Troubleshoot Disconnected SRX Series Firewalls
Troubleshoot disconnected and get packet captures (PCAP) for additional insights.
Troubleshoot SRX Series Firewalls Shown as Disconnected
If the Juniper Mist™ portal shows a Juniper Networks® SRX Series Firewall as disconnected when it is online and reachable locally, you can troubleshoot the issue using the steps listed in this topic. You need console access or SSH access to the firewall to perform the troubleshooting steps.
Troubleshoot SRX Series Firewalls Using Packet Captures
SRX Series Firewalls support manual packet captures (PCAP). Packet capture is a tool that helps you to analyze network traffic and troubleshoot network problems. It captures real-time data packets traveling over the network for monitoring and logging.
SRX Series Firewalls do not support dynamic packet capture.
Manual packet captures are initiated by users from the WAN Edge Packet capture page.
To initiate manual PCAP for an SRX Series Firewall:
Go to Site > WAN Edge Packet Captures.
On the WAN tab, click Add WAN Edge + and select an SRX Series Firewall.
Figure 1: WAN Edge Packet Capture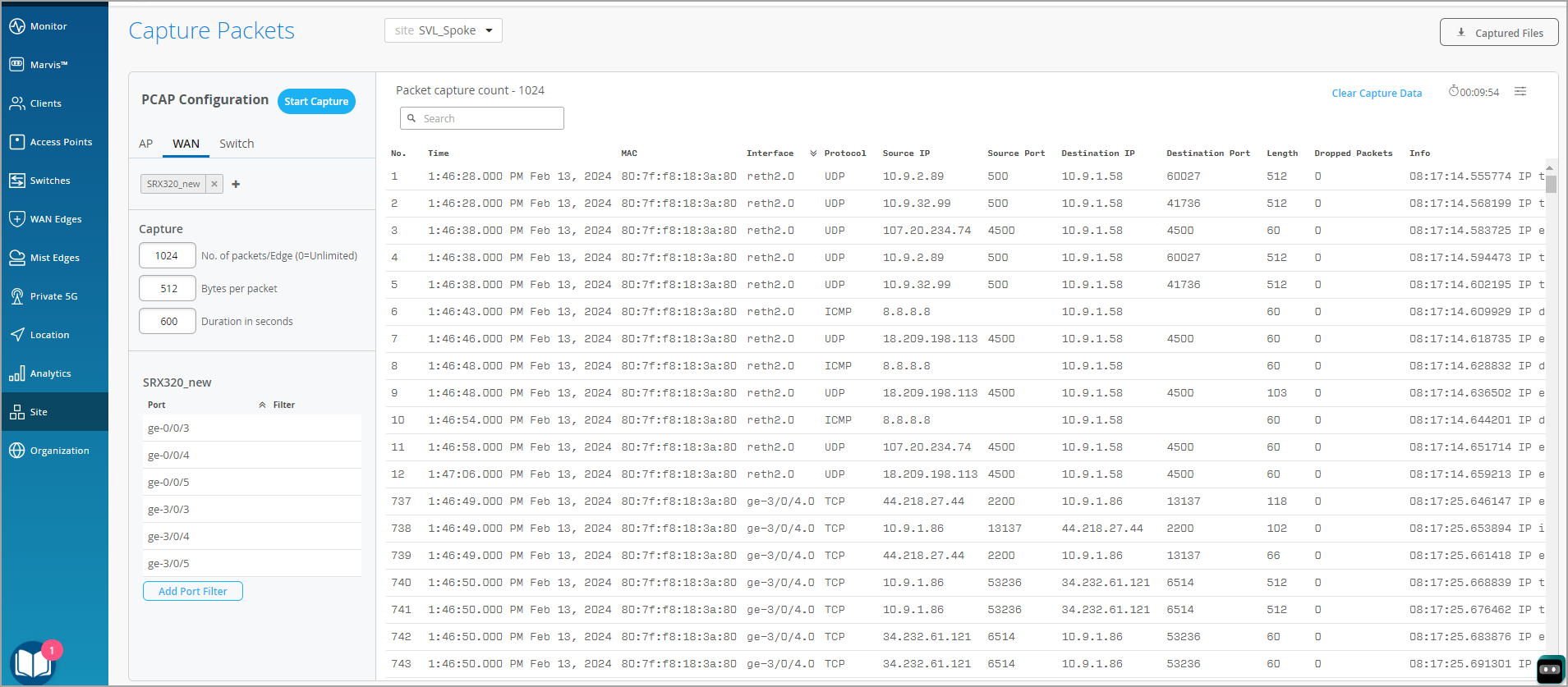
Specify the number of packets captured, packet size in bytes, and the duration of the capture session.
