Create a Remote Access VPN—NCP Exclusive Client
Before You Begin
-
Read the IPsec VPN Overview topic.
-
Review the IPsec VPN main page for an understanding of your current data set. See IPsec VPN Main Page Fields for field descriptions.
-
Create addresses and address sets. See Creating Addresses and Address Groups.
-
Create VPN profiles. See Creating VPN Profiles.
-
Define extranet devices. See Creating Extranet Devices.
The Network Control Protocol (NCP) Exclusive Remote Access Client is part of the NCP Exclusive Remote Access solution for Juniper SRX Series Gateways. The VPN client is only available with NCP Exclusive Remote Access Management. Use the NCP Exclusive Client to establish secure, IPsec-based data links from any location when connected with SRX Series Gateways.
To configure a remote access NCP exclusive client:
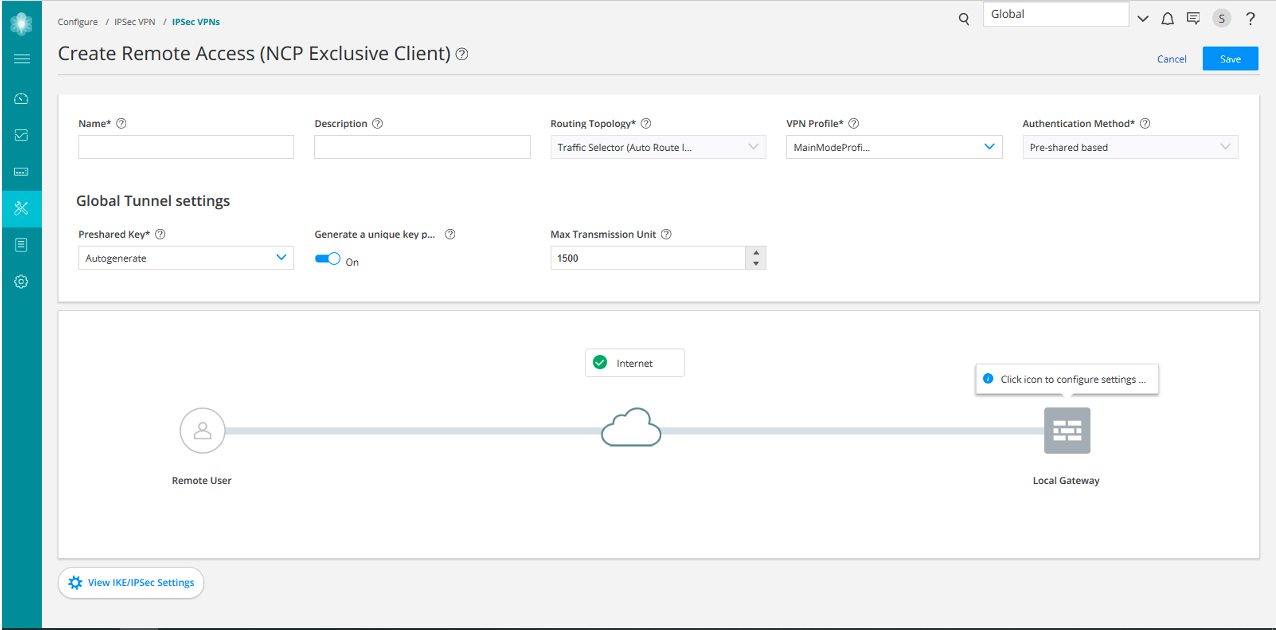
|
Settings |
Guidelines |
|---|---|
|
Name |
Enter a unique string of alphanumeric characters, colons, periods, dashes, and underscores; spaces are not allowed; maximum length is 62 characters. |
|
Description |
Enter a description for the VPN; maximum length is 255 characters. |
|
Routing Topology |
Traffic Selector (Auto Route Insertion)—A traffic selector is an agreement between Internet Key Exchange (IKE) peers to permit traffic through a tunnel if the traffic matches a specified pair of local and remote addresses. |
|
VPN Profile |
Select a VPN profile from the drop-down list based on the deployment scenario. Default profile is applicable to a particular IPsec VPN only. You can view and edit the details by clicking View IKE/IPsec settings on the Create IPsec VPN page. Shared profile can be used by one or more IPsec VPNs. You can only view the details of the shared profiles by clicking View IKE/IPsec settings on the Create IPsec VPN page. If you select the VPN Profile value as Default, then while saving the IPsec VPN, you’ll need to save the new profile as either VPN specific or shared. If you are saving it as shared, then the profile will be listed on the VPN Profiles page. |
|
Authentication Method |
Select an authentication method from the list that the device uses to authenticate the source of Internet Key Exchange (IKE) messages.
