Add a Bonjour Gateway to a WLAN
To enable Apple devices and services to discover one another, add a Bonjour gateway to your WLAN.
Bonjour is a standards-based protocol from Apple that provides a way for devices and services on the same network to discover one another. It works by forwarding multicast Domain Name System (mDNS) frames to clients on the LAN so they can automatically discover and connect to the advertised service (such as a printer or AirPlay device).
On wireless networks, however, it is common for clients and the various services to connect to the same WLAN from different VLANs. As such, to use the Bonjour services, it becomes necessary to bridge mDNS frames originating on one VLAN to wireless clients connected on another VLAN. You do this by setting up a Bonjour gateway on the WLAN. The gateway can bridge local VLANs on the WLAN (it can also do so by tunneling through a Mist Edge, for which you should contact Juniper technical support).
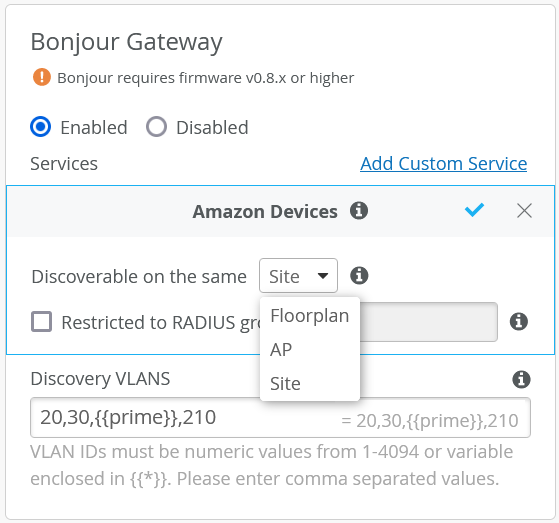
In Mist, the Bonjour gateway receives discovery queries from eligible clients on the Wi-Fi network and forwards them to VLANs listed in the Discovery VLANs field of the gateway configuration. These VLANs can be part of the WLAN, or a part of the wired infrastructure. Responses from any Bonjour device on the network are forwarded to the requesting client and added to the local cache. In this way, the gateway learns and builds a list of all users and devices that need to discover each other. The network here can be the WLAN, a wireless VLAN, or a wired VLAN,
Access Control
When setting up a Bonjour gateway, you can also use it to achieve passive access control by making a given Bonjour service discoverable only to a specified user roles or location. In a classroom setting, for example, you could you could leverage existing RADIUS roles for students and teachers to restrict Apple AirPlay screen casting to teachers only. Students would not see the the service. When setting up wireless printing service, you could leverage the Bonjour gateway so that wireless printers are only discoverable by users located on the same floor as the printer.
Custom Bonjour Services
Bonjour service labels use syntax that include the following: airplay._tcp._local. If you need to add a service that is not already on the list, you add your own custom service by providing the service-name portion of the label, for example, homeconnect in the Add Custom Service option. The rest of the label (the ._tcp._local part) will be appended automatically to that name.
Role-based Bonjour Discovery
Role-based access lets you limit Bonjour service discovery within a WLAN to specified user role(s). It requires a RADIUS server for providing users' authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) profile, and Mist user labels in order to map those attributes so they can be used in the Mist policy framework. The result is that you can use labels to filter out non-matching users so they cannot discover the selected Bonjour service, while at the same time it is available to authorized users. See Example: Creating and Applying Labels for Bonjour Filtering.
Best Practices
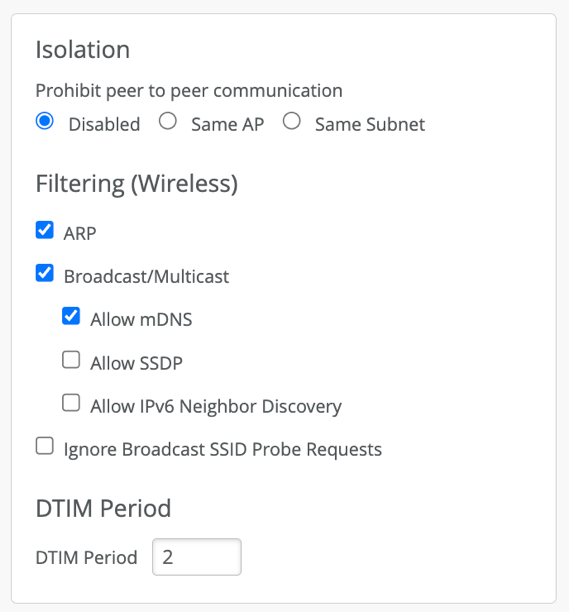
Juniper recommends that you filter (that is, drop) most broadcast and multicast frames on the wireless network so APs don't waste airtime in sending them. By default, this filtering includes mDNS frames when Bonjour is enabled.
Design your WLAN to minimize the volume of protocol chatter. Both SSDP (for plug-n-play devices) and mDNS can be very chatty protocols. As such, they can quickly degrade wireless performance by flooding the channel and consuming airtime. The design principles below can help reduce the chatter:
-
Define a flood boundary for the Bonjour gateway.
-
Pool Bonjour devices to use the minimal number of discovery VLANs.
-
Use location or role-based service discovery.
-
Test on the small scale before deploying in the network, especially before using custom Bonjour applications.
-
Enable broadcast and multicast filtering on the wireless network.
To add a Bonjour gateway to a WLAN: