Hypervisor and Fabric VLAN Config Mismatch Probe
Hypervisor & Fabric VLAN Config Mismatch Probe Overview
| Purpose |
Calculate VLAN mismatch between configured virtual networks on leaf devices and VLANs needed by VMs running on hypervisors attached to leaf devices. (Formerly known as Virtual Infra VLAN Match). Detects misconfiguration of hypervisor trunk logical switches when VLAN tag is configured inside a VM (not on the bridge itself). |
||||||||||||||||
| Source Processors |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Additional Processor(s) |
|
Usage with NSX-T Integration
- From the blueprint, navigate to Analytics > Probes
and click Hypervisor & Fabric VLAN Config Mismatch in
the probe name list to go to its details. When the VLANs between the data center
fabric and the NSX-T transport nodes match, then the probe looks similar to the
image below:
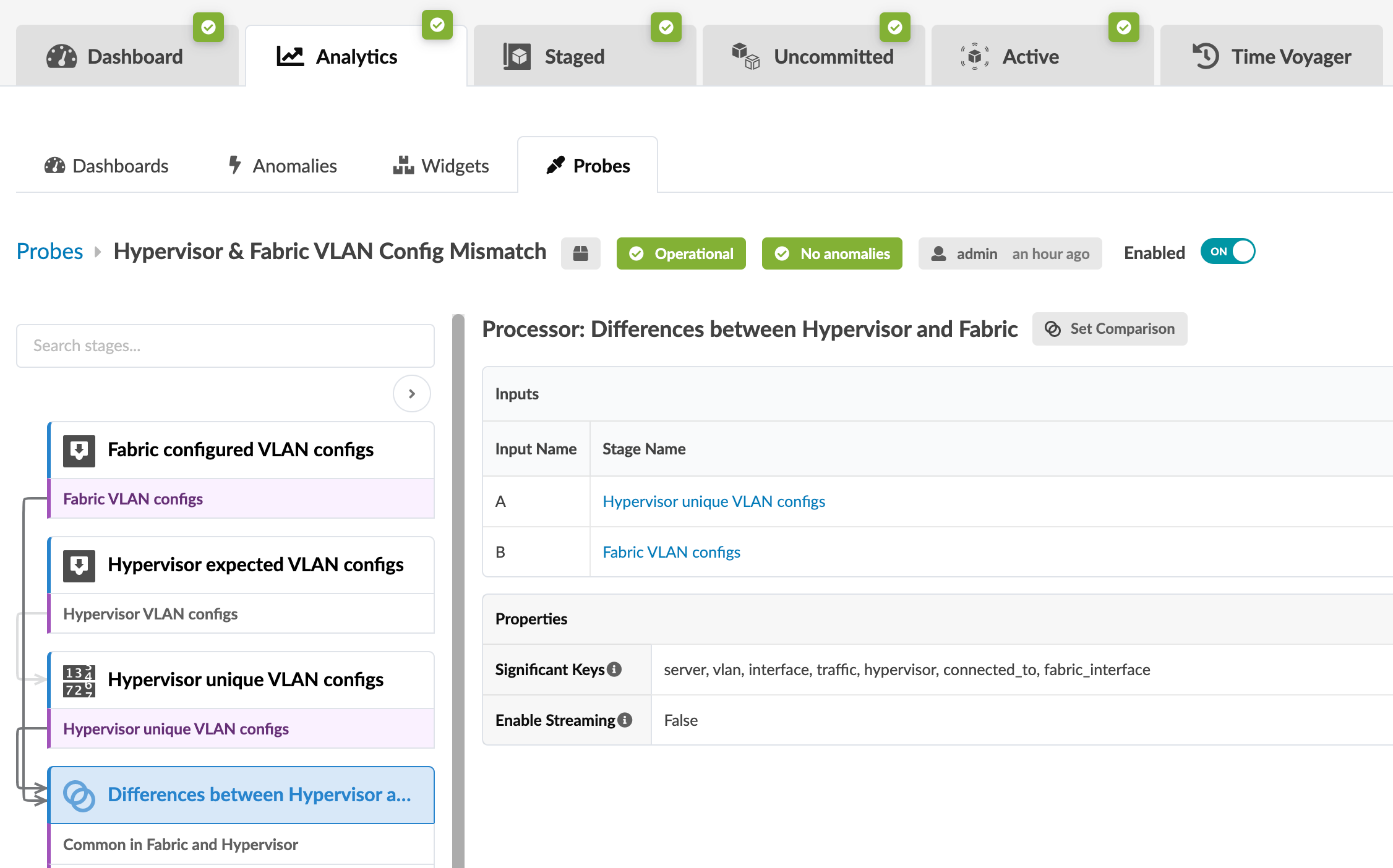
- Click the Fabric VLAN Configs stage to show the VLANs
tagged towards NSX-T transport nodes on fabric ToR leaf devices as shown below:
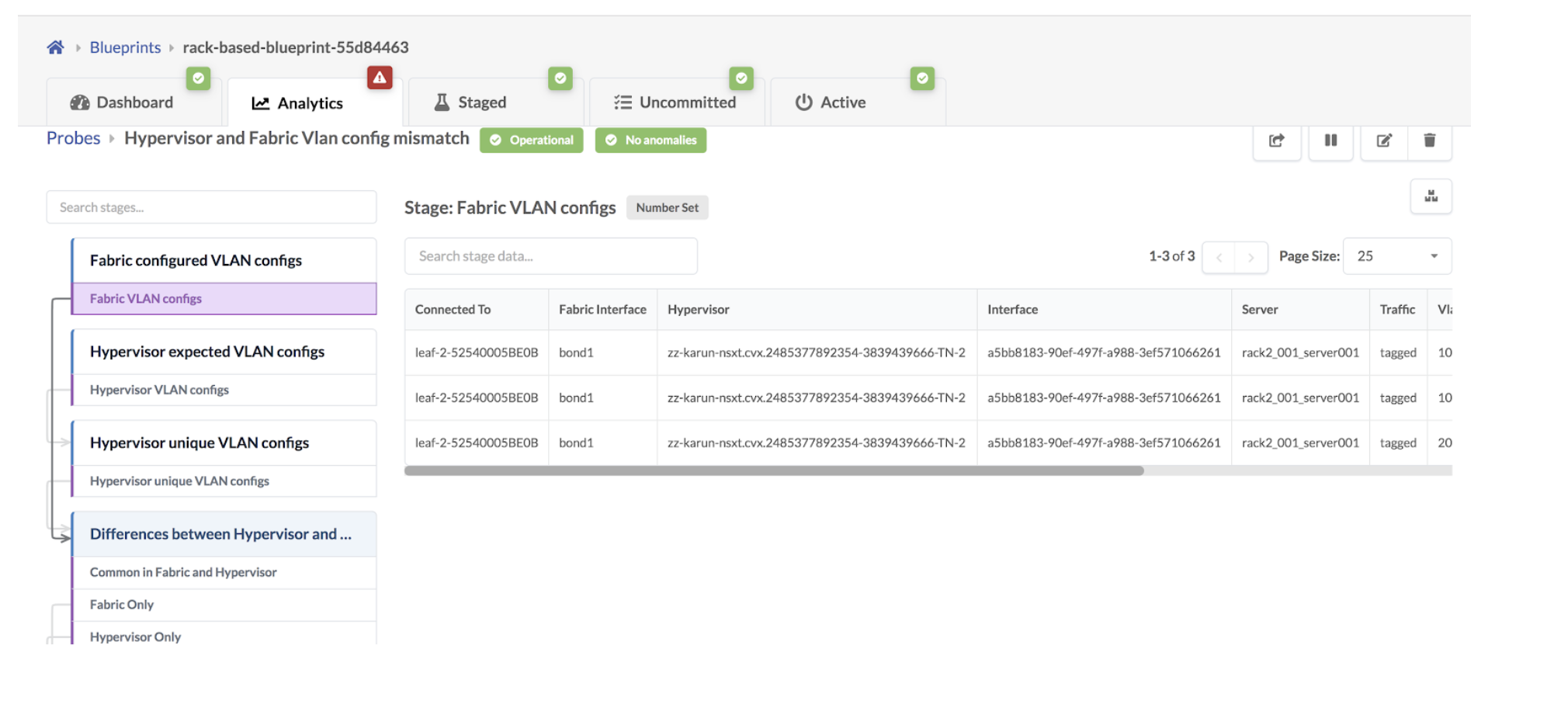
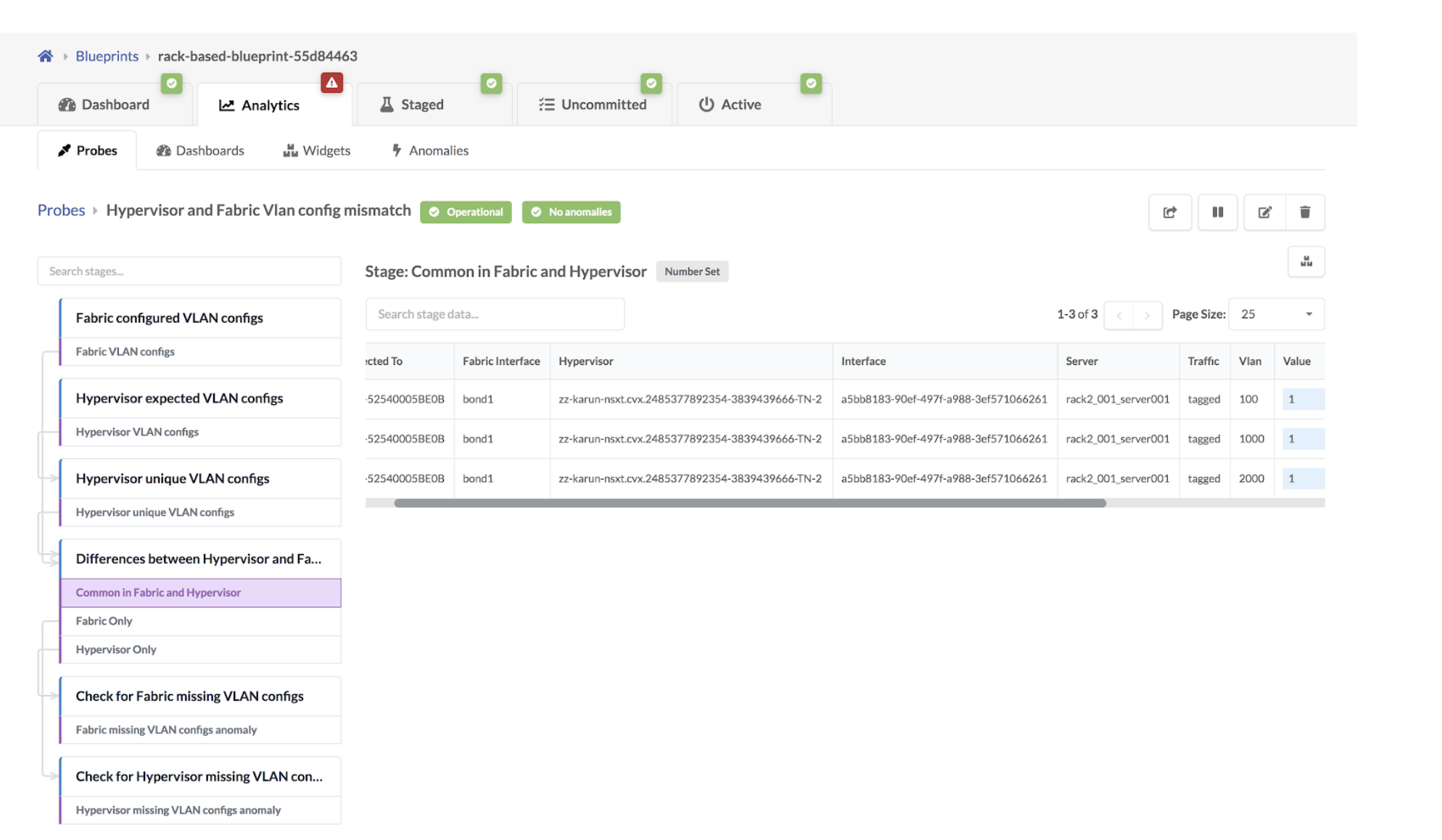
- Click the Common in Fabric and Hypervisor stage to show
that VLANs in the NSX-T transport nodes and the fabric match.