- Use the
Add
Port
Filter
option to specify
the port.
In this pane, you can also enter filters in the TCPDUMP Expression text box.
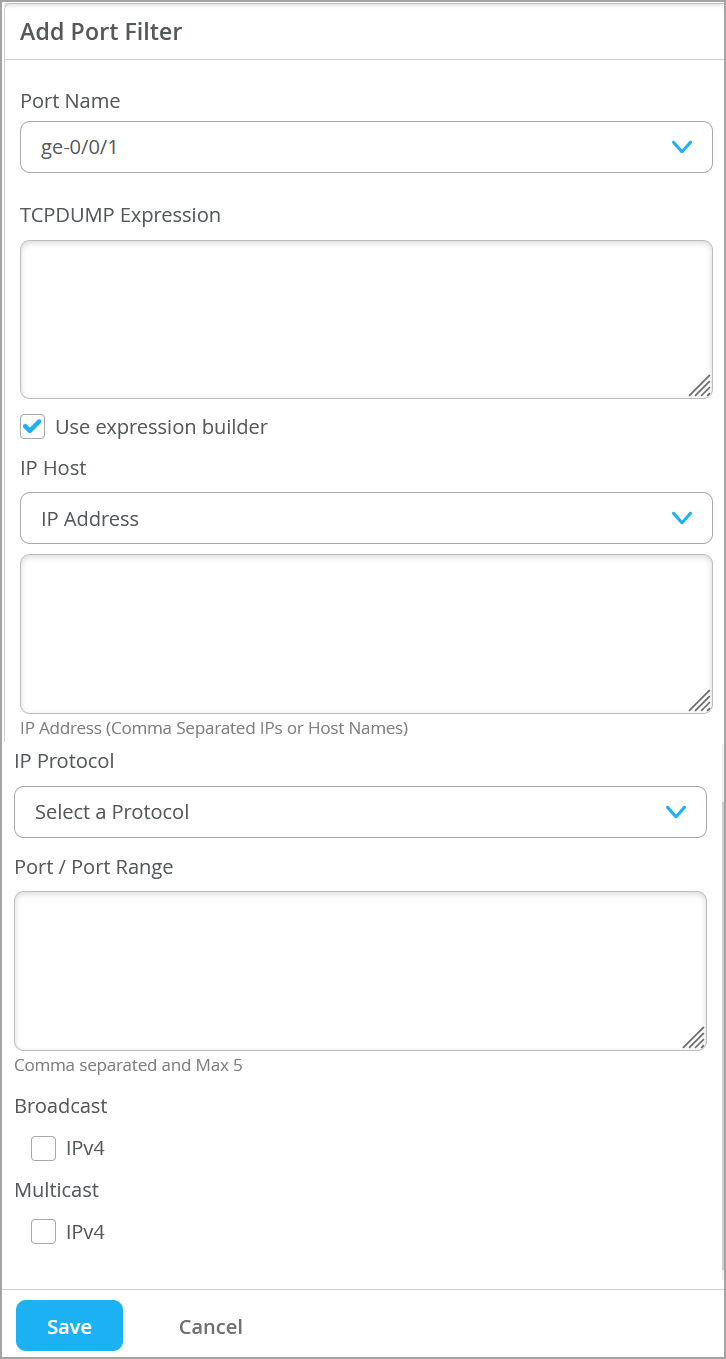
- Optionally, select
Use
Expression
builder
to build the expression for
packet
capture. Expression builder is an interactive GUI tool to build custom filters
in tcpdump syntax for use in the capture session. You can let the builder start
the filter entry and then add to or delete from the entry manually. You can
specify the following options:
- IP host
- Protocols
- Port and port ranges
- IP broadcast
- IP multicast
When you enter addresses and protocols into the expression builder, the portal automatically generates the tcpdump expression on the page. You can edit the expression if needed.
Click Start Capture. The packet capture content is streamed on the page.
- You can download the file for offline analysis by clicking Captured Files on the top right side of the page.
See also: Dynamic and Manual Packet Captures.
