Create Virtual Network
Create Virtual Networks (using GUI)
-
From the blueprint, navigate to Staged > Virtual > Virtual
Networks and click Create Virtual
Networks.
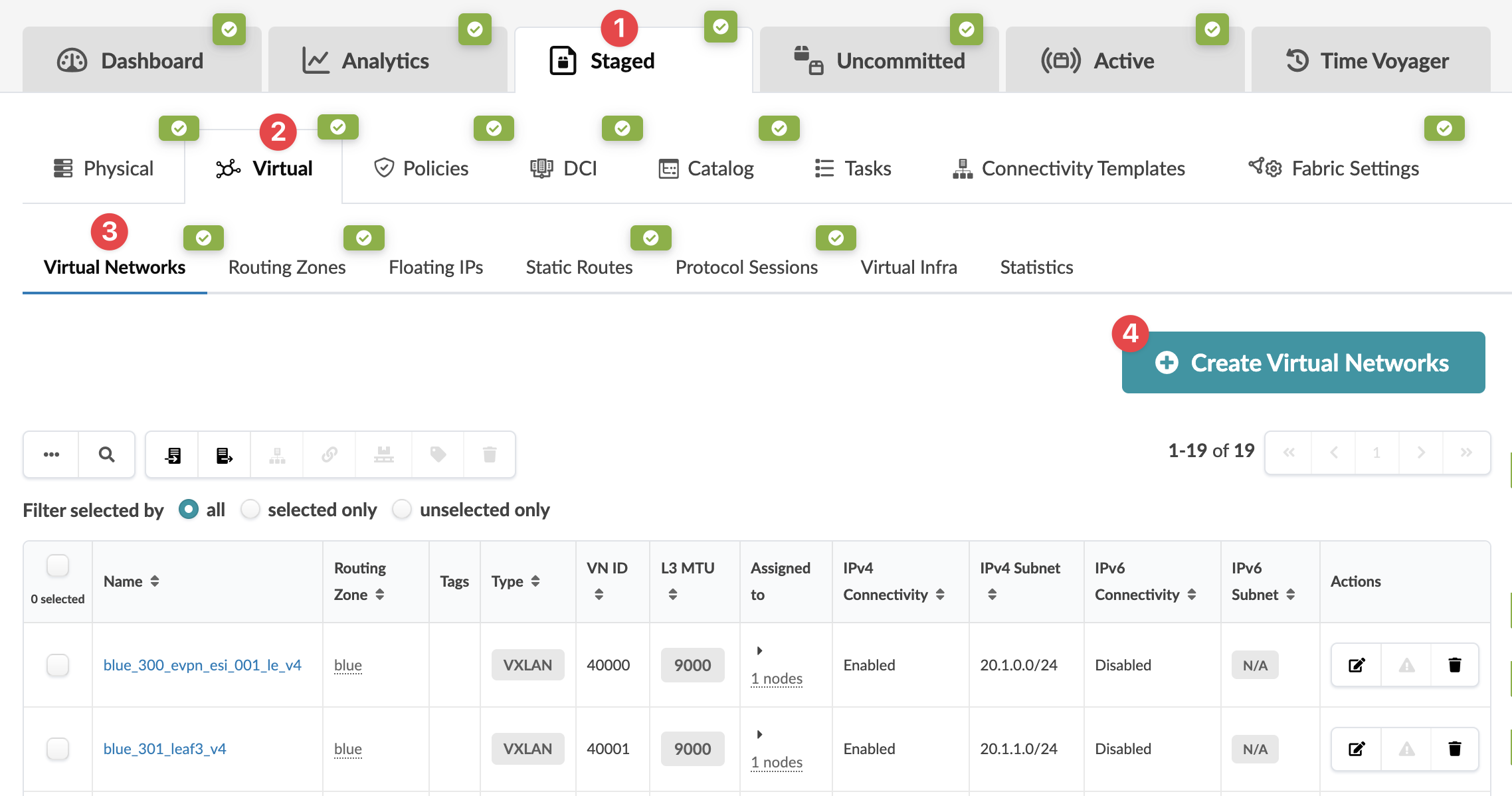 The Creating Virtual Network dialog opens.
The Creating Virtual Network dialog opens. -
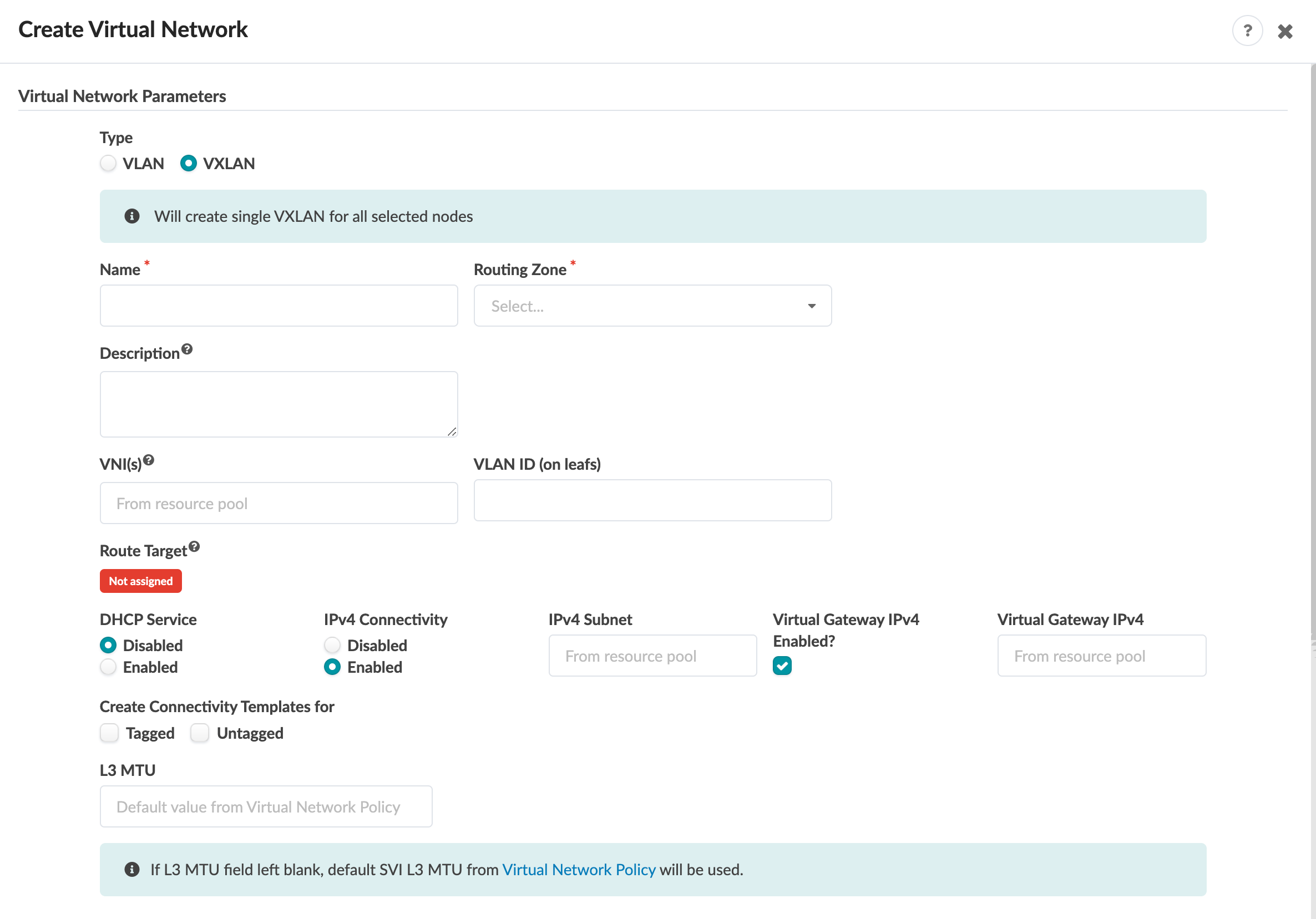
Enter Virtual Networks Parameters details as
described below. (For more details about each parameter, see What are Virtual
Networks.)
-
Select the type of virtual network(s) to create (VLAN, VXLAN),
enter a unique name, and (optional) description. (Description is new
in Apstra version 5.0.0.) The way the description is rendered in a
configuration depends on the NOS of the device:
-
Junos - Description is rendered under VLAN configuration (It's always present.)
-
SONiC - No description is rendered.
-
NX-OS - Description is rendered only on SVI, unless the IP address is disabled, then no description is rendered.
-
EOS - Description is rendered only on SVI, unless the IP address is disabled, then no description is rendered.
-
- Select the routing zone from the drop-down list to associate with the virtual network(s). (If the routing zone that you need is not in the list, you probably still need to create it.) (VLANs must use the default routing zone.)
- If you're creating VXLANs, specify VNIs. If you're creating VLANs, specify VLAN ID(s). You have the option of leaving this field blank to allow auto-assignment from a resource pool.
- If you're creating VXLANs and you enter a VLAN ID (on leaf devices), you can select the check box (that appears after entering a value) to Reserve across blueprint. This enforces the same rule across the fabric and helps you to honor the same VLAN policy across racks when adding new racks.
- The Route Target field represents the built-in Apstra Route-target for the L2 VNI. When using EVPN DCI Gateway features, this route-target must be included in L2 VNI import and export route-targets for EVPN fabrics outside of the Apstra blueprint. You can't modify the build-in route-target. If this value displays Not Assigned, it means a VNI must be associated with the virtual network.
- If you enable DHCP Service, enter a subnet. A DHCP relay forwarder is configured on the SVI. This option also implies Layer 3 routing on this SVI. (You assign the DHCP server in the routing zone.)
- If you enable IPv4 Connectivity, enter a subnet, unless you're batch-creating virtual networks. If so, enter an IPv4 CIDR length, or leave subnet blank to allow auto-assignment.
- If you enable Virtual Gateway IPv4, enter an IPv4 address.
- If IPv6 is enabled in the blueprint (Policies > Fabric Addressing Policy), and you enable IPv6 Connectivity, enter a subnet, unless you're batch- creating VNs. If so, enter an IPv6 CIDR length, or leave subnet blank to allow auto-assignment.
- If you enable Virtual Gateway IPv6, enter an IPv6 address.
- To create connectivity templates for the VN(s), check the box for Tagged and/or Untagged, as applicable.
- To override the default MTU value, enter a value for L3 MTU.
-
Select the type of virtual network(s) to create (VLAN, VXLAN),
enter a unique name, and (optional) description. (Description is new
in Apstra version 5.0.0.) The way the description is rendered in a
configuration depends on the NOS of the device:
-
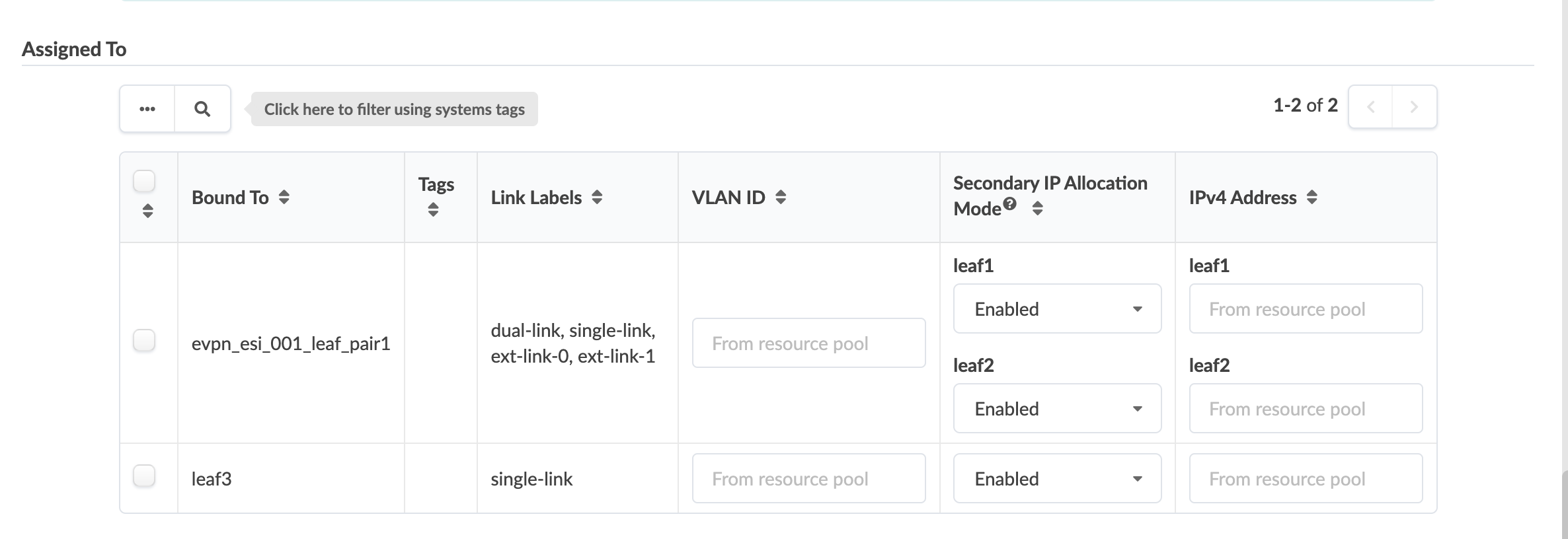
In the Assigned To section of the dialog, select the
applicable rack(s) to assign the virtual networks to and configure them. As
of Apstra version 5.0.0, you can leverage system tags for filtering when you
create virtual networks. This helps speed-up the definition of a virtual
network footprint in large-scale deployment. It nicely complements the
tag-driven interface assignment at the connectivity template level. As of
Apstra version 5.0.0, you can skip virtual network assignment during
creation and assign them later.
-
In the Route Target Policies section of the dialog,
add import and export route targets, as applicable
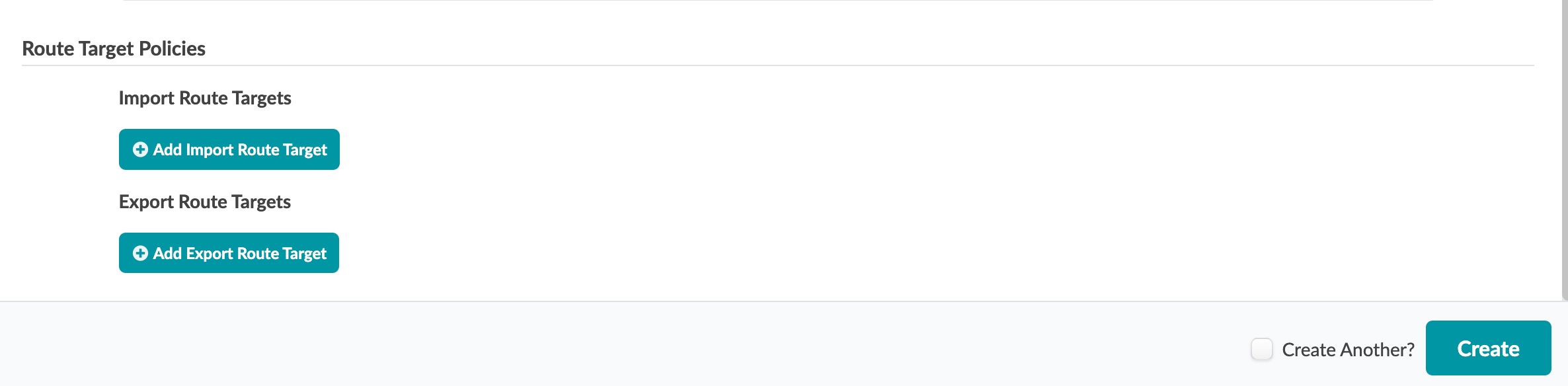
- Click Create to stage the new virtual network(s) and return to the Virtual Networks table view.
- Assign IPv4 (IPv6) resources for SVI subnets. Navigate to Staged > Virtual > Virtual Networks and assign resources in the Build panel (right-side).
-
For VXLAN only: Assign VTEP IPs. Navigate to Staged > Virtual
> Virtual Networks and assign resources in the
Build panel (right-side). (You can display the VTEPs list in the
nodes table (Staged > Physical > Nodes). Select the type of VTEP to
display from the Columns drop-down list (above the table).)
- Single Leaf Nodes require one VTEP IP and an anycast VTEP IP for all switches in the VN.
- MLAG Leaf-pair Nodes require a common VTEP IP for the leaf-pair and an anycast VTEP IP for all switches in the VN.
When you're ready to activate your changes, go to the Uncommitted tab to review and commit (or discard) your changes.
Create Virtual Networks (using CSV File)
-
From the blueprint, navigate to Staged > Virtual > Virtual
Networks and click Export all virtual
networks.
- Click Copy to copy the contents or click Save As File to download the file. (Close the dialog to return to the table view.)
- Paste the contents, or open the CSV file, in a spreadsheet program (such as Google Sheets or Microsoft Excel). (Any virtual networks that were previously created are included in the file.)
-
Enter virtual networks details into the spreadsheet leaving the
vn_node_idfield blank for new VNs, then save the file. -
In the Apstra GUI, from the blueprint, navigate to Staged >
Virtual > Virtual Networks and click Import
virtual networks.