|
| Global Tunnel Settings | |
|
Pre-shared Key |
Establish a VPN connection using preshared keys, which is essentially a password that is same for both parties. Select the type of pre-shared key you want to use:
Note:
This is applicable only if the authentication method is pre-shared-based. |
|
Max Transmission Unit |
Select the maximum transmission unit (MTU) in bytes. This defines the maximum size of an IP packet, including the IPsec overhead. You can specify the MTU value for the tunnel endpoint. The valid range is 68 to 9192 bytes. The default value is 1500 bytes. |
|
Settings |
Guidelines |
|---|---|
|
Endpoint |
Select a device to add it as an endpoint. |
|
Available |
View all devices from the current and child domains, with view parent enabled. Devices from the child domain with view parent disabled are not shown. Select a device and add it as an endpoint. The following filter criteria are applied for the device selection:
|
|
Settings |
Guidelines |
|---|---|
|
External Interface |
Select the outgoing interface for IKE security associations (SAs). This interface is associated with a zone that acts as its carrier, providing firewall security for it. |
|
Tunnel Zone |
Select the tunnel zone. They are logical areas of address space that can support dynamic IP (DIP) address pools for NAT applications to pre and post-encapsulated IPsec traffic. Tunnel zones also provide great flexibility in combining tunnel interfaces with VPN tunnels. |
|
User Authentication |
Select the authentication profile from the list that will be used to authenticate a user accessing the remote access VPN. Click Add to create a new access profile. For more information on creating a new access profile, see Creating Access Profiles. Note:
LDAP authentication is not supported in a remote VPN. |
|
SSL VPN Profile |
Select a SSL VPN profile from the list to terminate the remote access connection. To create a new SSL VPN profile:
|
|
NAT Traffic |
Enable this option so that all traffic from the Juniper Secure Connect client is NATed to the selected interface by default. If disabled, you must ensure that you have a route from your network pointing to the SRX Series devices for handling the return traffic correctly. |
|
Certificate |
Select a certificate to authenticate the virtual private network (VPN) initiator and recipient. |
|
Trusted CA/Group |
Select the certificate authority (CA) profile from the list to associate it with the local certificate. This is applicable when authentication method is RSA-Signatures. |
|
Protected Networks |
Configure the addresses type for the selected device to protect one area of the network from the other. Note:
You can also create addresses by clicking Add New Address. |
|
Settings |
Guidelines |
|---|---|
| IKE Settings | |
|
IKE Version |
Select the required IKE version, either V1 or V2, that is used to negotiate dynamic security associations (SAs) for IPsec. By default, IKE V2 is used. |
|
Mode |
Select an IKE policy mode.
Note:
Mode is applicable when the IKE Version is V1. |
|
Encryption-algorithm |
Select the appropriate encryption mechanism. |
|
Authentication-algorithm |
Select an algorithm. The device uses this algorithm to verify the authenticity and integrity of a packet. |
|
Deffie Hellman group |
Select a group. Diffie-Hellman (DH) groups determine the strength of the key used in the key exchange process. |
|
Lifetime-seconds |
Select a lifetime of an IKE security association (SA). The valid range is from 180 through 86,400 seconds. |
|
Dead Peer Detection |
Enable to permit the two gateways to determine if the peer gateway is up and responding to the Dead Peer Detection (DPD) messages that are negotiated during IPsec establishment. |
|
DPD Mode |
Select a DPD Mode.
|
|
DPD Interval |
Select an interval in seconds to send dead peer detection messages. The default interval is 10 seconds, with a permissible range of 2 to 60 seconds. |
|
DPD Threshold |
Select the failure DPD threshold value. This specifies the maximum number of times the DPD messages must be sent when there is no response from the peer. The default number of transmissions is 5 times, with a permissible range of 1 to 5. |
| Advance Configuration | |
|
IKEv2 Re Fragmentation Support |
IKEv2 fragmentation splits a large IKEv2 message into a set of smaller ones so that there is no fragmentation at the IP level. |
|
IKEv2 Re-fragment Size |
Select the size of the packet at which messages are fragmented. By default, the size is 576 bytes for IPv4. Range is 570 to 1320. |
|
NAT-T |
Enable Network Address Translation-Traversal (NAT-T) if the dynamic endpoint is behind a NAT device. |
|
Keep Alive |
Select a value. NAT keepalives are required to maintain the NAT translation during the connection between the VPN peers. Range is from 1 to 300 seconds. |
|
IKE Connection Limit |
Select the number of concurrent connections that the VPN profile supports. When the maximum number of connections is reached, no more Remote Access User (VPN) endpoints attempting to access an IPsec VPN can begin Internet Key Exchange (IKE) negotiations. |
| IPSec Settings | |
|
Encryption Algorithm |
Select the necessary encryption method. This is applicable if the Protocol is ESP. |
|
Perfect Forward Secrecy |
Select Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) as the method that the device uses to generate the encryption key. The PFS generates each new encryption key independently from the previous key. The higher numbered groups provide more security but require more processing time. |
| Advance Configuration | |
|
VPN Monitor |
Enable this option to send Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) to determine if the VPN is up. |
|
Optimized |
When VPN monitoring optimization is enabled, the SRX Series device only sends ICMP echo requests (pings) when there is outgoing traffic and no incoming traffic from the configured peer, through the VPN tunnel. If there is incoming traffic through the VPN tunnel, the SRX Series device considers the tunnel to be active and does not send pings to the peer. |
|
Anti Replay |
By default, Anti-Replay detection is enabled. IPsec protects against a VPN attack by using a sequence of numbers that are built into the IPsec packet—the system does not accept a packet for which it has already seen the same sequence number. It checks the sequence numbers and enforces the check, rather than just ignoring the sequence numbers. Disable it if there is an error with the IPsec mechanism that results in out-of-order packets, preventing proper functionality. |
|
Install interval |
Select the maximum number of seconds to allow for the installation of a re-keyed outbound security association (SA) on the device. |
|
Idle Time |
Select the appropriate idle time interval. The sessions and their corresponding translations typically time out after a certain period if no traffic is received. |
|
DF Bit |
Select an option to process the Don’t Fragment (DF) bit in IP messages.
|
|
Copy Outer DSCP |
Enable copying of Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) field from the outer IP header encrypted packet to the inner IP header plain text message on the decryption path. The benefit in enabling this feature is that after IPsec decryption, clear text packets can follow the inner class-of-service (CoS) rules. |
|
Lifetime Seconds |
Select a lifetime of an IKE security association (SA). The valid range is from 180 through 86,400 seconds. |
|
Lifetime kilobytes |
Select the lifetime (in kilobytes) of an IPsec security association (SA). The range is from 64 through 4294967294 kilobytes. |