If the VLAN defined in the Uplink Transport Zone used for BGP peering is modified
in the NSX-T Manager, then VLAN mismatch anomalies are raised. 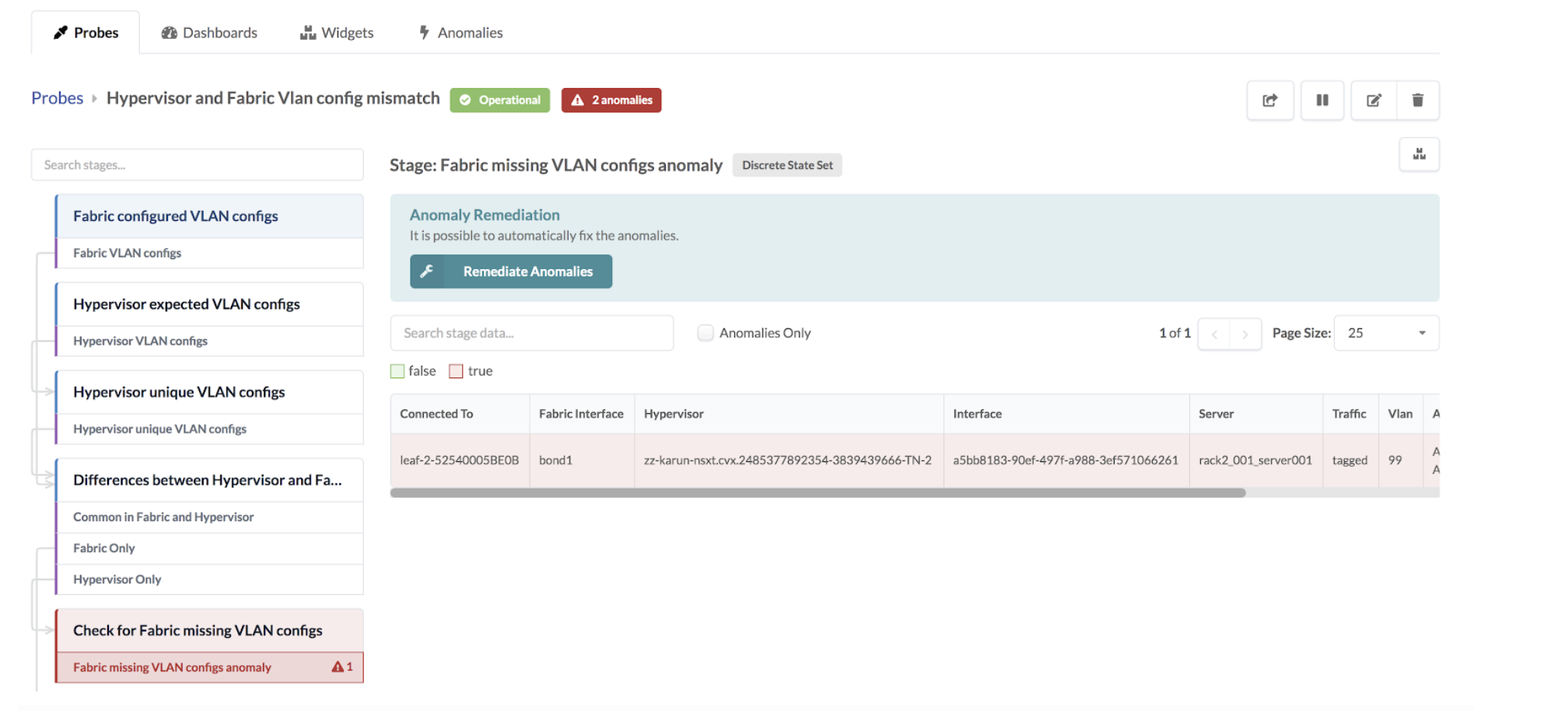
Some other reasons for mismatching include the following:
- If the configured VLAN NSX-T transport node is missing in the fabric.
- If the configured VLAN NSX-T transport node is in the fabric, but the end VMs or servers are not part of this virtual network or VLAN.
- If a segment is created in NSX-T for either an overlay or VLAN-based transport zone. It could be that the configured VLAN spanning the logical switch/segment on the transport node is missing on the fabric.
- If L2 bridging for VMs in different overlay logical segments is broken because one VM exists in one logical switch/segment and the other VM exists in a separate uplink logical switch/segment.