-
Either click Choose File and navigate to the file on
your computer, drag and drop the file onto the dialog window, or as shown in
the screenshot below, directly paste CSV file contents. Virtual network
details are displayed for your review.
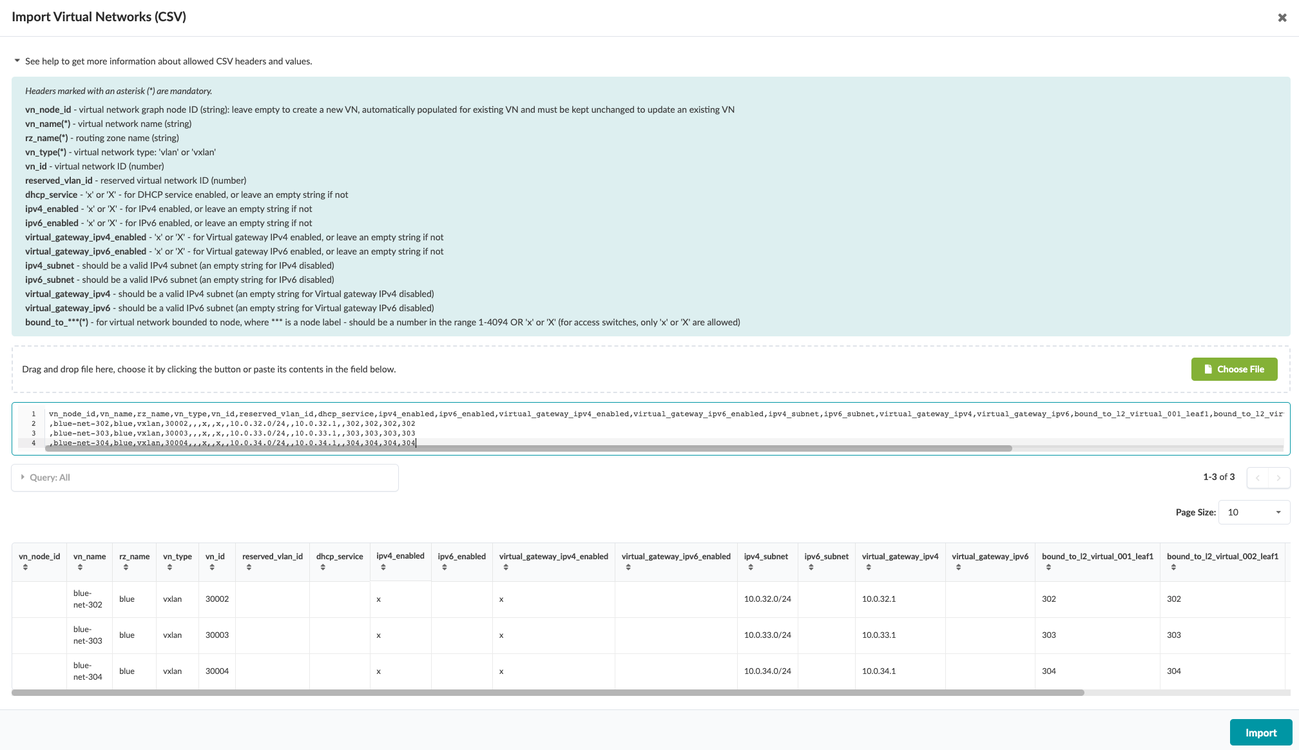
- Click Import to import the virtual networks, stage the changes, and return to the Virtual Networks table view.
- Assign IPv4 (IPv6) resources for SVI subnets. Navigate to Staged > Virtual > Virtual Networks and assign resources in the Build panel (right-side).
-
For VXLAN only: Assign VTEP IPs. Navigate to Staged > Virtual
> Virtual Networks and assign resources in the
Build panel (right-side). (You can display the VTEPs list in the
nodes table (Staged > Physical > Nodes). Select the type of VTEP to
display from the Columns drop-down list (above the table).)
- Single Leaf Nodes require one VTEP IP and an anycast VTEP IP for all switches in the VN.
- MLAG Leaf-pair Nodes require a common VTEP IP for the leaf-pair and an anycast VTEP IP for all switches in the VN.
When you're ready to activate your changes, go to the Uncommitted tab to review and commit (or discard) your changes.
