Troubleshooting the MX960 Power System
Problem
Description
The power system is not functioning normally.
Solution
Check the LEDs on each power supply faceplate.
If an AC power supply is correctly installed and functioning normally, the AC OK and DC OK LED’s light steadily, and the PS FAIL LED is not lit.
If a DC power supply is correctly installed and functioning normally, the PWR_OK, INPUT OK, and BREAKER ON LED’s light steadily.
Issue the CLI show chassis environment pem command to check the status of installed power supply modules. As shown in the sample output, the value Online in the rows labeled State indicates that each power supply is functioning normally:
user@host> show chassis environment pem PEM 0 status: State Online Temperature OK DC output OK PEM 1 status: State Online Temperature OK DC output OK
If a power supply is not functioning normally, perform the following steps to diagnose and correct the problem:
If a red alarm condition occurs, issue the show chassis alarms command to determine the source of the problem.
Check that the AC input switch (—) or DC circuit breaker (|) is in the on position and that the power supply is receiving power.
Verify that the source circuit breaker has the proper current rating. Each power supply must be connected to a separate source circuit breaker.
Verify that the AC power cord or DC power cables from the power source to the router are not damaged. If the insulation is cracked or broken, immediately replace the cord or cable.
Connect the power supply to a different power source with a new power cord or power cables. If the power supply status LEDs indicate that the power supply is not operating normally, the power supply is the source of the problem. Replace the power supply with a spare.
If all power supplies have failed, the system temperature might have exceeded the threshold, causing the system to shut down.
Note:If the system temperature exceeds the threshold, the Junos OS shuts down all power supplies so that no status is displayed.
The Junos OS also can shut down one of the power supplies for other reasons. In this case, the remaining power supplies provide power to the router, and you can still view the system status through the CLI or display.
To restart a high-capacity AC power supply after a shut down due to an over-temperature situation:
Move the power switch on the power supply to the off (o) position.
Turn off power to where the AC line goes into the power distribution module (PDM) area.
Wait for the power supply LEDs to fade out and for the fans inside the power supply to shutdown. This can take up to 10 seconds.
CAUTION:Do not attempt to power-on the power supply if the LED is still lit and the fan is still running. If you do, the router will not reboot.
Turn on power to where the AC line goes into the power distribution module (PDM) area.
Move the power switch on the power supply to the on (|) position.
Verify that the LEDs on the power supply faceplate are properly lit.
Issue the CLI show chassis environment pem command and verify the State is
ONLINEand the Temperature isOK.
To restart a high-capacity DC power supply after a shut down due to an over-temperature situation:
Switch off the circuit breaker(s) on the DC distribution panel to remove power to the chassis and power supplies.
Switch on the circuit breaker(s) on the distribution panel to power up the chassis and power supplies.
Note:The power switch on the power supplies is not part of the outer or inner DC circuits and therefore does not need to be switched off when restarting the chassis.
If output power is not load-balancing correctly in the same zone on an MX960 with a high-capacity AC or DC power supply module, connect two feeds and change the DIP switch to 1 to boost the voltage on the power supply module.
Each High Capacity AC or DC power supply accepts two AC or DC feeds in two unique AC or DC receptacles. It is possible to operate with one feed, but there is a reduction in the power supply output. The DIP switch must be set according to the number of AC or DC feeds that are present for the power supply.
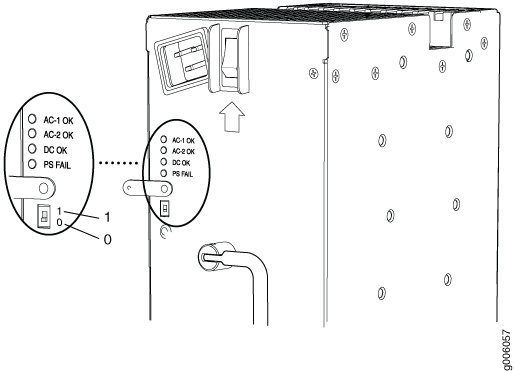
Position – 0 indicates that only one AC or DC feed is provided.
Position – 1 indicates that two AC or DC feeds are provided.
To check the DIP switch position:
Issue the
show chassis powercommand and check to see how many feeds are connected. The following example shows there are two AC input feeds connected for PEM 0 and one AC input feed connected for PEM 1. This indicates that the DIP switch for PEM 0 is in position 1 and the DIP switch for PEM 1 is in position 0. These are the proper settings.# run show chassis power PEM 0: State: Online AC input: OK (2 feed expected, 2 feed connected) Capacity: 4100 W (maximum 4100 W) DC output: 855 W (zone 0, 15 A at 57 V, 20% of capacity) PEM 1: State: Online AC input: OK (1 feed expected, 1 feed connected) Capacity: 1700 W (maximum 4100 W) DC output: 969 W (zone 1, 17 A at 57 V, 57% of capacity)
Issue the
show chassis alarmscommand to see if there are any active alarms on the DIP switch:> show chassis alarms 4 alarms currently active Alarm time Class Description 2013-01-11 14:48:26 UTC Minor PEM 0 Dipswitch 0 Feed Connection 2
If the
show chassis alarmsoutput shows an alarm onDipswitch, issue theshow chassis powercommand to check the DIP switch position.# run show chassis power PEM 0: State: Online AC input: OK (1 feed expected, 2 feed connected) Capacity: 4100 W (maximum 4100 W) DC output: 855 W (zone 0, 15 A at 57 V, 20% of capacity)
In this example, the DIP switch is in the wrong position since there is one AC feed expected but two AC feeds are connected. Change the DIP switch to position 1. This should clear the alarm.
Note:Changing the DIP switch position does not impact traffic. However, it is always recommended to do so in a maintenance window.
