What are Virtual Networks
You can create an overlay network in an Apstra blueprint by creating virtual networks (VN)s to group physically separate endpoints into logical groups. These collections of Layer 2 forwarding domains are either VLANs or VXLANs.
VLANs have the following characteristics:
- Single rack (rack-local)
- Single leaf devices or leaf pairs
- Can deploy in Layer 2-only mode (for example, isolated cluster networks for database replication)
- Can deploy with Layer 3 gateway (SVI) IP address on rack leaf, hosted with or without first-hop redundancy
VXLANs have the following characteristics:
- Fabric-wide for ubiquitous Layer 2 (inter-rack)
- Combination of single rack leaf devices or leaf pairs (MLAG)
- Can deploy in Layer 2-only mode
- Can deploy with Layer 3 gateway functionality
- The control plane selected (Pure IP Fabric or MP-EBGP EVPN) when configuring the template for your blueprint determines what is configured in the VN. (MP-EBGP EVPN provides a control plane for VXLAN routing.)
- VXLAN-EVPN capabilities for VXLAN VNs are dependent on network device makes and models.
For more information see the
evpn_support_addendum:Apstra EVPN Support Addendum.
For complete VN feature compatibility for supported Network Operating Systems (NOS), see the Apstra Feature Matrix for the applicable release (in the Reference section). For detailed capability information for a device, contact your network device vendor or Juniper Support.
VNs contain the following details:
|
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Name |
30 characters or fewer. Underscore, dash, and alphanumeric characters only. |
|
Description |
The way the description is rendered in a configuration depends on the NOS of the device:
|
|
Type |
|
|
Tags |
Tags |
| Routing Zone |
|
|
Tenant |
|
| Default VLAN ID (VLAN only) |
|
| VNI(s) (VXLAN only) | Layer 2 VXLAN ID on the switch that the VN is assigned to. If left blank, it's auto-assigned from resource pools. Create up to 40 VNs at once by entering ranges or individual VNI IDs separated by commas (for example: 5555-5560, 7777). Commit the first 40 VNs before creating additional ones. |
| VLAN ID (on leaf devices) | VLAN ID |
| Reserve across blueprint (VXLAN only) | Option to use same VLAN ID on all leaf devices |
| DHCP server | Enabled/Disabled - DHCP relay forwarder configuration on SVI. Implies L3 routing on SVI |
| IPv4 Connectivity | Enabled/Disabled - for SVI routing |
| IPv4 subnet (if connectivity is enabled) |
|
| Virtual Gateway IPv4 | The IPv4 address, if enabled |
| IPv6 Connectivity | Enabled/Disabled - IPv6 connectivity for SVI routing. You must enable IPv6 in blueprint. If the template uses IPv4 spine-to-leaf link types, you can't use IPv6 in default routing zone and for VLAN type VNs. |
| IPv6 subnet (if connectivity is enabled) |
|
| Virtual Gateway IPv6 | The IPv6 address, if enabled |
| Create connectivity templates for |
|
| L3 MTU | Default value is from Virtual Network Policy. You can update the value here for these specific virtual networks. |
| Assigned to | The racks that the VN is assigned to. For more information, see table below. |
| Assigned To Details | Description |
|---|---|
|
Pod Name (5-stage) |
5-stage Clos networks include pods, and you can select leaf devices within each pod to extend VNs to those devices. |
|
Bound to |
The racks assigned. For MLAG racks, the leaf pair is shown. For VLANs, if more than one rack is selected, multiple rack-local VLAN-based VNs are created. |
|
Tags |
Leverage system tags for filtering when you create virtual networks. This helps speed-up the definition of a virtual network footprint in large-scale deployment. It nicely complements the tag-driven interface assignment at the connectivity template level. |
|
Link Labels |
Label assigned to rack (for example, ext-link-1, single-link, single-link, ext-link-0) |
|
VLAN ID |
Can use for batch creating VNs |
|
Secondary IP Allocation Mode |
|
|
IPv4 Address / IPv6 Address |
You can set the first-hop-redundancy IP address for the SVI (VRRP, VARP and so on). If left blank, the SVI IP address is assigned from the selected pool. When you bind an EVPN connectivity template to a Layer 2 application point, the SVI IP address is used as the source / destination for the BGP session, static routes and so on. |
From the blueprint, navigate to Staged > Virtual > Virtual Networks to go to the Virtual Networks table view.
