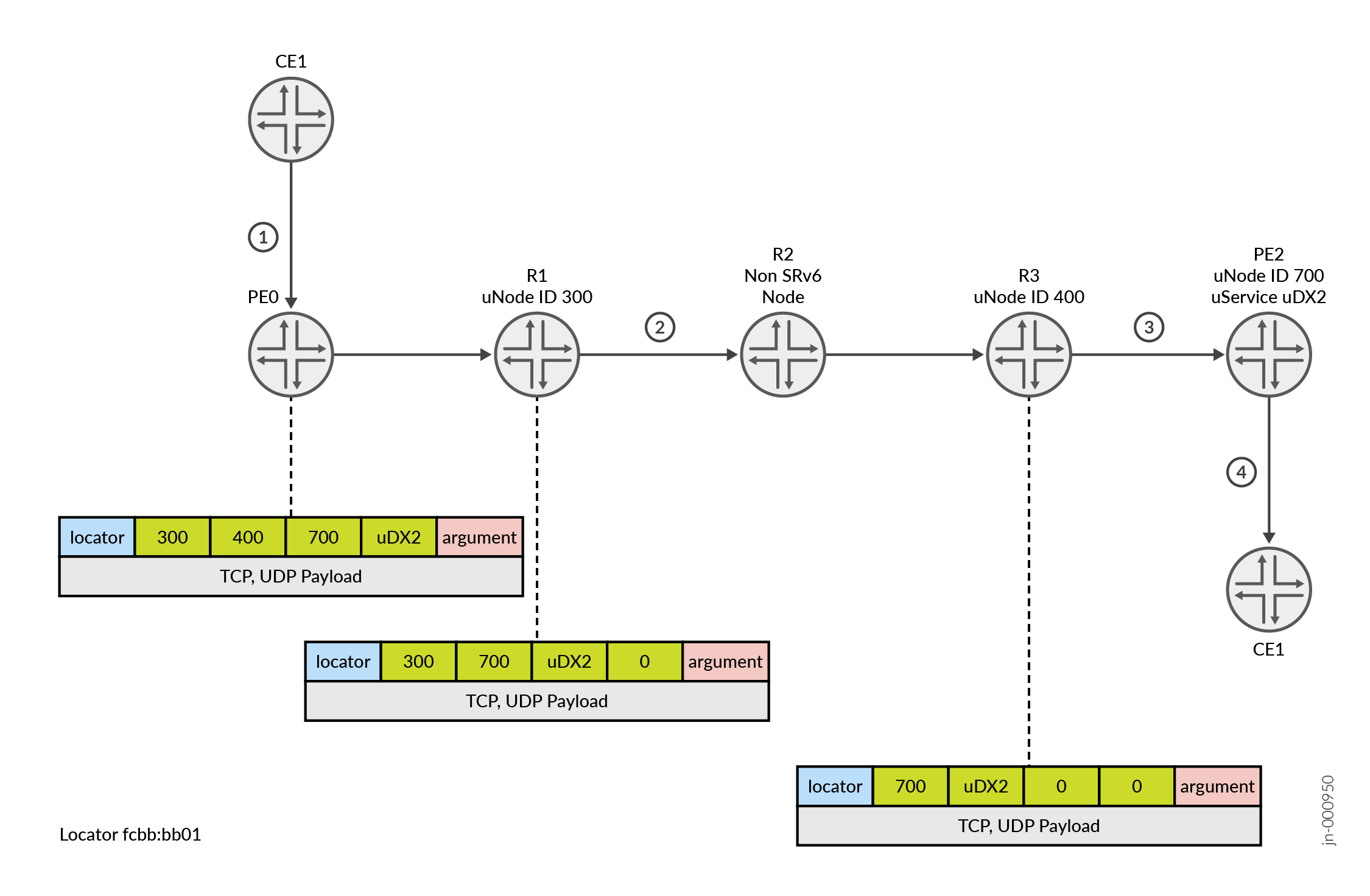
Figure 1 shows the DA as a packet moves through different nodes in SRv6 topology 1. The nodes, ID/function, and SIDs advertised by the nodes are listed in Table 1.