As an example, a VLAN is missing in NSX-T 3.0 Host Transport node on the Overlay
segment connected to ToR leaf devices and respective VXLAN VN is present in
Juniper Apstra Fabric and ports towards Hypervisors are assigned in a Virtual
Network based Connectivity Template as below: 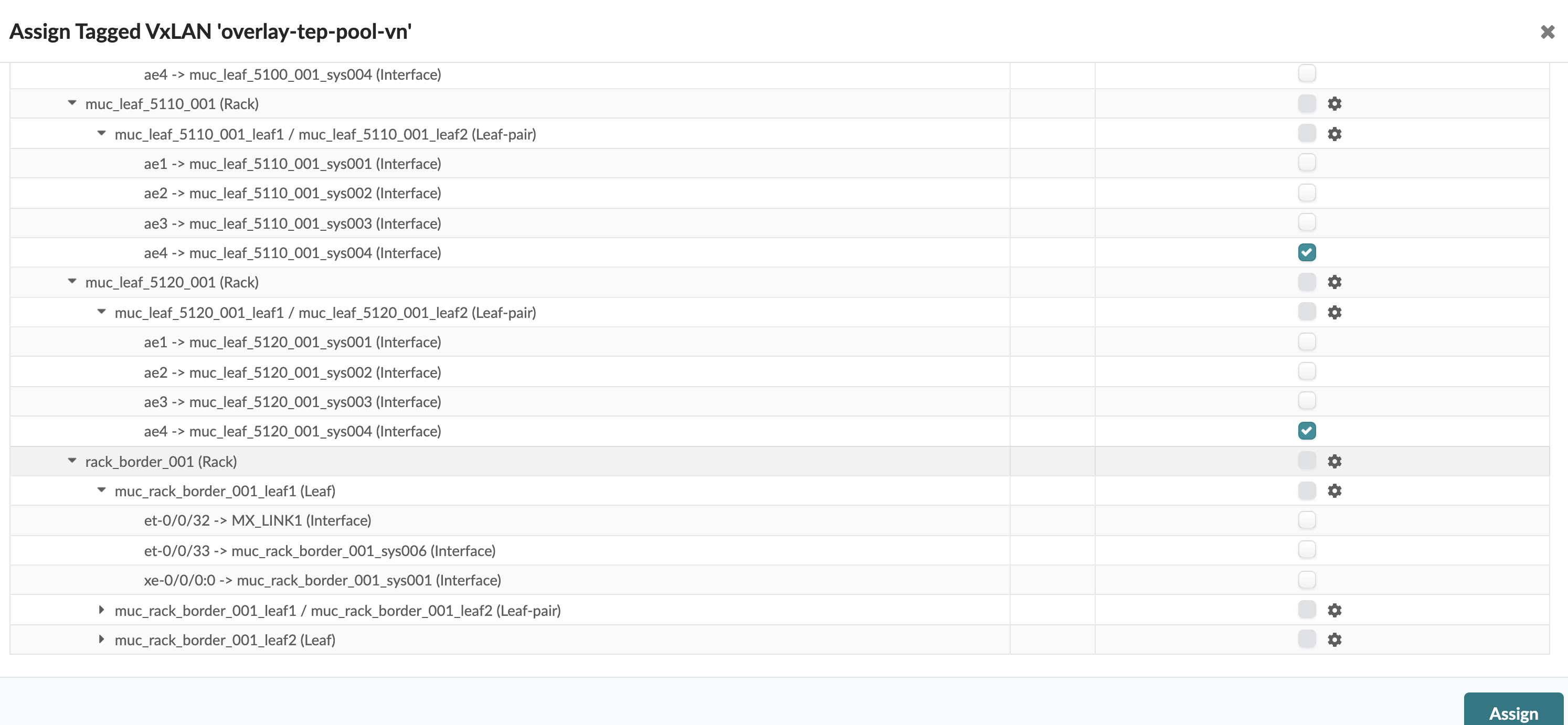
A Hypervisor missing VLAN Configs anomaly is raised as
shown below: 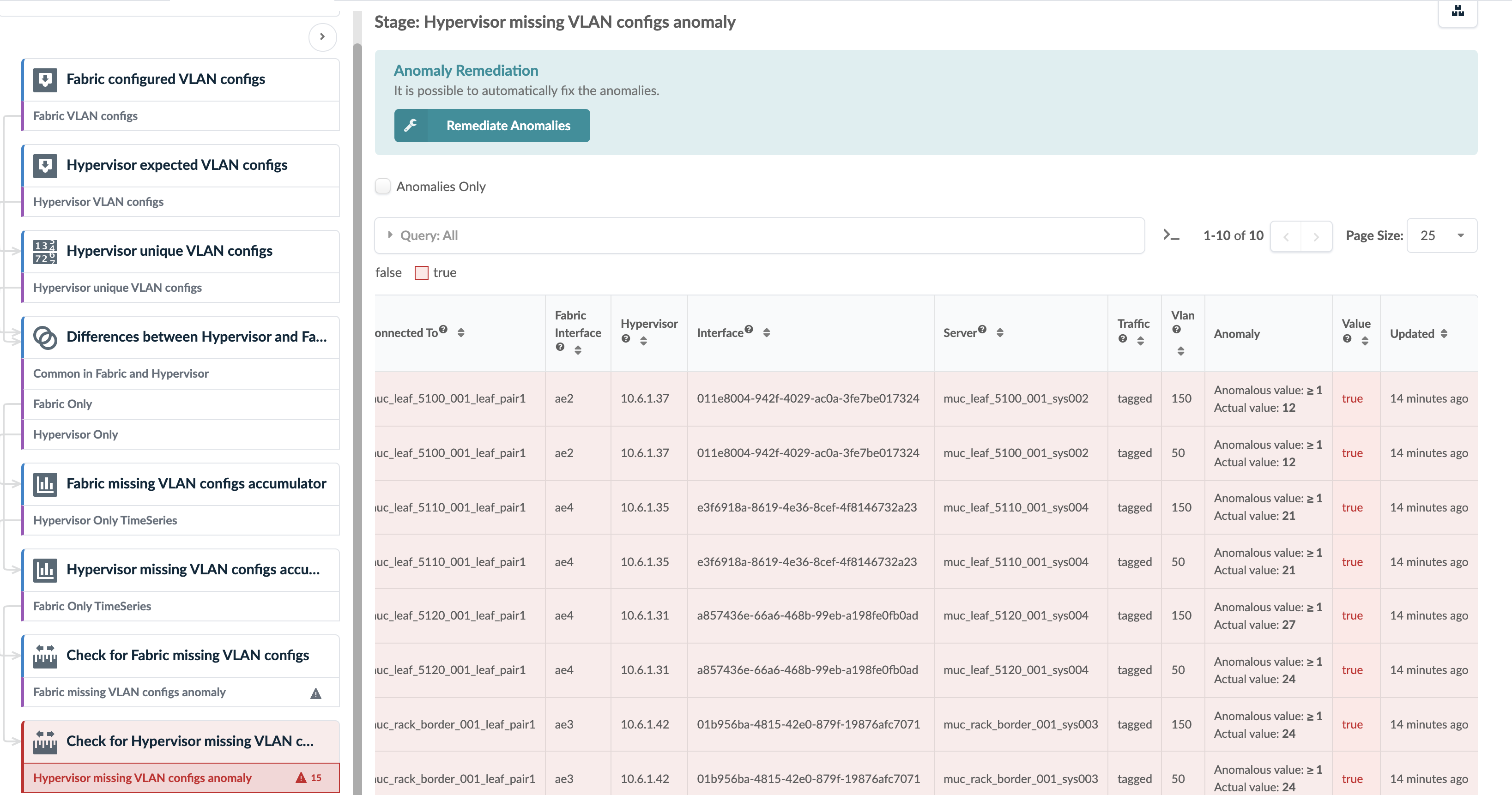
In some scenarios, a VLAN mismatch anomaly can be remediated. If so, the Remediate Anomalies button appears on the probe details page as shown in the screenshot above. Example scenarios include:
- NSX-T transport nodes use an uplink profile to define transport VLAN over which overlay tunnel comes up. Fabric could be missing the rack-local VN for transport VLAN on hypervisors. One-click remediation can be provided by creating a new rack-local virtual network with the proper VLAN ID in the fabric.
- A rack-local virtual network is defined with VLAN ID Y, however, the connected virtual infra nodes (i.e hypervisors) do not have the VLAN ID in the logical segment/switch. One-click remediation can be provided by removing the endpoint from the affected VLAN ID.
If the Remediate Anomalies button appears under the stage
name, you can click it to automatically stage the changes required to remediate
the anomaly. You can see the staged changes on the
Uncommitted tab. 
Review the staged configuration, add any necessary resources (such as IP subnet address, virtual gateway IP, as so on), then commit the configuration.
Usage with VCenter Integration
Some anomalies, that are raised because of a VLAN config mismatch between vCenter and the fabric, can automatically be remediated, such as the following.
- If the vCenter Distributed Virtual Switch (vDS) port group does not have a corresponding rack-local VN (VLAN) for VLAN ID X. With one-click remediation, a new rack-local virtual network (VLAN) with the proper VLAN ID is created.
- If endpoint X in a rack-local VN with VLAN ID Y, does not have a corresponding dVS port group. With one-click remediation, the endpoint is removed from the affected VLAN ID.
Note
vCenter vDS must be used with VLAN specific ID allocation on the port group for L2 network segmentation at the hypervisor level.
A VLAN-based rack-local virtual network is extending each VLAN segment defined on the vDS, across servers within the same rack. For example, vDS port group VLAN 10 = rack-local virtual network with VLAN 10.
For more information about this probe, from the blueprint, navigate to Analytics > Probes, click Create Probe, then select Instantiate Predefined Probe from the drop-down list. Select the probe from the Predefined Probe drop-down list to see details specific to the probe.