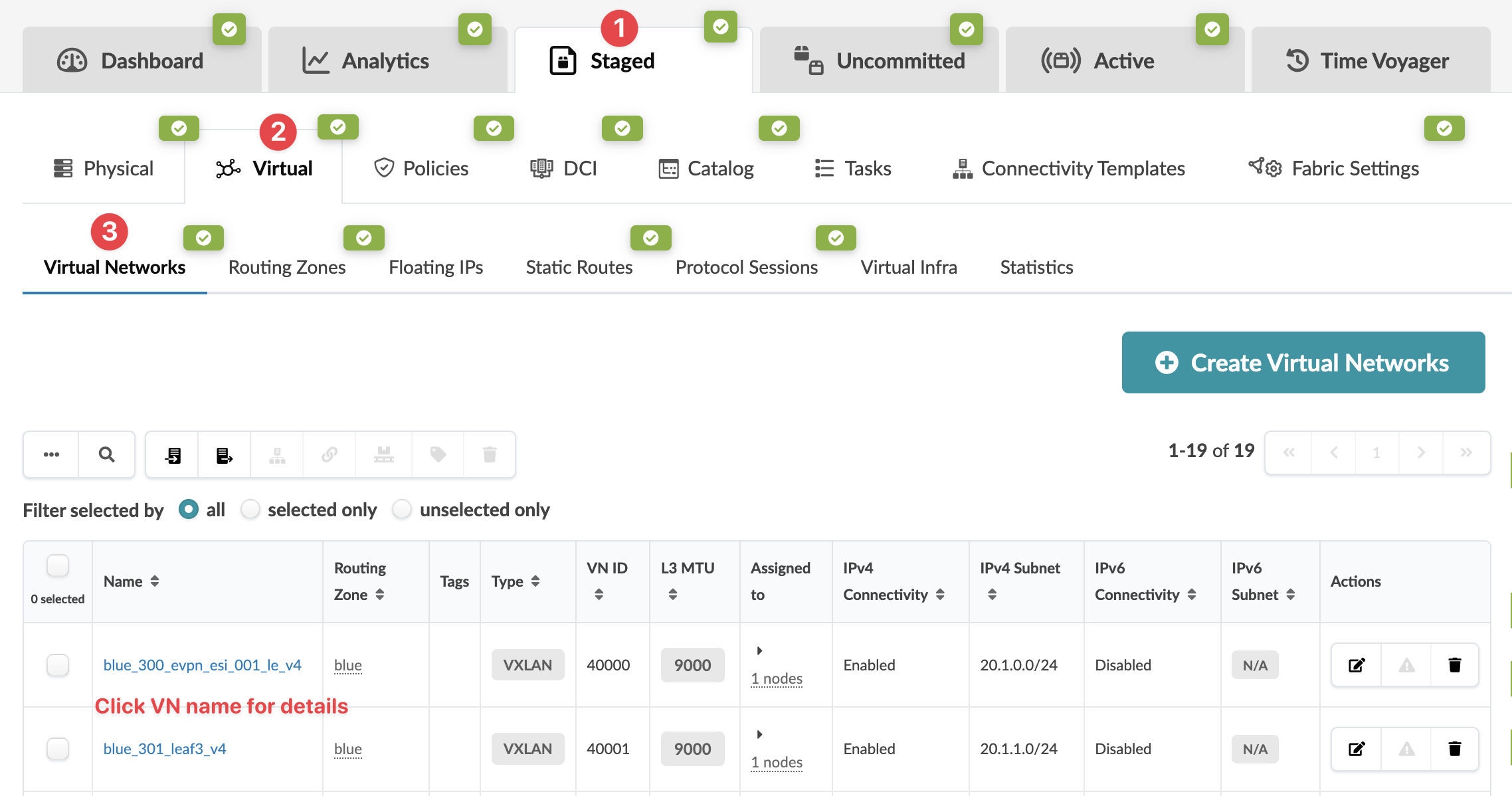
To go to the details of a virtual network, click its name in the table.