|
Node |
Micro-Node ID/Micro-Node Function |
SIDs Advertised by each Node |
|---|---|---|
|
R1 |
300 |
2001:db8:300:0:0:0:0:0 |
|
R3 |
400 |
2001:db8:400:0:0:0:0:0 |
|
PE2 |
700 |
2001:db8:700:0:0:0:0:0 |
|
PE2 |
f001 |
2001:db8:700:f001:0:0:0:0 |
At the ingress device, PE1 compresses the micro-SIDs for the nodes (R1, R3, and PE2) into one DA. 2001:db8:300:400:700:f001.
R1 processes the DA by consuming its own uSID 300 and forwards the packet with a DA of 2001:db8:400:700:f001:0.
R3 processes the DA by consuming its own uSID of 400 and forwards the packet with a DA 2001:db8:700:f001:0:0.
At the egress device, PE2 consumes its own uSID of 700 and processes the microservices function.
Benefits of uSIDs
-
Reduces network bandwidth by reducing the number of SRv6 addresses in the SRH.
-
Reduces the SRH processing overhead on the node.
Configuring EVPN-VPWS over SRv6 Network with uSIDs
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure EVPN-VPWS over SRv6 with uSIDs, copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your configuration, copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level. Enter commit from configuration mode.
set chassis network-services enhanced-ip set routing-options resolution preserve-nexthop-hierarchy set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 instance-type evpn-vpws set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 protocols evpn encapsulation srv6 set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 protocols evpn interface ge-0/0/1.1 vpws-service-id local 102 remote 201 set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 protocols evpn interface ge-0/0/1.1 vpws-service-id source-packet-routing srv6 locator u_loc set routing-options source-packet-routing srv6 block usid_blk_with_statics 2001:db8::/32 set routing-options source-packet-routing srv6 block usid_blk_with_statics local-micro-sid maximum-static-sids 2000 set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 protocols evpn interface ge-0/0/1.1 vpws-service-id source-packet-routing srv6 locator micro-dx2-sid 0xF900 set routing-options source-packet-routing srv6 locator u_loc 2001:db8:100::/48 set routing-options source-packet-routing srv6 locator u_loc micro-sid block-name usid_blk_with_statics set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 route-distinguisher 65000:100 set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 vrf-target target:65000:200 set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 interface ge-0/0/1.1
We describe the uSID configuration on PE1. To provision a static uSID, you must first configure a static local range of addresses that can be used on all the devices. Use the same statements on PE2 unless differences in the configuration on PE2 are called out.
Enable
enhanced-ipsupport on all MX devices.[edit] user@PE1# set chassis network-services enhanced-ip
Enable expanded next-hop hierarchy support for source packet routing.
[edit] user@R1# set routing-options resolution preserve-nexthop-hierarchy
Enable an
evpn-vpwsrouting instance.[edit] user@PE1# set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 instance-type evpn-vpws
Configure the SRv6 encapsulation type for the EVPN-VPWS1 routing instance.
[edit] user@PE1# set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 protocols evpn encapsulation srv6
Configure the interface with the local and remote VPWS SID for the EVPN-VPWS1 routing instance.
PE1
[edit] user@PE1# set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 protocols evpn interface ge-0/0/1.1 vpws-service-id local 102 remote 201
PE2
[edit] user@PE2# set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 protocols evpn interface ge-0/0/1.1 vpws-service-id local 201 remote 102
Enable uSID for the EVPN-VPWS routing instance.
user@PE1# set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 protocols evpn interface ge-0/0/1.1 vpws-service-id source-packet-routing srv6 locator u_loc
To configure a block for the uSID, specify the prefix and length for a block of IPv6 address. This reserves the block for local static micro-SIDs. For maximum compression, all nodes should have same block prefix.