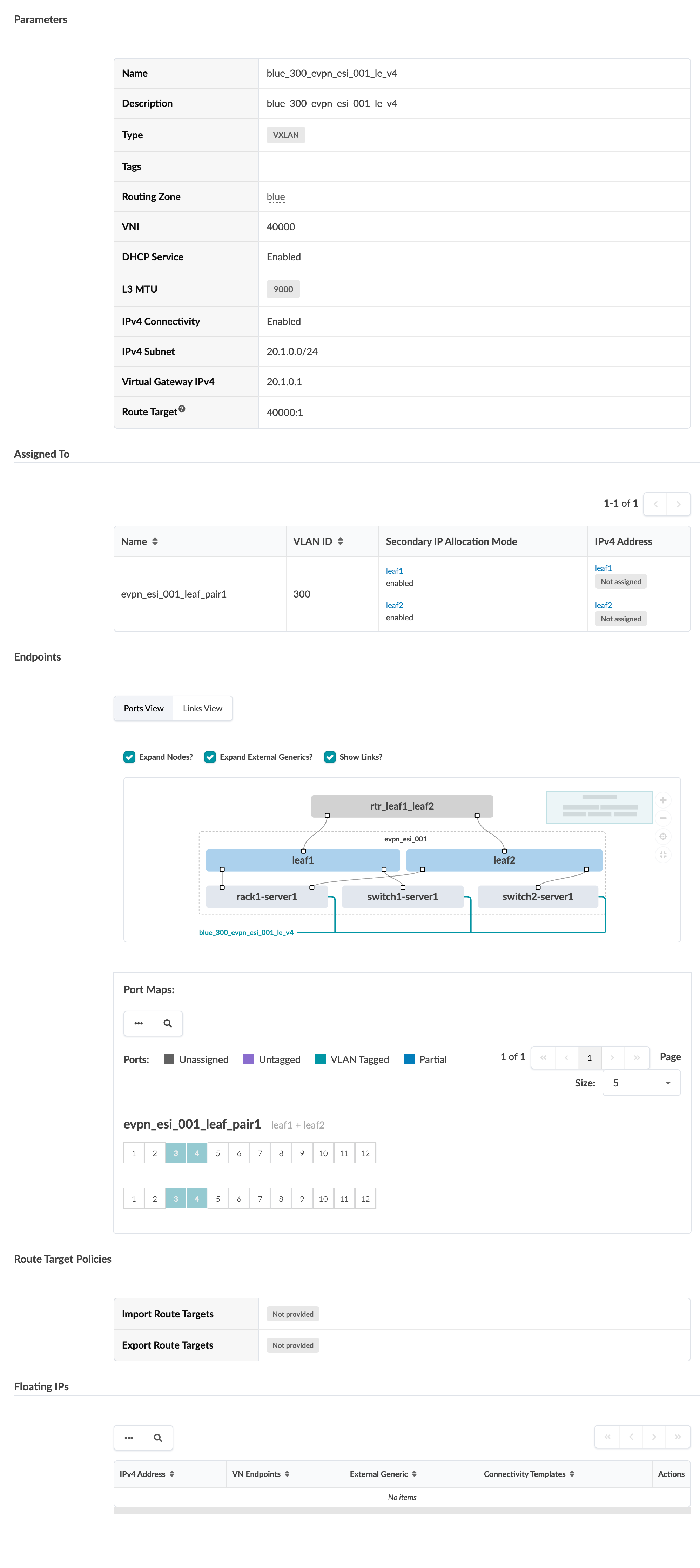
You can create, edit, import, export, tag, and delete virtual networks.