When defining the uSID function for the locator associated with this block (as described in Step 9), be sure that the micro-SID value falls within the static SID range of the local micro-SIDs. See Checking the Static SID Rangeuser@PE1# set routing-options source-packet-routing srv6 block usid_blk_with_statics 2001:db8::/32
Specify the maximum number of static SID that will be used as micro-SIDs.
user@PE1# set routing-options source-packet-routing srv6 block usid_blk_with_statics local-micro-sid maximum-static-sids 2000
Configure the uSID function for the locator. The uSID function for micro-dx2 is 0xF900.
Note:The micro-SID value must be in the static SID range of local micro-SIDs. You can check that the static SID range for the local micro-SID with the
.show srv6 blockcommand. See Checking the Static SID RangeNote: Junos displays hex values as decimal values in the output of theshow configurationconfigurationuser@PE1# set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 protocols evpn interface ge-0/0/1.1 vpws-service-id source-packet-routing srv6 locator micro-dx2-sid 0xF900
Configure a range of address that the locator can use.
PE1
user@PE1# set routing-options source-packet-routing srv6 locator u_loc 2001:db8:100::/48
PE2
user@PE2# set routing-options source-packet-routing srv6 locator u_loc 2001:db8:200::/48
Enable the uSID locator by specifying the name of the locator and block name that was reserved for the uSID.
user@PE1# set routing-options source-packet-routing srv6 locator u_loc micro-sid block-name usid_blk_with_statics
Configure the vrf target and route distinguisher for the routing instance.
[edit] user@PE1# set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 route-distinguisher 6500:100 user@PE1# set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 vrf-target target:65000:200
Assign the interface to the routing instance.
set routing-instances EVPN-VPWS1 interface ge-0/0/1.1
Checking the Static SID Range
You must assign a uSID value that is inside the static SID range of the local uSIDs. To
display the range of local static SIDs in the local uSID, use the show srv6
block command. The acceptable uSID value is between 0xF830-0xFFFF.
user@host> show srv6 block usid_blk_with_statics
Block: usid_blk_with_statics
Block Prefix: 2001:db8::, Block length: 32, Micro-sid length: 16
Global Micro SIDs:
Static SID range: 0x0-0xDFFF, Dynamic SID range: -
Allocated static SID count: 1, Allocated dynamic SID count: 0
Available static SID count: 57343, Available dynamic SID count: 0
Local Micro SIDs:
Static SID range: 0xF830-0xFFFF, Dynamic SID range: 0xE000-0xF82F
Allocated static SID count: 0, Allocated dynamic SID count: 1
Available static SID count: 2000, Available dynamic SID count: 6191
Dynamic uSID Allocation
The following is a sample configuration for configuring dynamically allocated uSID EVPN-VPWS instance. It builds on the EVPN-VPWS dynamic SID allocation configuration EVPN-VPWS.
set routing-options source-packet-routing srv6 block usid_blk_with_statics 2001:db8::/32 set routing-options source-packet-routing srv6 locator u_loc 2001:db8:100::/48 set routing-options source-packet-routing srv6 locator u_loc micro-sid set routing-instances evpn-vpws-mh instance-type evpn-vpws set routing-instances evpn-vpws-mh protocols evpn interface ae0.0 vpws-service-id local 103 set routing-instances evpn-vpws-mh protocols evpn interface ae0.0 vpws-service-id remote 301 set routing-instances evpn-vpws-mh protocols evpn interface ae0.0 vpws-service-id source-packet-routing srv6 locator u_loc set routing-instances evpn-vpws-mh protocols evpn interface ae0.0 vpws-service-id source-packet-routing srv6 locator micro-dx2-sid set routing-instances evpn-vpws-mh route-distinguisher 65000:100 set routing-instances evpn-vpws-mh vrf-target target:65000:200 set routing-instances evpn-vpws-mh interface ge-0/0/1.1
